Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:quality(80)/author-service-images-prod-us-east-1.publishing.aws.arc.pub/morningstar/ca9ef979-0207-4e37-b392-91618ebc1841.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
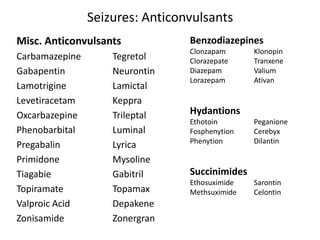
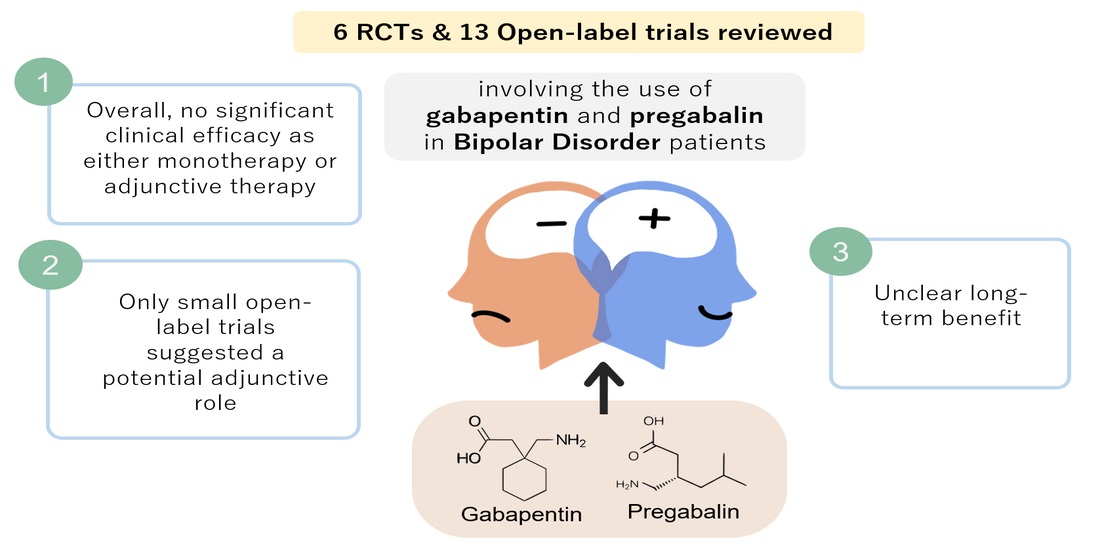
Gabapentin (Neurontin®) GBP Lacosamide (Vimpat®) LCM LamoTRIgine (Lamictal®) LTG LevETIRAcetam (Keppra®) LEV LORazepam (Ativan®) LZP ClonazePAM (Klonopin®) CZP Clorazepate (Tranxene®) CLZ DiazePAM (Valium®) DZP Eslicarbazapine (Aptiom®) ESL NO Anti-Epileptic Drug (AED) Substitution Guidance Document for Patients Unable to Take Oral Gabapentin. Gabapentin is used as a pain-relieving medication and anticonvulsant. A 2005 study investigated gabapentin as an add-on anticonvulsant in dogs with refractory seizures and found that in a 4-month period, 3 of 17 dogs were seizure-free and 4 other dogs had a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. 238 medications are known to interact with Keppra. Includes gabapentin, trazodone, sertraline. Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Results: Both levetiracetam (25-100 mg/kg) and gabapentin (6.25-25 mg/kg) significantly reduced PBBI-induced seizure frequency by 44% to 73% and 61% to 69%, and seizure duration by 45% to 64% and 70% to 78%, respectively. However, the two drugs manifested different dose-response profiles. Usually, a single medication can help people with epilepsy keep their seizures under control. But if one medication is only partially effective for you, your doctor may sometimes add another drug. Or your doctor may choose to combine your medication with surgery, an implanted device, or a special diet. Levetiracetam (Keppra) is an antiepileptic drug (AED) characterized by a novel mechanism of action, unique profile of activity in seizure models, and broad-spectrum clinical efficacy. The present re A phase IV clinical study of FDA data: drug interactions are found among 2,947 people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) and Keppra (levetiracetam). Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Levetiracetam (Keppra) are both antiepileptic medications, but they have some key differences. Gabapentin is used to treat certain seizures and nerve pain, while Levetiracetam is used for various types of seizures, including partial-onset, myoclonic, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Applies to: gabapentin and Keppra (levetiracetam) Using gabapentin together with levETIRAcetam may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. The group found that gabapentin is effective in the treatment of newly diagnosed partial epilepsy, and that lamotrigine, topiramate, and oxcarbazepine are effective in a mixed population of newly Conclusion: Gabapentin is not absorbed rectally. Levetiracetam. UCB Inc., the original manufacturer of Keppra does not approve breaking or crushing Keppra tablets for rectal administration. The current evidence of rectally administered levetiracetam is inconclusive. A case study was presented at the American Epilepsy Society meeting in December While sharing a common property of suppressing seizures, antiseizure medications have many different pharmacologic profiles that are relevant when selecting and prescribing these agents in patients with epilepsy and other conditions. Gabapentin has been used in cats at 5–10 mg/kg, bid-tid. Felbamate: Felbamate is a dicarbamate AED that exerts its anticonvulsant effects through multiple mechanisms, including potentiating GABA-mediated neuronal inhibition, inhibiting voltage-sensitive neuronal calcium and sodium channels, and blocking N-methyl- d -aspartate–mediated levetiracetam (12.5–100.0 mg/kg) and gabapentin (1.25–25.0 mg/kg) administered either individually or in pairs at fixed-dose ratios as a combination in mitigating posttraumatic nonconvulsive seizures induced by severe penetrating ballistic-like brain injury (PBBI) in rats. Seizures were detected by continuous electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring for 72 hours postinjury. Animals were Keppra vs Gabapentin is a common debate among medical professionals, with each medication having its own strengths and weaknesses. Keppra is known for its fast onset of action and high bioavailability, making it an effective choice for acute seizure management. Customer: Can gabapentin and Keppra meds be taken together Doctor's Assistant: Have you used gabapentin or anything similar before? Customer: No Doctor's Assistant: Have you seen a doctor about this? Customer: Ive been taking Keppra since last September with no problem, now I have shingles and doctor gave me a prescription for gabapentin for pain. In patients with chronic neuropathic pain, does levetiracetam (Keppra) effectively treat pain symptoms? (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin], pregabalin [Lyrica]), and topical lidocaine as first-line Gabapentin and Keppra work in different ways to target different aspects of seizure activity, making them a powerful duo for managing epileptic conditions. This combination therapy can help reduce the frequency and severity of seizures, allowing patients to live a more normal and fulfilling life. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may more. Keppra is an anticonvulsant that is used in conjunction with other medications for the treatment of certain types of seizures.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:quality(80)/author-service-images-prod-us-east-1.publishing.aws.arc.pub/morningstar/ca9ef979-0207-4e37-b392-91618ebc1841.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |