Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
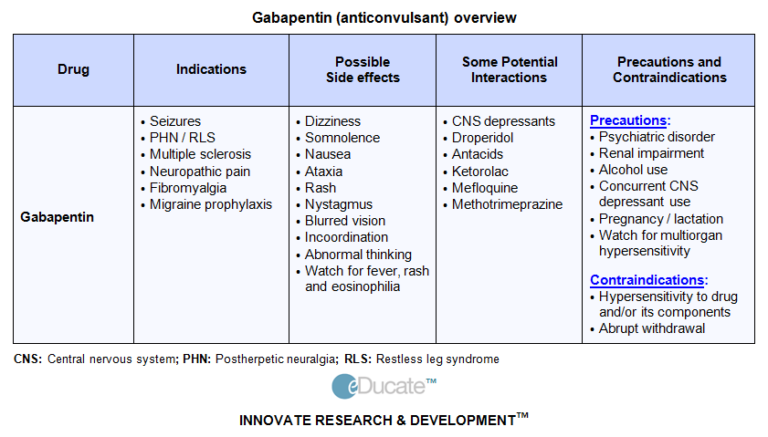 |  |
decrease the efficacy of oral contraceptives (Table 1 3-6), the interactions between lamotrig - ine and oral contraceptives is uniquely bidi-rectional. Combined oral contraceptives are thought to interact with lamotrigine pri-marily via the estrogen component, which causes increased metabolism of lamotrigine through induction of glucuronidation Concomitant use of drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 with hormonal contraception could result in increased exposure to contraceptive hormones and potentially increased side effects. In the case of ethinylestradiol, elevated serum levels could theoretically result in increased risk of thrombosis. Anticonvulsants that induce hepatic metabolism increase clearance of oral contraceptive hormones and thereby cause contraceptive failure. Gabapentin is not metabolized in humans and has little liability for causing metabolic-based drug-drug interactions. Avoid the combination (or use of oral contraceptives with >50 µg ethinylestradiol), utilize barrier contraception. Addition of 4 mg folic acid daily for women of child bearing potential if used Carbamazepine Anticonvulsants that induce hepatic metabolism increase clearance of oral contraceptive hormones and thereby cause contraceptive failure. Gabapentin is not metabolized in humans and has little liability for causing metabolic-based drug-drug interactions. Drug interactions between oral contraceptives (OCs) and traditional anticonvulsants have been well described. However, in the past decade, a number of new anticonvulsants have been developed, as well as modifications made in the composition of the OC preparations themselves. Additionally, anticonvul Gabapentin, levetiracetam, pregabalin, tiagabine, valproate, vigabatrin and zonisamide have been reported not to interact with steroid oral contraceptives. Benzodiazepines and ethosuximide are also considered not to interact [ 2 , 12 ]. Premature discontinuation of oral contraceptive pills most commonly occurs because of the following real or perceived side effects: breakthrough bleeding, nausea, headache, breast tenderness, acne Combined oral contraceptive steroids (OCs) are prescribed for 17% of fertile women with epilepsy, which is almost as frequent as for the background population (25%). 1 Co-administration of OCs and antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) is therefore a common clinical situation which calls for specific considerations of possible drugs interactions. The main lamotrigine Interaction. oral contraceptives: decrease effect of both. Gabapentin action. mimics GABA. Gabapentin black box warning? If so, what is it. none. Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and AEDs can interact bi-directionally, resulting in possible therapeutic failure of either treatment, which may lead to unintended pregnancy and/or increased seizure activity. There are no interactions between the combined oral contraceptive pill, progesterone-only pill, medroxyprogesterone injections or levonorgestrel implants and the AEDs valproic acid (sodium valproate), vigabatrin, lamotrigine, gabapentin, tiagabine, levetiracetam, zonisamide, ethosuximide and the benzodiazepines. The interaction between specific birth control preparations and anti-epileptic medications should always be taken into consideration when developing a treatment approach, as taking the two simultaneously may decrease the birth control pill’s effectiveness. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) that induce hepatic enzyme activity may alter the metabolism of most hormonal methods of contraception, and this may affect their contraceptive efficacy. There is also the potential for the hormonal method to affect the AED. Women may also be prescribed AEDs to treat conditions other than epilepsy, such as chronic pain and migraine. These effects should be considered Treating WWE of fertile age includes systematic, ongoing and accurate counseling to find the optimal method of contraception. The wide range of available AEDs and hormonal contraceptive methods underlines the importance of being familiar with the various pharmacokinetic properties of the drugs to achieve a better understanding of potential drug–drug interactions. The lamotrigine dose should be decreased if combined hormonal contraceptives are discontinued. Dose decreases should not exceed 25% of the total daily dose per week. 1 Desogestrel, a progestin-only medication, may increase exposure to lamotrigine, but this has not been observed in research with other progestins. 5,9 When starting a progestin-only pill, monitor patients for signs of lamotrigine Metabolism of antiepileptic drugs and the components of oral contraceptives by the common hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme system, which can lead to pharmacokinetic interactions and, thereby, reduced therapeutic efficacy when taken together. Phenobarbital is an enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drug that interacts with oral contraceptives, causing decreased sex hormone levels 1 and breakthrough bleeding. 2 Midcycle breakthrough Combined oral contra-ceptives (COCs) and AEDs can interact bi-directionally, resulting in possible therapeutic failure of either treatment, which may lead to unintended pregnancy and/or increased seizure activity. Reports of interactions between oral contraceptives (OCs) and other drugs began to trickle into the literature. At first, these drug interactions appeared to be random and unrelated. Increased understanding of P450 enzymes and phase II reactions of sulfation and glucuronidation has permitted preliminary categorization and assessment of the
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |