Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
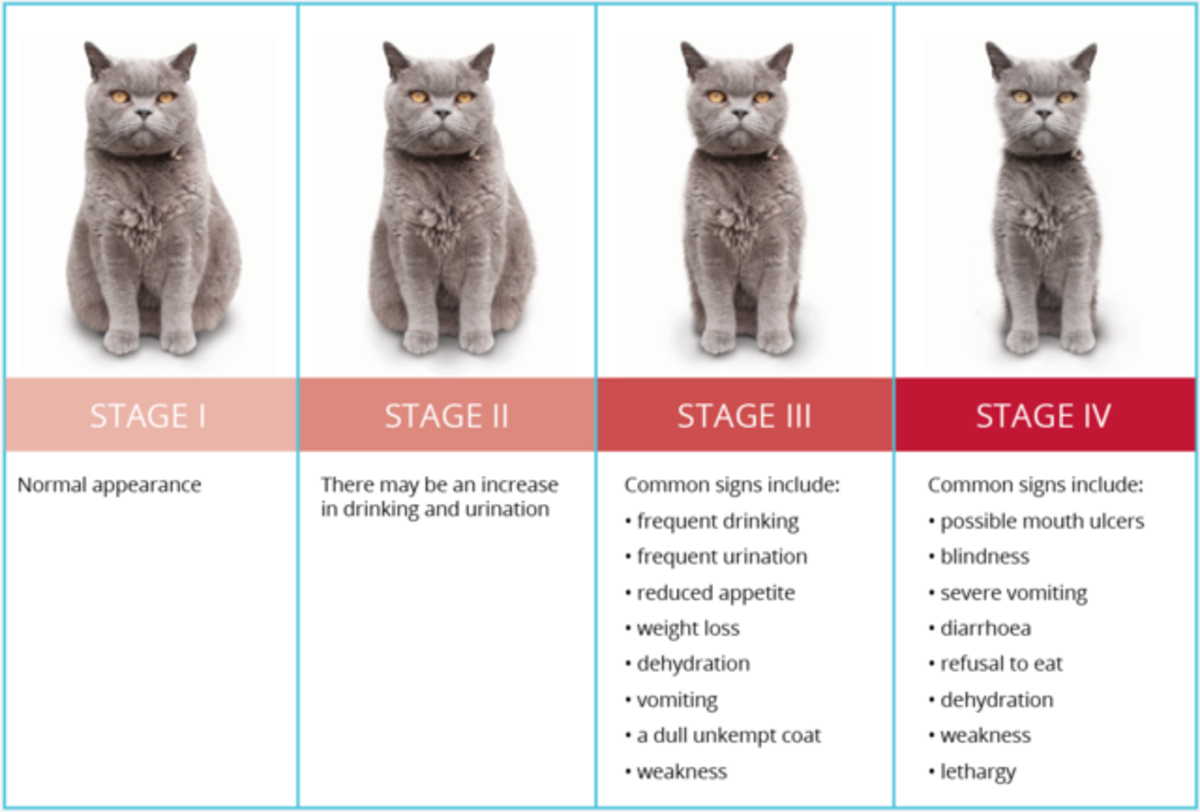 |  |
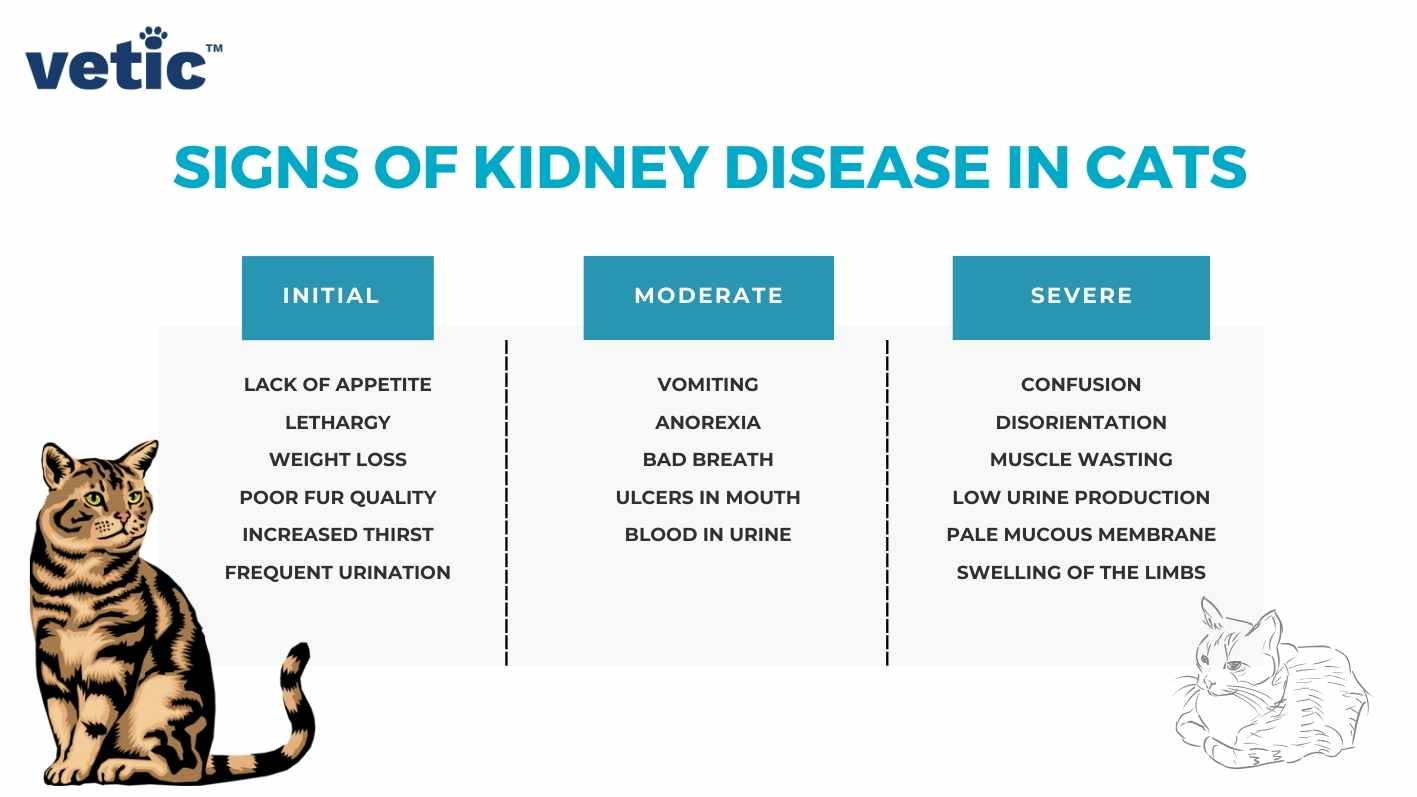
Gabapentin and Kidney Disease. It’s essential to exercise caution when using gabapentin in cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Higher doses can lead to excessive sedation and hypotension in these patients. A dose decrease of at least 50% is often used in these cases. It’s imperative to consult with your veterinarian if your cat has CKD. Objectives: The purpose of this study was to assess serum concentrations of gabapentin in cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) vs clinically healthy cats. Methods: Five healthy cats were enrolled in a pharmacokinetic study. A single 20 mg/kg dose of gabapentin was administered orally and blood was obtained at 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 8 Kidney Disease: Cats with kidney disease might be more sensitive to the effects of gabapentin, potentially experiencing more pronounced sedation or hypotension. Lower doses are often required in these cases, sometimes by at least 50%. Investigating appropriate dosing for gabapentin sedation in cats with and without chronic kidney disease (2017) Winn Feline Foundation reports on the study's goals and Gabapentin sedation in cats with and without chronic kidney disease (2020) Winn Feline Foundation gives an update, stating that CKD cats seem to have much higher levels of Concern #13: Can Gabapentin be used in cats with liver or kidney disease? Answer: Gabapentin should be used with caution in cats with liver or kidney disease, as these conditions can affect how the medication is metabolized in the body. Your veterinarian may recommend adjusting the dosage or exploring alternative treatment options in these cases. The question of whether gabapentin is harmful for cats with kidney disease is complex and doesn’t have a simple yes or no answer. While gabapentin isn’t inherently nephrotoxic (toxic to kidneys), its use in cats with pre-existing kidney issues requires careful consideration and monitoring. 1. Is gabapentin safe for cats with kidney disease? Yes, gabapentin is considered safe for use in cats with kidney disease when dosed appropriately and monitored closely by a veterinarian. 2. Will gabapentin interact with other medications my cat is taking? The question of whether gabapentin is safe for cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is complex and requires careful consideration. The short answer is: it can be safe when used judiciously, but it’s not without risks and requires dosage adjustments due to the kidneys’ role in its elimination. An early study concluded that a dose of 20mg/kg was effective for this purpose in healthy cats, but this dose may be inappropriate for elderly cats, specifically those with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Human studies have recommended Gabapentin doses be reduced in CKD patients, but no studies have been done in cats. Investigating appropriate dosing for gabapentin sedation in cats with and without chronic kidney disease (2017) Winn Feline Foundation reports on the study's goals and Gabapentin sedation in cats with and without chronic kidney disease (2020) Winn Feline Foundation gives an update, stating that CKD cats seem to have much higher levels of Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess serum concentrations of gabapentin in cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) vs clinically healthy cats. Methods Five healthy cats were enrolled in a pharmacokinetic study. A single 20mg/kg dose of gabapentin Gabapentin for cats with chronic kidney disease: Cats with chronic kidney disease often experience pain and discomfort as a result of their condition. Gabapentin can be used to help manage the pain associated with kidney disease, improving the cat 's comfort and overall quality of life. 7. The 20 mg/kg stress-reduction dose of gabapentin may be beneficial to facilitate preventive veterinary care in younger, healthy cats, but this dose may be inappropriate for elderly cats, specifically those with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Gabapentin is eliminated almost entirely through renal excretion, and decreased renal function significantly influences the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in humans. 14 While doses of gabapentin in the range of 50–150 mg/cat have been used in normal cats, 4,5,11 it should be noted that higher doses may be unsuitable for cats with CKD. 15 In a What is the recommended gabapentin dosage for cats with kidney disease? While the standard dosage for healthy cats is 20mg/kg, cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) should be given a reduced dose of 10mg/kg. Cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) exhibit higher serum concentrations of gabapentin, indicating a need for dose adjustment. It’s essential to administer lower doses to avoid potential toxicity and monitor their response closely. Gabapentin should be used cautiously in cats with liver or kidney disease, as we may see it take longer for the effects to wear off. Its use should typically be avoided in pregnant queens. Sixteen chronic kidney disease (CKD cats) – (ten IRIS Stage 2, twelve IRIS Stage 3) – have completed the limited sampling PK study at 10 mg/kg. Samples from eight CKD cats have been analyzed to date to test the model. The model performed well and the data for normal cats demonstrated that half-life was similar to previous published reports. Gabapentin may decrease arterial BP in cats with and without CKD and these findings should be taken into account when gabapentin is administered to patients in which measurement of BP is needed. Visits to the veterinary clinic can be a source of stress for both the feline patient and the caregiver. Study demonstrates that companion cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) will exhibit compliance during veterinary visits on a lower dosage of gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |