Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
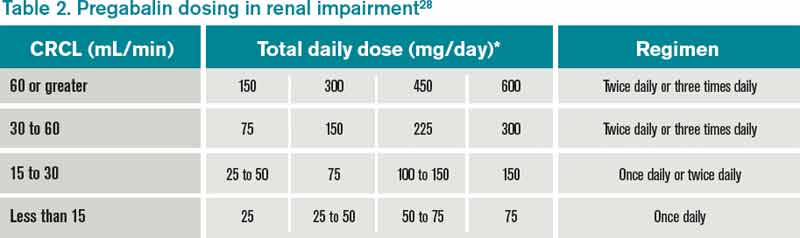 |  |
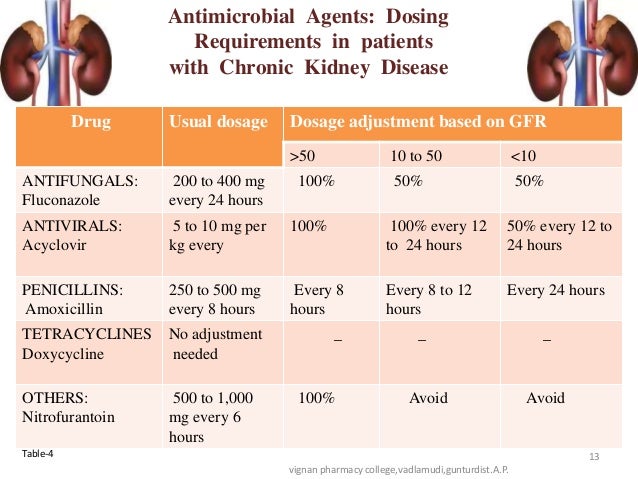
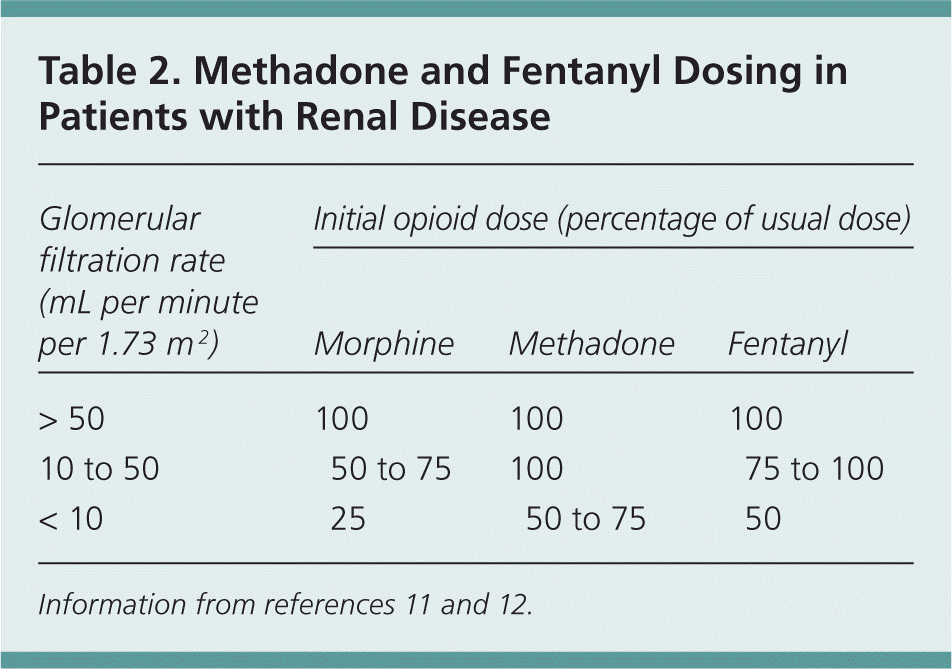
Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Renal clearance (CLr) and CLr adjusted for body surface area also declined with age; however, the decline in the renal clearance of gabapentin with age can largely be explained by the decline in renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/ min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption.1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Background: Gabapentin and pregabalin are well-tolerated medications primarily cleared by the kidney. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Renal clearance of gabapentin (CL R) correlates well with creatinine clearance (CrCL), which can be used as a predictor of CL R. 22 In patients with anuria, gabapentin can be effectively removed via dialysis. 23 Gabapentin produced from hydrolysis of gabapentin enacarbil is also eliminated via the renal clearance pathway.16, 17 The In individuals with normal renal function, gabapentin clearance is 100 ml/min, which is equivalent to a normal creatinine clearance. On the other hand, in patients with ESRD and on HD, gabapentin clearance with HD is approximately 142 ml/min with an elimination half-life of about four hours with HD, which makes HD an effective treatment option View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal to 600‒1800 mg daily in 3 divided doses if creatinine clearance 50‒79 mL/minute. Kidney Tests: Monitor creatinine clearance regularly. Your doctor might check your kidney function regularly. Kidney Problems: Report worsening kidney problems or severe side effects (e.g., double vision ). Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. The mean gabapentin half-life ranged from about 6.5 hours (patients with creatinine clearance >60 mL/min) to 52 hours (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) and gabapentin renal clearance from about 90 mL/min (>60 mL/min group) to about 10 mL/min (<30 mL/min). The risk of respiratory depression should be assessed when initiating gabapentin in patients with respiratory comorbidities, neurological disease, renal impairment and in combination with other respiratory depressants such as opioids. Gabapentin clearance due to residual kidney func-tion fits the equation: Renal Clearance 5 0:78 3 CL cr 2 0:24 The equation is valid even at low single-digit CL cr values.5 Her residual CL cr of 3.9 mL/min predicts a renal gabapentin clearance of 2.80 mL/min. The clearance due to PD equals the total clearance (14 mL/min) minus the nonrenal I currently take gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia and have CKD stage 3. Take 900-1200 gabapentin daily over past 20 years. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Not a substrate, inducer, or inhibitor of CYP450 isoenzymes. Elimination. Half-life: 5-7 hr. Dialyzable: Yes. Renal clearance: 225 mL/min; In patients with stable renal function, creatinine clearance can be reasonably well estimated using the equation of Cockcroft and Gault. The use of gabapentin capsules in patients less than 12 years of age with compromised renal function has not been studied.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |