Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
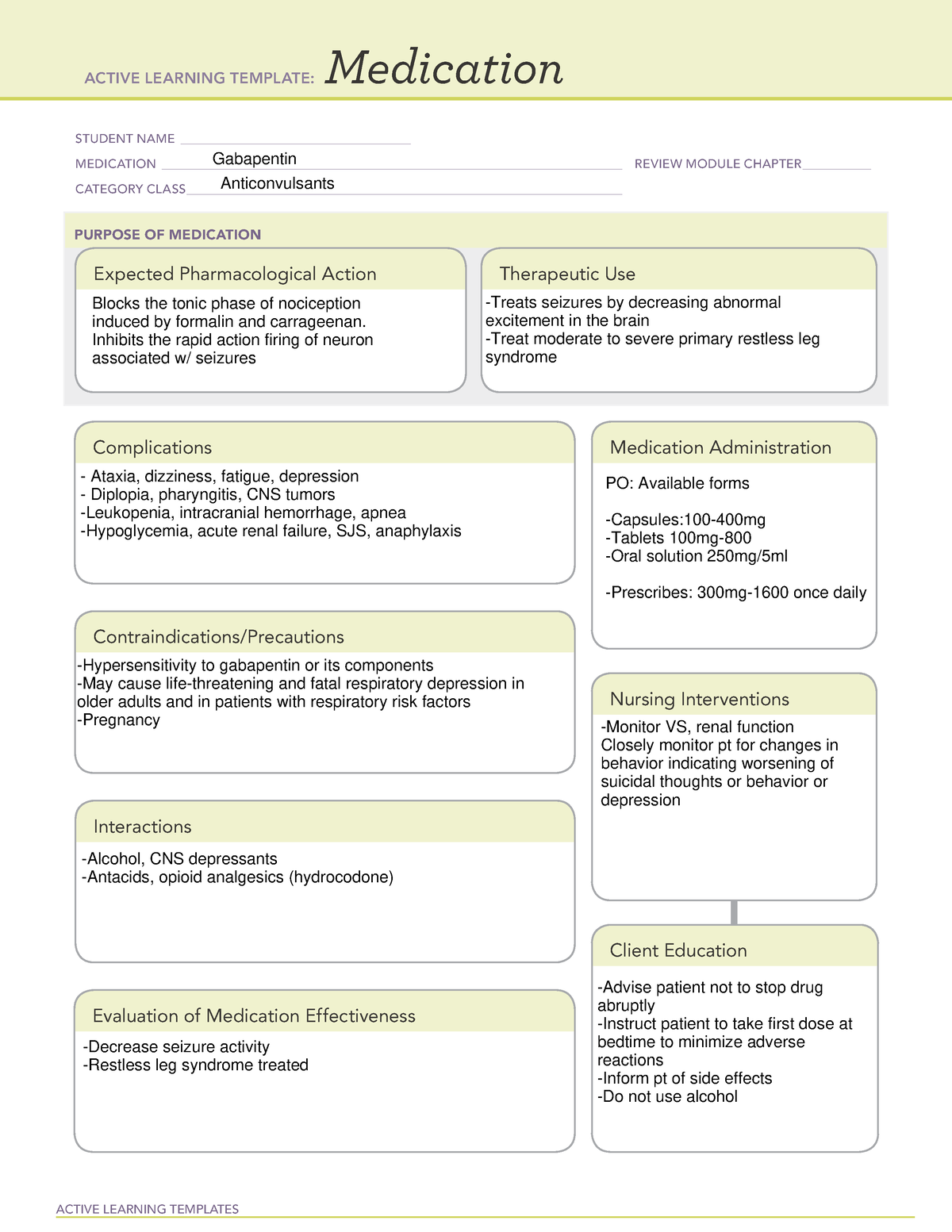
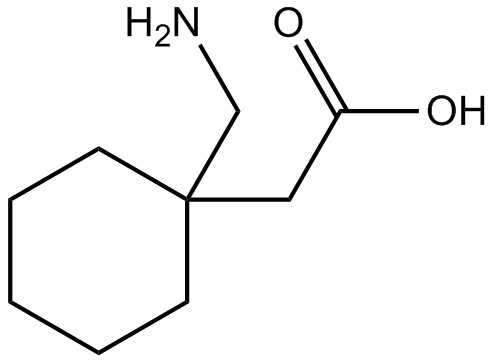
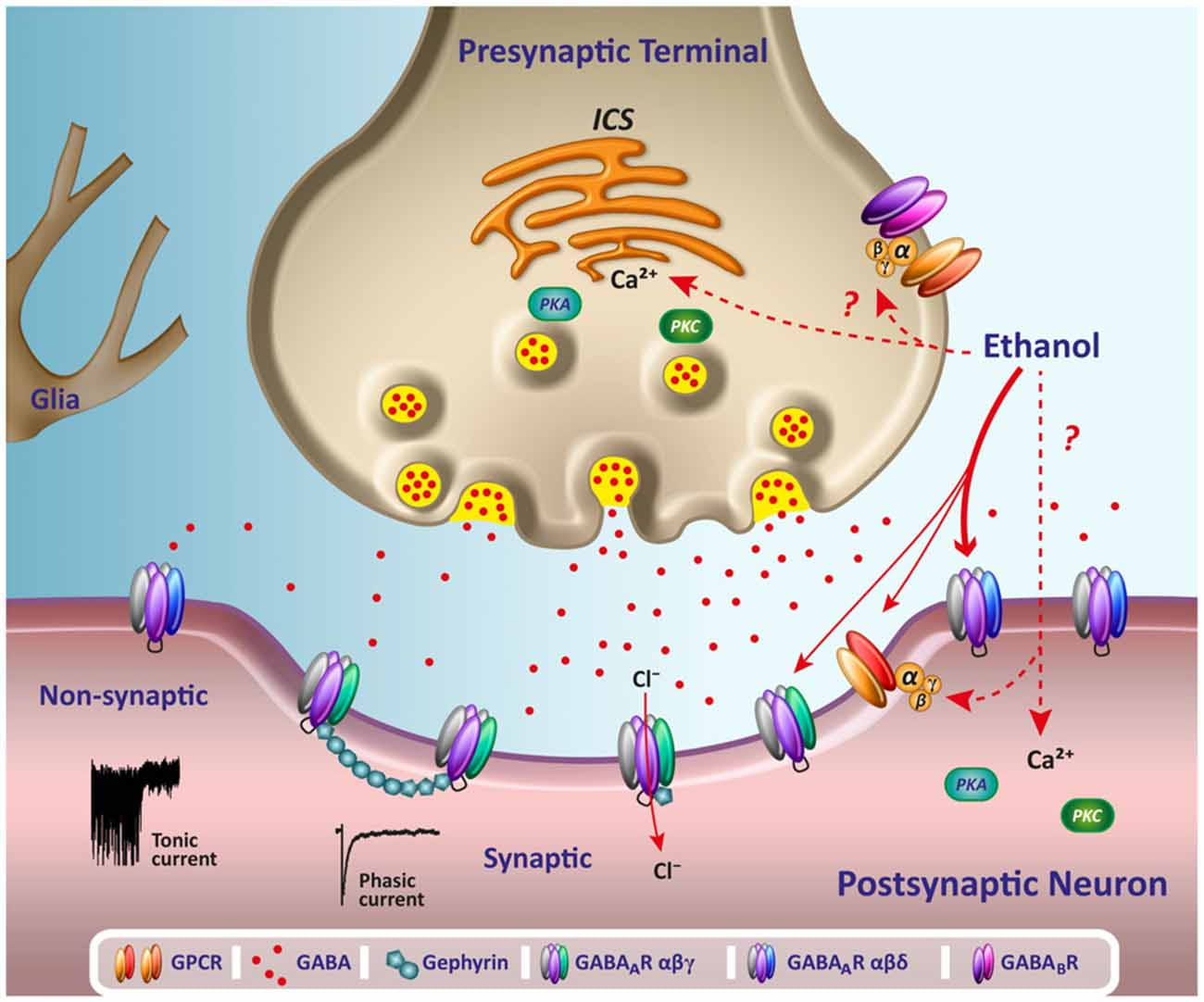
Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Gabapentin (3-cyclohexyl-GABA) is designed as a lipophilic analogue of GABA for blood-brain barrier penetration and closely resembles pregabalin. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Gabapentin is a GABA agonist and anticonvulsant that increases GABA concentrations in the central nervous system, possibly via inhibition of GABA-transaminase (Cai et al., 2012). While more commonly trialed in combination with flumazenil, as described above, one double-blind RCT ( Heinzerling et al., 2006 ) examined gabapentin as an individual Gabapentin is an alkylated GABA analog. The exact mechanism of action is unknown. Gabapentin acts as an antagonist on presynaptic voltage-gated channels. It binds to the alpha-2 delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels, which inhibit inward calcium currents and decrease neurotransmitter release. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Despite the fact that gabapentinoids are GABA analogues, gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors, do not convert into GABA Tooltip γ-aminobutyric acid or GABA receptor agonists in vivo, and do not modulate GABA transport or metabolism. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin are two substances often discussed in the context of brain health and neurological treatments. While they share some similarities in their impact on the nervous system, they are fundamentally different in terms of their structure, function, and applications. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: GABA molecules are relatively large, and there is debate among researchers about whether supplemental GABA can effectively cross the blood-brain barrier to exert its calming effects directly in the brain. Some studies suggest that GABA ingested through supplements may not effectively reach the central nervous GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. In people experiencing nerve pain after having had shingles, gabapentin is thought to change the way pain signals are sent through the body and brain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |