Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
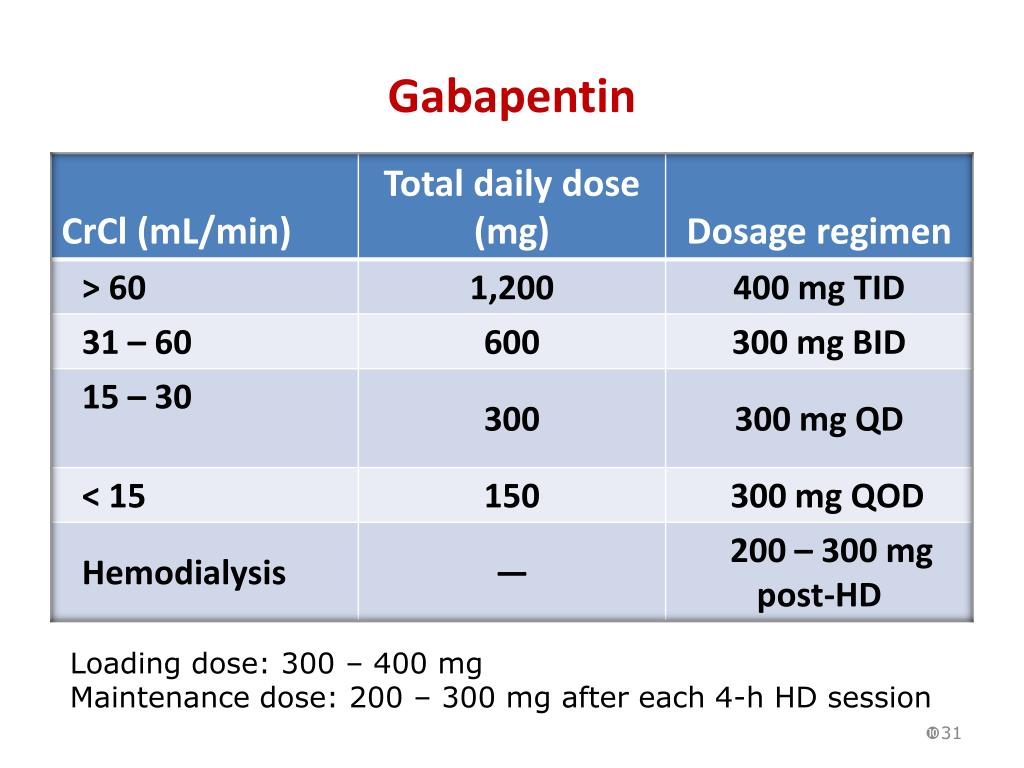
BACKGROUND: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Chronic kidney disease has become a global epidemic, and frequently its significance has been underestimated. 22,23 The present study revealed several deficiencies in our current state of care for patients with chronic kidney disease who are receiving long-term gabapentin. First, the gabapentin dosage adjustment for these patients was insufficient. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Discussion: Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. In summary, we can conclude that although it happens infrequently, gabapentin may cause myotoxicity, rhabdomyolysis and renal failure even in patients whose renal function was previously normal. .table_layout tbody td{ font-size:0.95em;} Usual Gabapentin Dosing (Adults) Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg Gabapentin Renal Dosing [>60 ml/min]: Give usual dosage : Dosage range: 400-1400mg/day (divided doses - Usually bid) : Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. : 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. the kidney, and pharmacokinetic studies show a stepwise prolongation in the elimination half-life of gabapentin and pregabalin as kidney function declines.9,10 Gabapentinoids should therefore be started at lower doses in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD; guidelines are summarized in Table S1).1-3,11 Although the risk of gabapentinoid Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the dosage in patients with renal insufficiency to avoid severe adverse effects. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. Chronic kidney disease has become a global epidemic, and frequently its significance has been underestimated. 22, 23 The present study revealed several deficiencies in our current state of care for patients with chronic kidney disease who are receiving long-term gabapentin. First, the gabapentin dosage adjustment for these patients was Gabapentin isn’t known to cause liver or kidney problems. However, it can cause an allergic reaction called DRESS syndrome, which can lead to liver or kidney damage. But this is extremely rare. If you have existing kidney problems, your healthcare provider may start you at a lower gabapentin dose. Materials and methods: A retrospective analysis of adult CKD and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients hospitalized from 2014 to 2020 and receiving GPs was conducted. Patients were grouped based on whether the average daily dose prescribed was higher than recommended (inappropriately dosed, (ID)) or as recommended (appropriately dosed (AD It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Rationale & objective: Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |