Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
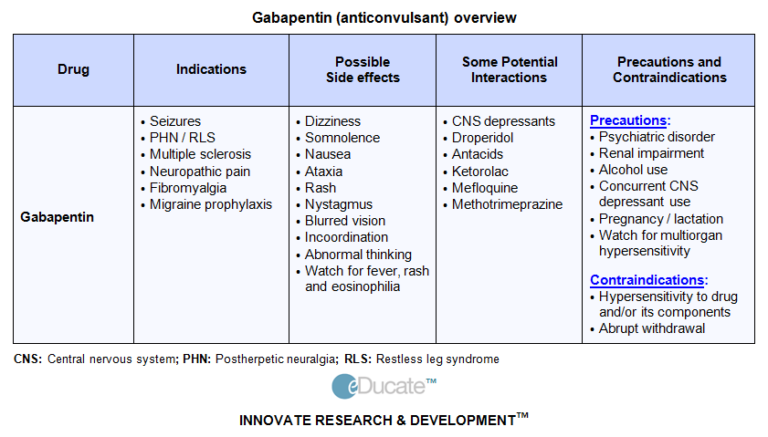
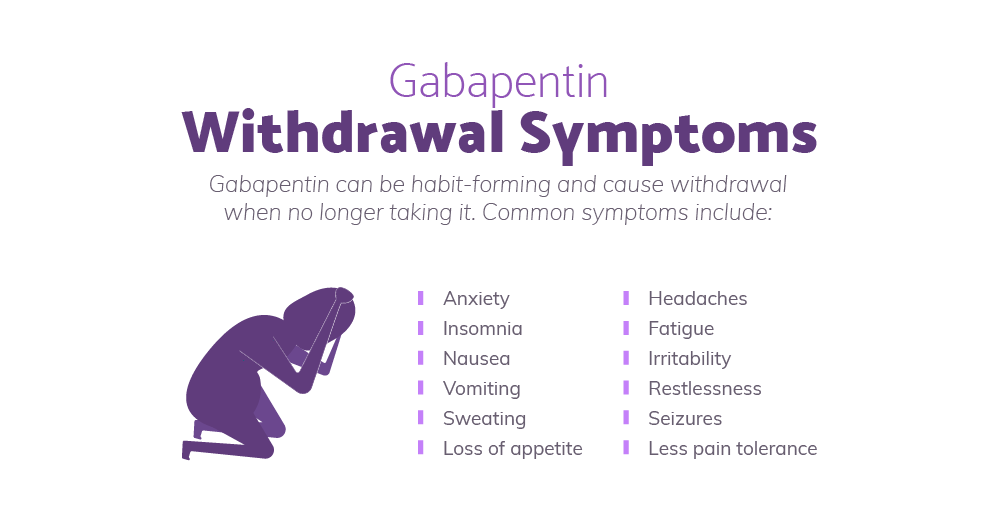
Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Though physicians often struggle or fail to recognize the benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome, patients are even more liable to fail to recognize that their drug may be their problem because increasing the dose may temporarily relieve tolerance symptoms, or more frequent dosing or switching to a benzodiazepine with a longer half-life (e.g., from Very small studies and case reports have shown that drugs such as gabapentin, carbamazepine, and propranolol may help as aids in withdrawal. Trazodone, mirtazapine, and quetiapine may be helpful in some for insomnia. Some patients have reported relief of withdrawal symptoms with the use of CBD oil or medical marijuana. The withdrawal from Gabapentin is probably different than you think. Because it works as an antagonist on the thrombospondin receptors, the receptor which is responsible for things like the formation of new synapses, what exactly happens to your brain after a long period of abstention is a little unclear. Interdose withdrawal occurs when withdrawal symptoms emerge in between scheduled doses. It is common in people who are prescribed benzodiazepines, especially when they are taken daily and beyond the recommended 2-4 week timeframe. While interdose withdrawal typically occurs with short half-life benzodiazepines, like Ativan (lorazepam) or Xanax (alprazolam), it can and does occur with longer Among the documented cases, gabapentin withdrawal began between 12 hours and 7 days after the last dose. The majority saw withdrawal symptoms within 24 to 48 hours. Among the cases reported, gabapentin withdrawal symptoms typically peaked three days after someone’s last dose. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for seizures and nerve pain, can lead to physical dependence. Those who develop a dependency may face challenging withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing the drug. A structured gabapentin taper chart helps ease withdrawal and minimize risks, but knowing what works—and what doesn’t—matters just as much. Learn more. Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. Typically, people in the lay withdrawal community conclude that they are experiencing interdose withdrawal if their emotional, mental, or physical symptoms worsen as they are approaching their next dose, but these symptoms improve slightly or fully after they take their next regular dose. If you stop taking gabapentin suddenly, you may begin to experience withdrawal symptoms as soon as 12 hours after your final dose. However, some people do not experience symptoms for up to a week after their last dose. dangerous; withdrawal can be severe or even life-threatening. Taper schedules should be sant (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin]) should be considered for high-dosage withdrawal. Gabapentin interdose withdrawal is a common issue faced by individuals who rely on the medication for pain management or treatment of other conditions. This withdrawal occurs when the level of gabapentin in the body drops between doses, leading to unpleasant symptoms and a decreased quality of life. When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal. So she took about 1200 mg gabapentin for a few days and now it seems like she's expiriencing interdose withdrawal from the gabapentin. If she goes more that 5-6 hours without dosing the severe anxiety/tremors return. She has never experienced interdose withdrawal from gabapentin before. Withdrawal effects are more likely where someone is on high dose gabapentinoid or has been taken for more than 6 weeks. Where a gabapentinoid has to be discontinued due to medical reasons it is recommended this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week independent of the indication3. This will profile the baseline symptom pattern, revealing ADRs, including paradoxical effects, interdose (also known as rebound or breakthrough) withdrawal, 135–137 drug interactions, or withdrawal symptoms from dosage reduction. A patient developed apparent withdrawal symptoms beginning two days after gabapentin therapy was discontinued. The symptoms were unresponsive to treatment with benzodiazepines but completely resolved with the reinitiation of gabapentin therapy. There have been numerous documented cases of gabapentin abuse, dependence, and withdrawal. Even though gabapentin is sometimes considered as a treatment option for alcohol and substance abuse, it is important to monitor for drug-seeking behaviors. A history of alcohol or substance abuse appears to b Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. See tables 1 through 5 for case reports describing gabapentin tapers.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |