Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
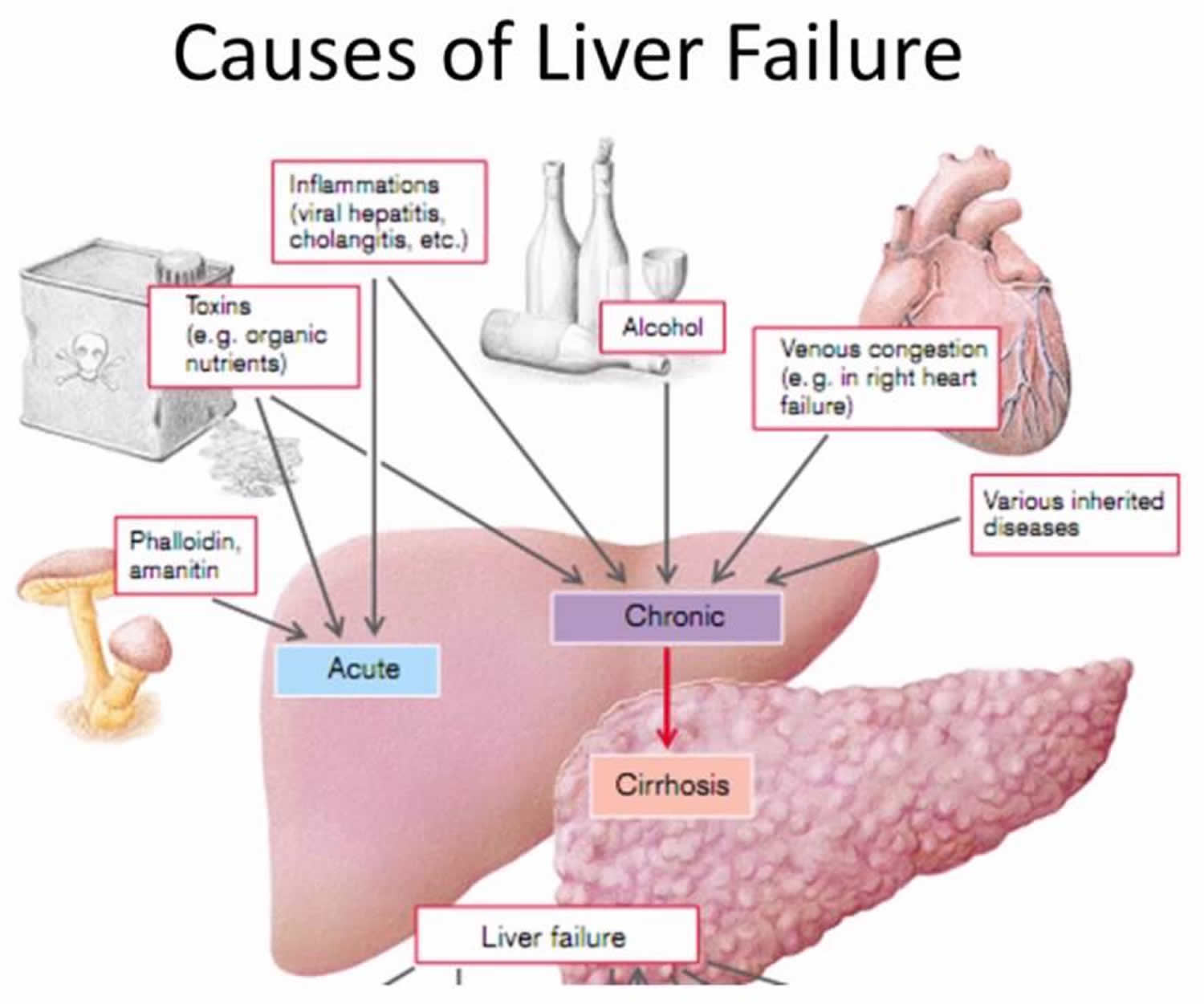
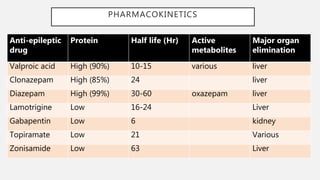
Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease Hi, Gabapentin is exclusively excreted by the Kidneys and undergoes no appreciable metabolism by the Liver. As to whether it is toxic to your Kidneys is probably a question that you should be asking your prescribing doctor. While no cases of acute liver failure or chronic liver injury have been definitively and solely attributed to gabapentin, some reports suggest that gabapentin can, in rare instances, cause hepatocellular injury. This means damage to the cells of the liver. Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology. Introduction. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin is not absolutely contraindicated in kidney disease, but it demands meticulous management. The key to its safe use is careful dose adjustments, rigorous monitoring for toxicity, and an open dialogue with your healthcare provider. Can Gabapentin Affect Your Liver and Kidneys? Written By Daphne Berryhill, RPh Published on Sep 25, 2023. How Does Benadryl Affect Your Kidneys, Liver, and Heart? Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. No cases of acute liver failure or chronic liver injury due to gabapentin have been described. There is no information about cross reactivity with other compounds having similar structure (pregabalin). Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Drug manufacturer Pfizer classifies abnormal liver function tests as an infrequent side effect for gabapentin 5. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Gabapentin is approved by the FDA for treating seizure disorders and neuropathic pain, except for trigeminal neuralgia. However, it is frequently used off-label to treat other pain conditions and psychological disorders, such as anxiety. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. What is Gabapentin used for? 🩺 Primarily for pain management and seizure control in dogs. Are there long-term side effects? 🐕 Yes, common ones include sedation, coordination issues, and weight gain. Does Gabapentin affect the liver or kidneys? 💊 Rarely, but in high doses or prolonged use, it can strain these organs. Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |