Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 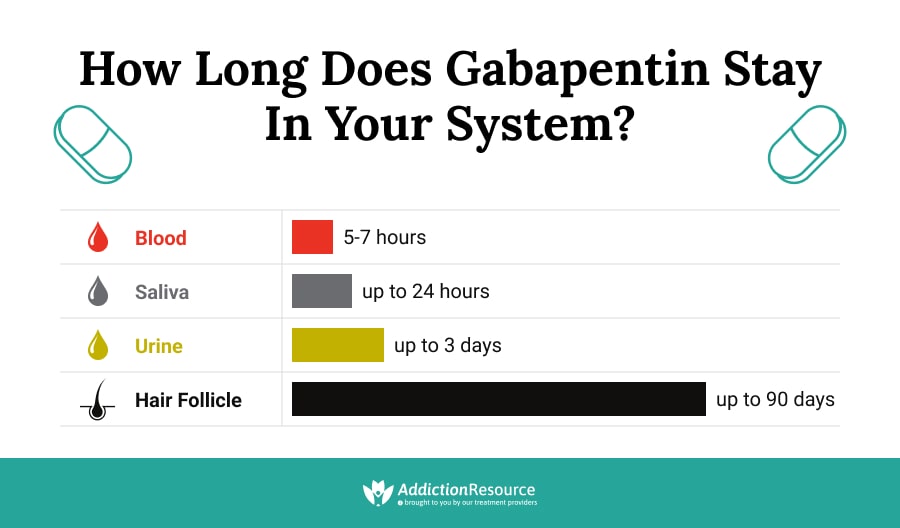 |
This paper describes the pharmacokinetic studies of 1-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexane acetic acid (gabapentin, Gö 3450, CI-945) conducted with the 14C-labelled substance following intravenous and intragastric administration to rats and dogs and oral administration to humans. Gabapentin does not undergo significant hepatic metabolism, which is a key differentiator from many other antiepileptic drugs. It does not induce hepatic enzymes or inhibit the metabolism of other drugs, making it a safer option for patients on multiple medications . Gabapentin is excreted unchanged in humans but is metabolized to N-methyl-gabapentin in dogs. Results in faster elimination and ability for shorter dose intervals in dogs as compared with humans 2 The metabolism of gabapentin has not been studied in cats, but pharmacokinetics demonstrates faster elimination than in humans, with similar gabapentin 1800 mg/day to pregabalin 300 mg/day and gabapentin 900 mg/day to hypersensitivity and suppresses medial prefrontal cortical glucose metabolism . in rats with neuropathic pain. Mol Gabapentin is available in two extended-release for-mulations in addition to the immediate release: a gas-tric retentive formulation (GBP-GR) and a gastro-retentive prodrug gabapentin enacarbil that are approved for the management of postherpetic neural-gia. The apparent absence or low rate of significant hepatotoxicity from gabapentin may be due to its minimal hepatic metabolism and rapid urinary excretion. The case reports of hepatic injury due to gabapentin were followed by complete recovery without evidence of residual or chronic injury. At present several laboratories have demonstrated that gabapentin treatment alters the metabolism or concentrations of glutamate, glutamine or GABA in brain tissues. Several laboratories also have demonstrated that gabapentin (and several endogenous amino acids) interact with an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels. Gabapentin is effective as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures in adults and pediatric patients 3 years of age and older. A lack of hepatic metabolism makes gabapentin an attractive option for patients on multiple antiepileptic drugs and patients with impaired hepatic function. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. Nevertheless, in renally compromised patients, the half-life may be considerably longer. 18 Since gabapentin is not bound to plasma proteins, there is no competition with other extremely protein-bound medications, for example phenytoin. 19 As well, the lack of hepatic metabolism or induction/inhibition of hepatic drug metabolizing enzyme Even though gabapentin is a structural GABA analogue, and despite its name, it does not bind to the GABA receptors, does not convert into GABA Tooltip γ-aminobutyric acid or another GABA receptor agonist in vivo, and does not modulate GABA transport or metabolism within the range of clinical dosing. [85] Summary: This paper describes the pharmacokinetic studies of 1-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexane acetic acid (gabapentin, Go 3450, CI-945) conducted with the '4C-labelled substance fal-lowing intravenous and intragastric administration to rats and dogs and oral administration to humans. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Because it is well known that excess branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) have a profound influence on neurological function, studies were conducted to determine the impact of BCAAs on neuronal and astrocytic metabolism and on trafficking between neurons and astrocytes. The first step in the metabolis The pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of gabapentin, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME), were investigated during the development of Neurontin®, an immediate-release (IR) formulation of gabapentin that is orally administered three-times daily. Background: Gabapentin is the most commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain in cats. Despite this common and chronic usage, clinically relevant pharmacokinetic data is lacking. Objectives: To evaluate the pharmacokinetics of clinically relevant dosing regimens of gabapentin in cats. Gabapentin is not protein-bound. A high volume of distribution indicates greater concentration in tissue than in plasma. It is not metabolized and does not induce hepatic enzymes or inhibit metabolism of other antiepileptic drugs. Gabapentin is a new antiepileptic drug (AED) with an attractive pharmacokinetic profile. It is absorbed by an active and saturable transport system, and has a high volume of distribution. Gabapentin is not bound to plasma proteins, does not induce hepatic enzymes and is not metabolized. At steady st Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |