Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
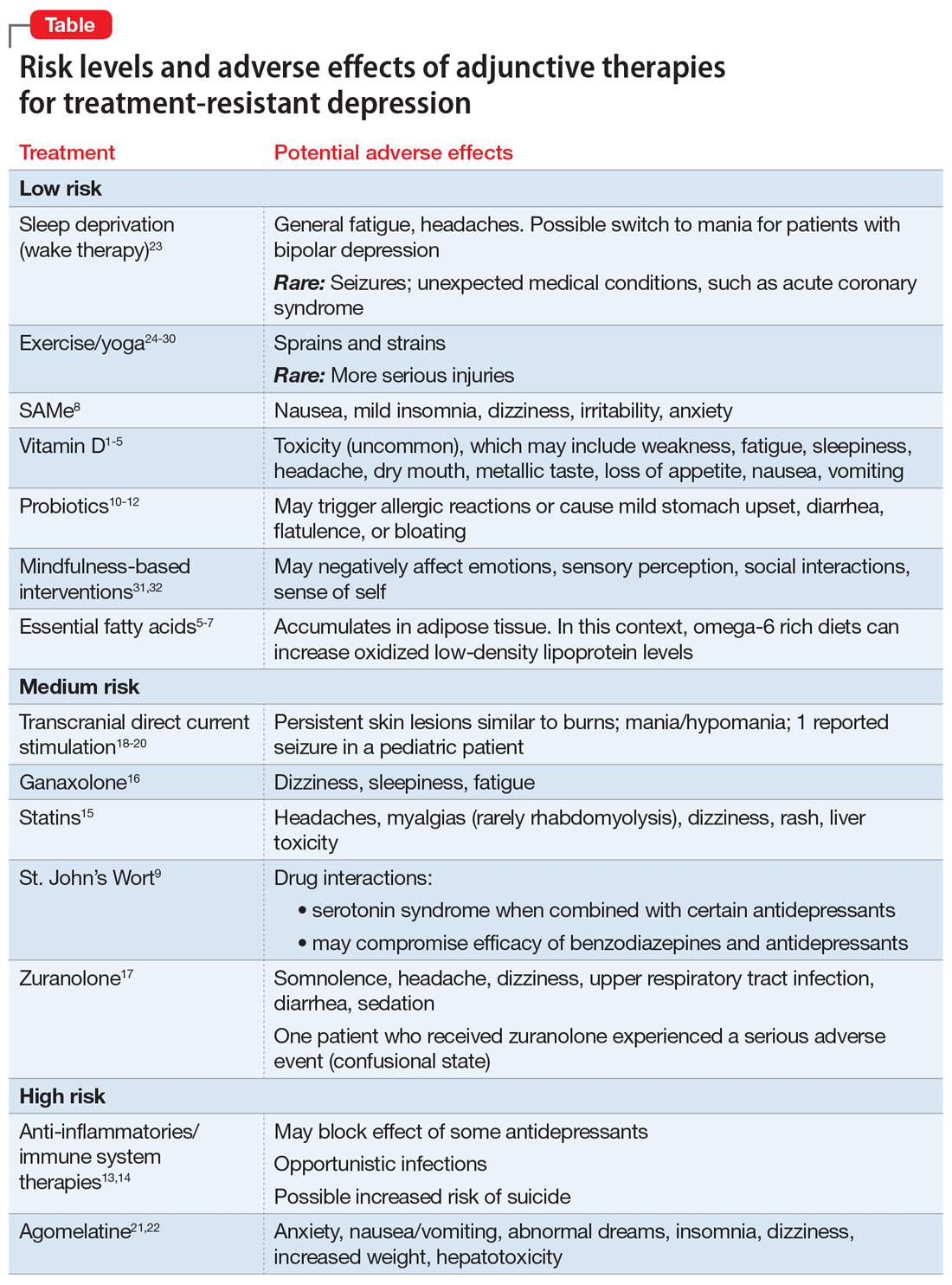
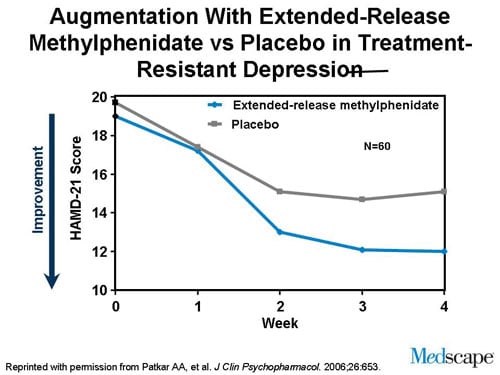
Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Request PDF | Adjunctive gabapentin in treatment-resistant depression: A retrospective chart review | Previous studies in predominantly bipolar patients have suggested that gabapentin may be In this review, the author examines the evidence for psychopharmacologic treatments among adults for generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder derived from clinical trials. For each disorder, major categories of drugs are reviewed, and then the evidence-based medications in each category are discussed. The author reviews key safety and tolerability Treatment-resistant depression is defined as failure to respond to one or more antidepressant medications at therapeutic doses and occurs in at least 12% of patients with depression. 1, 2 In Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Im 22 and have been suffering from severe depression and social anxiety since I was 15 years old. I tried 2 depth psychological therapies, one behavioral one and over 13 different meds (SSRI, SNRI, atypical, tetracyclic, moclobemide, neuroleptics) without any success. Gabapentin was well tolerated; the most common adverse effects were fatigue, sedation, dizziness, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Limitations: Treatment was uncontrolled and efficacy assessments were retrospective. Conclusion: These findings suggest that gabapentin may be of adjunctive benefit in the management of treatment-resistant depression. This report describes its efficacy and tolerability as an adjunctive agent in treatment-resistant depression. Methods: A chart review was conducted on 27 outpatients presenting with a depressive disorder in whom gabapentin was added to ongoing treatment with a conventional antidepressant to which patients had not responded after at least 6 weeks. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Gabapentin was well tolerated; the most common adverse effects were fatigue, sedation, dizziness, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Limitations: Treatment was uncontrolled and efficacy assessments were retrospective. Conclusion: These findings suggest that gabapentin may be of adjunctive benefit in the management of treatment-resistant depression. Background: Previous studies in predominantly bipolar patients have suggested that gabapentin may be useful in treating mood disorders. This report describes its efficacy and tolerability as an adjunctive agent in treatment-resistant depression. Treatment-resistant depression is a type of depression where someone doesn’t improve after two courses of different antidepressants. There are remedies available, such as changing medications Many patients presenting with unipolar major depression (major depressive disorder) do not recover after their initial treatment. As an example, one prospective observational study found that among 3671 outpatients who were treated with citalopram, remission occurred in only 37 percent [1]. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin may be effective in treatment-resistant depression 18 and refractory bipolar disorder 30 Can be rapidly titrated 32 Broad therapeutic index -- gabapentin can be prescribed in a wide range of doses, based on individual patient needs, without increased risk of dose-dependent side effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |