Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
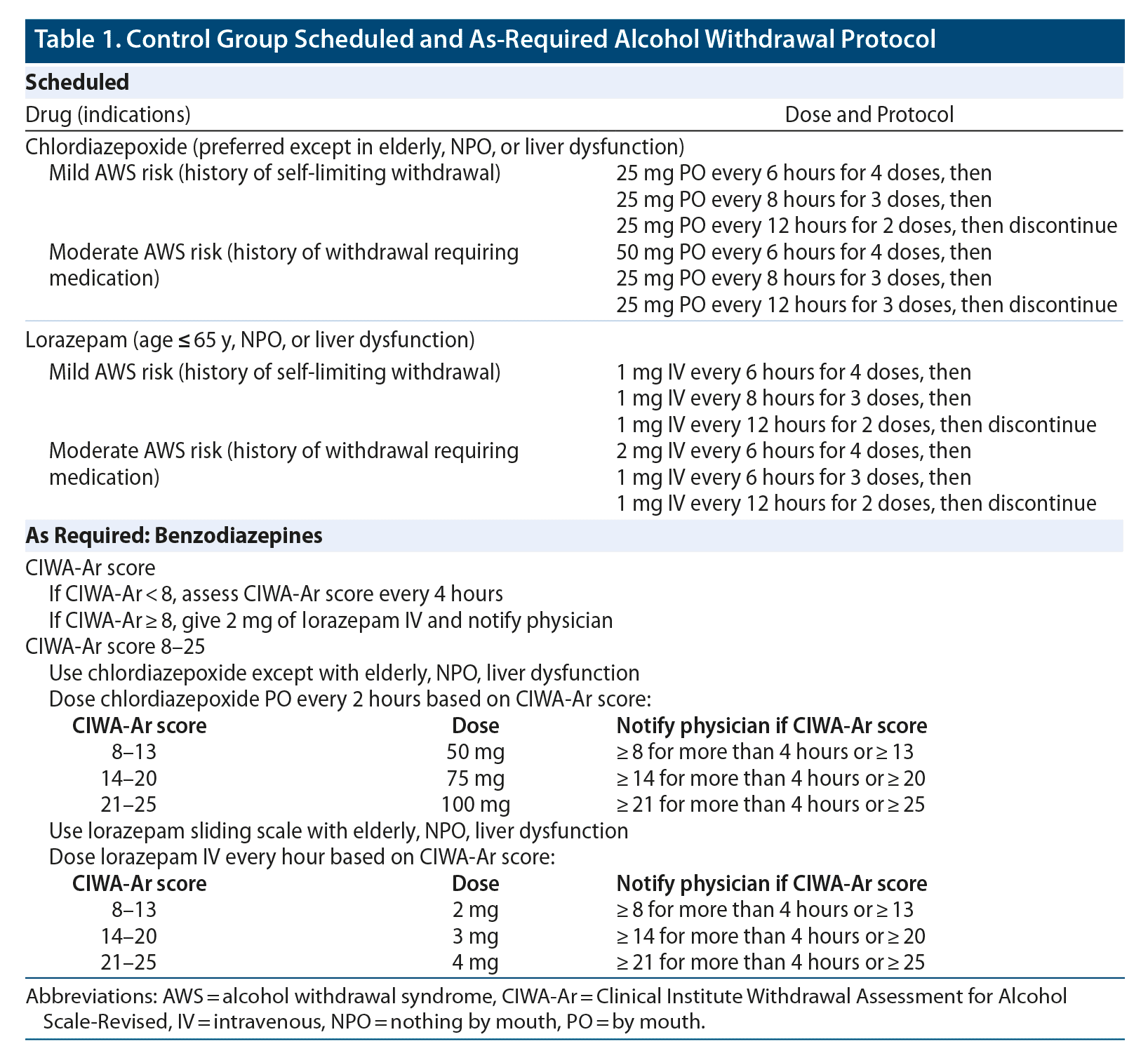 |  |
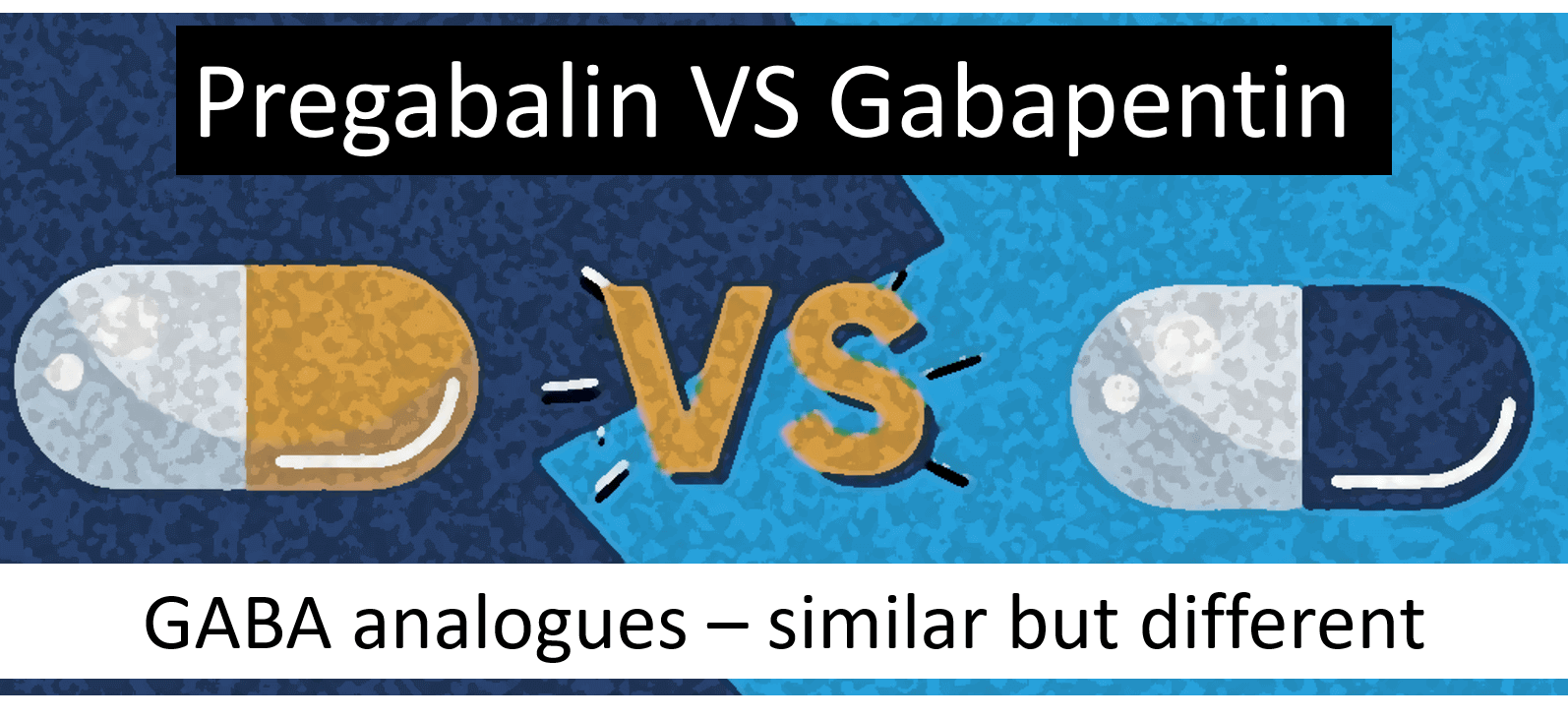
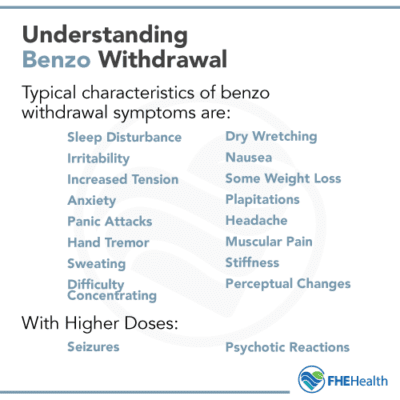
Coprescribing of benzodiazepines or gabapentinoids (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) with opioids is increasingly used in the multimodal treatment of acute and chronic pain, despite limited evidence That same study also found that gabapentin is prescribed along with one or more central nervous system depressant medications 60% of the time, with opioids and benzodiazepines being in the top three. Pharmacology. While benzodiazepines and other sedative-hypnotics typically act as ligands at GABA receptors, gabapentin (despite its name) does not. The combination of gabapentin and benzodiazepine can be safe in the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to data presented at American Psychiatric Association annual meeting, We highlight that the gabapentin with benzodiazepine group had a higher baseline CIWA score compared to the benzodiazepine-only group, indicating more severe withdrawal symptoms. Despite this, patients in the gabapentin group received a significantly lower cumulative dose of benzodiazepines. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy , postherpetic neuralgia , and central pain . [ 11 ] Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other medical conditions was associated with better outcomes of benzodiazepine withdrawal (N=57 gabapentin, N=115 no gabapentin). Neither: Gabapentin is used to treat partial seizures, pain related to post herpetic neuralgia as well as neuropathic pain. While it does modulate the activity of the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, gaba, it's mechanism of action is significantly different from that of a benzodiazepine or barbiturate. No, Gabapentin is not a Benzodiazepine drug. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat various types of nerve pain and to reduce seizure frequency in people with epilepsy. It has been used to treat anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and to help with alcohol withdrawal. We must first understand what Gabapentin is and how it relates to benzodiazepines. What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin — in the form of tablets, capsules, and oral solutions — is commonly prescribed to help control different types of seizures, especially for those suffering from epilepsy. Ativan vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? Ativan and Gabapentin are both medications commonly used to treat anxiety and seizures, but they work in different ways. Ativan is a benzodiazepine that works by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called GABA in the brain, leading to a calming effect. Keywords: gabapentin, benzodiazepine, treatment, alcohol withdrawal, inpatient. Introduction. Benzodiazepines have the largest and best evidence in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal and as a result are considered the gold standard for treatment. 1, 2 However, there are several limitations Gabapentin is primarily an anti-seizure (anticonvulsant) drug used also used for treating post-herpetic neuralgia, the pain that follows an episode of shingles. Xanax belongs to a different drug class called benzodiazepines, and is used to treat anxiety disorders and panic attacks. Benzodiazepines (also called “benzos”) are a class of agents that work in the central nervous system and are used for a variety of medical conditions. They act on specific receptors in the brain, called gamma-aminobutyric acid-A (GABA-A) receptors. Gabapentin does not exhibit affinity for benzodiazepine, opioid (mu, delta or kappa), or cannabinoid 1 receptor sites. Gabapentin misuse and abuse have been reported in the postmarketing setting and published literature. Most of the individuals described in these reports had a history of polysubstance abuse. efficacy of gabapentin in either replacing or augmenting benzodiazepine usage through the alcohol withdrawal period without sacrificing patient outcomes. Results from available literature since 2012 show evidence in support of gabapentin as an effective treatment, either alone or in conjunction with benzodiazepines, but it is not conclusive. Overall, Neurontin Gabapentin is a valuable treatment option for benzodiazepine withdrawal. Its ability to reduce withdrawal symptoms, stabilize mood, prevent seizures, improve sleep quality, and minimize discomfort make it an effective and supportive medication for individuals navigating the challenges of benzodiazepine withdrawal. is gabapentin a barbiturate or benzodiazepine?: Neither: It is an anti-seizure med. However, it may have some effects To address this query directly: No, Gabapentin is not a benzodiazepine. This distinction is crucial as it not only pertains to the drug’s classification but also to its role and implications in the treatment of substance abuse. While benzodiazepines affect the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the brain to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation, gabapentin primarily targets calcium channels and neurotransmitter release. It is used for different medical purposes, such as managing seizures and neuropathic pain, rather than solely for anxiety or sedation like Gabapentin utilization is common among opioid and/or benzodiazepine users. 11-20 While only FDA approved for partial seizures and post-herpetic neuralgia, gabapentin has become an essential component of several multimodal pain management strategies utilized by physicians. 11, 12 Not only that, gabapentin is also prescribed for the management of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |