Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
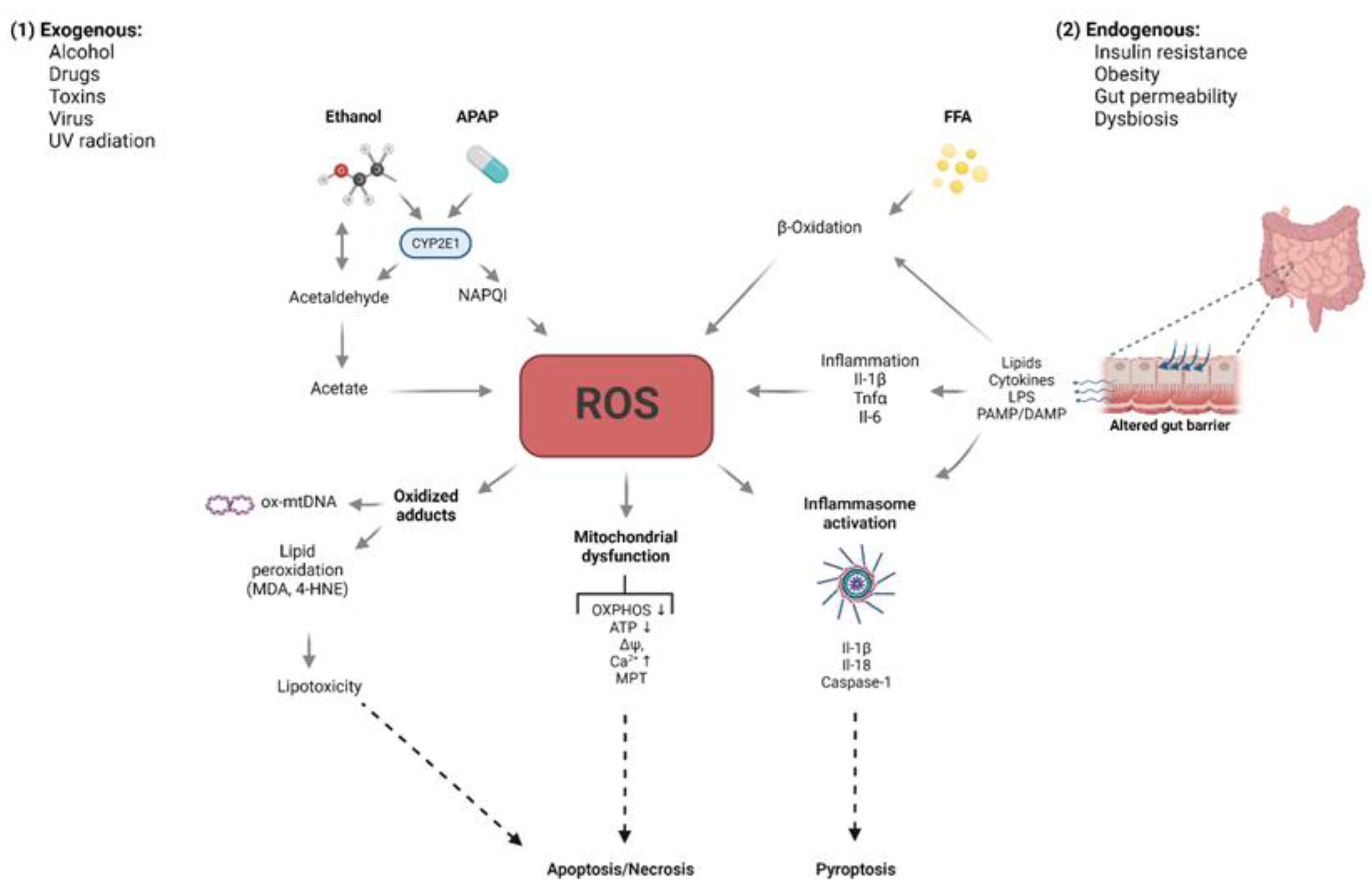 |  |
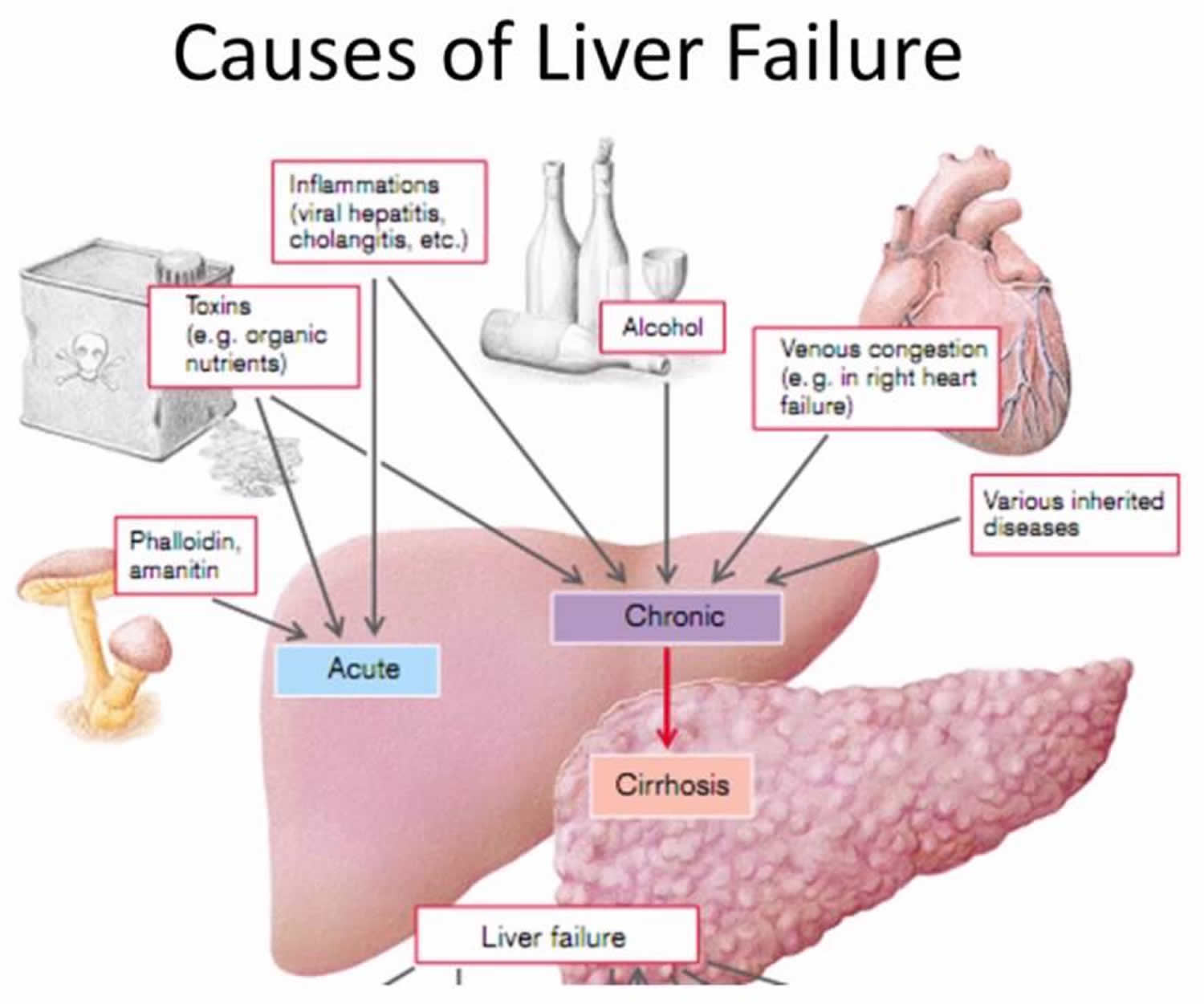
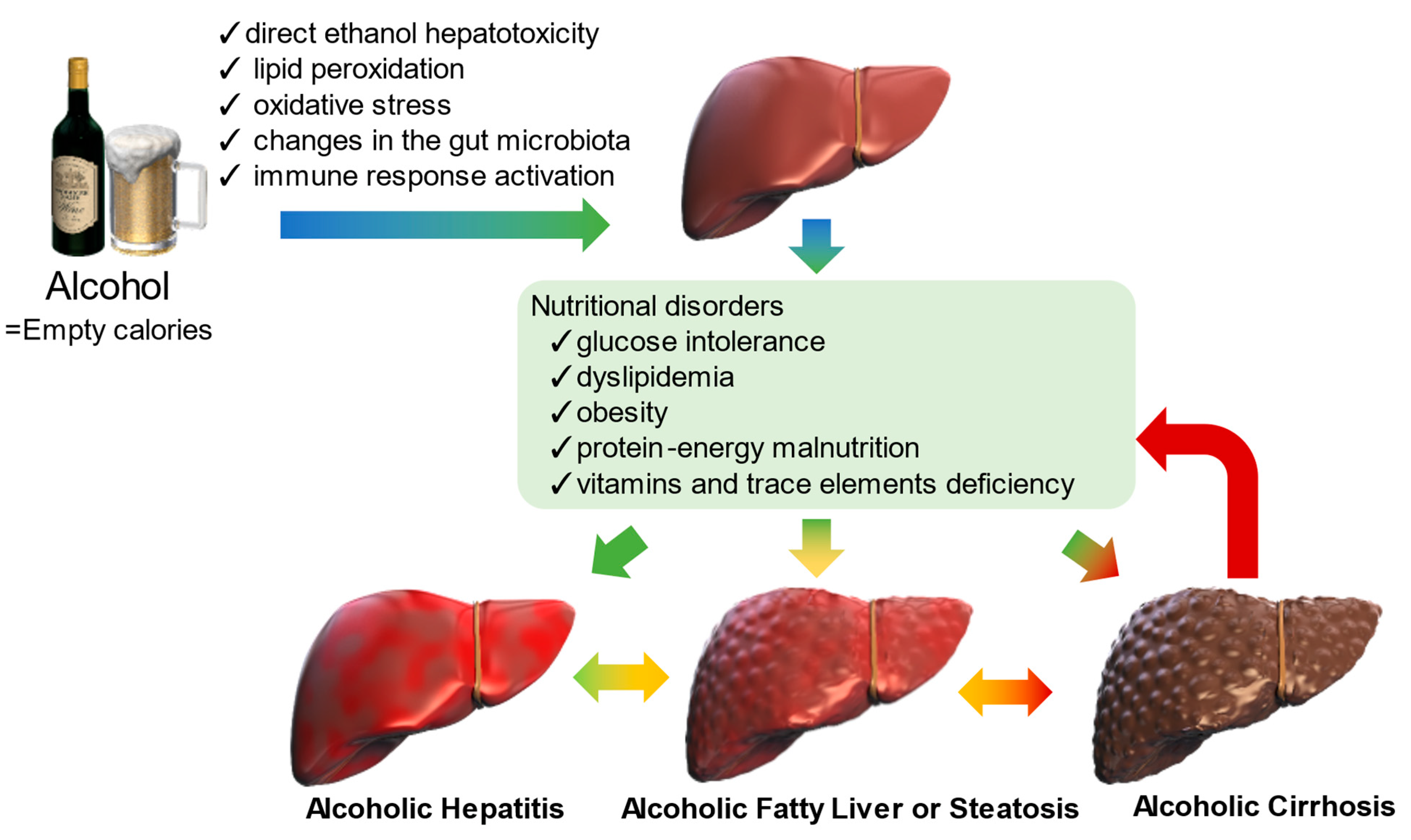
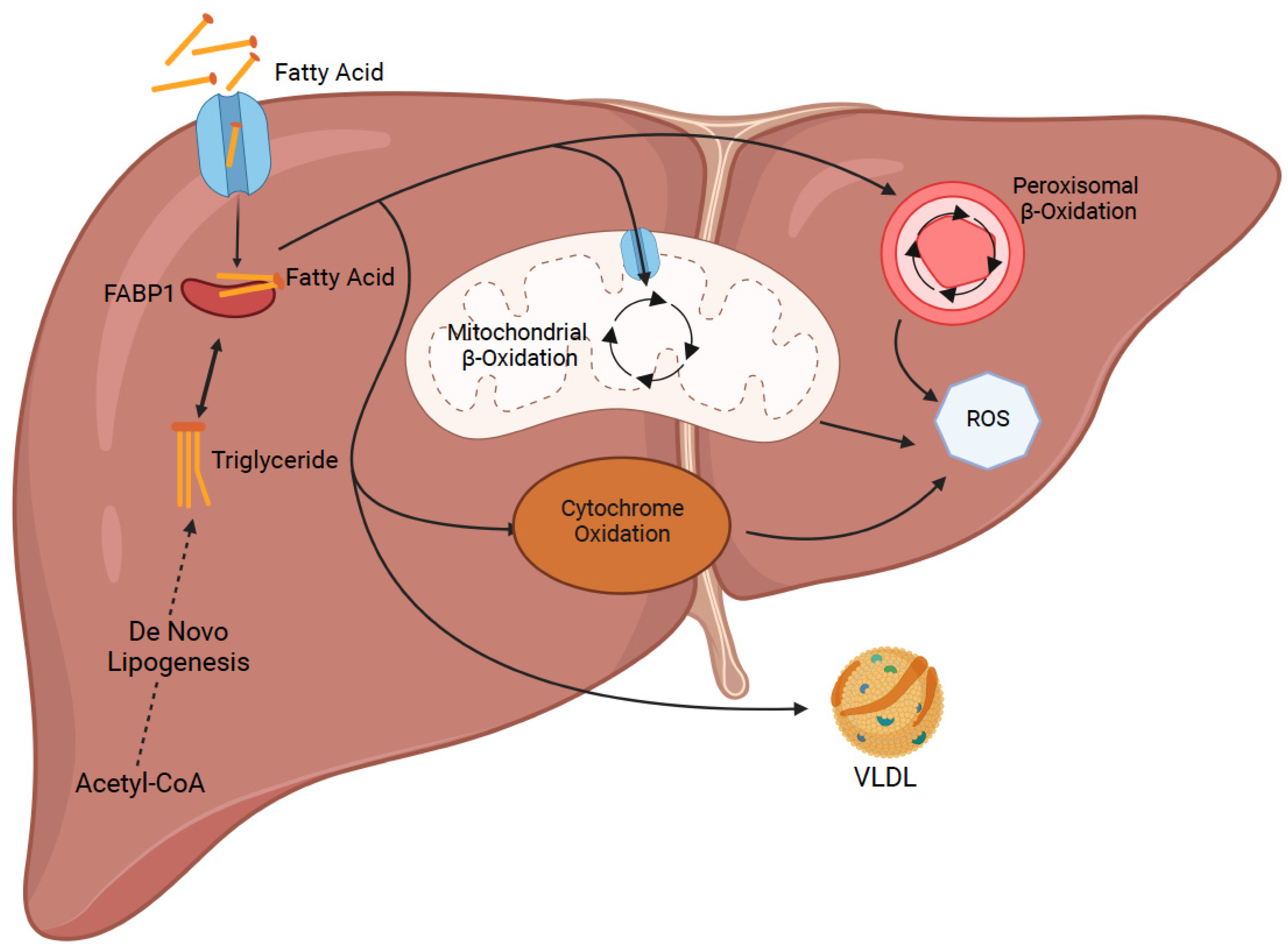
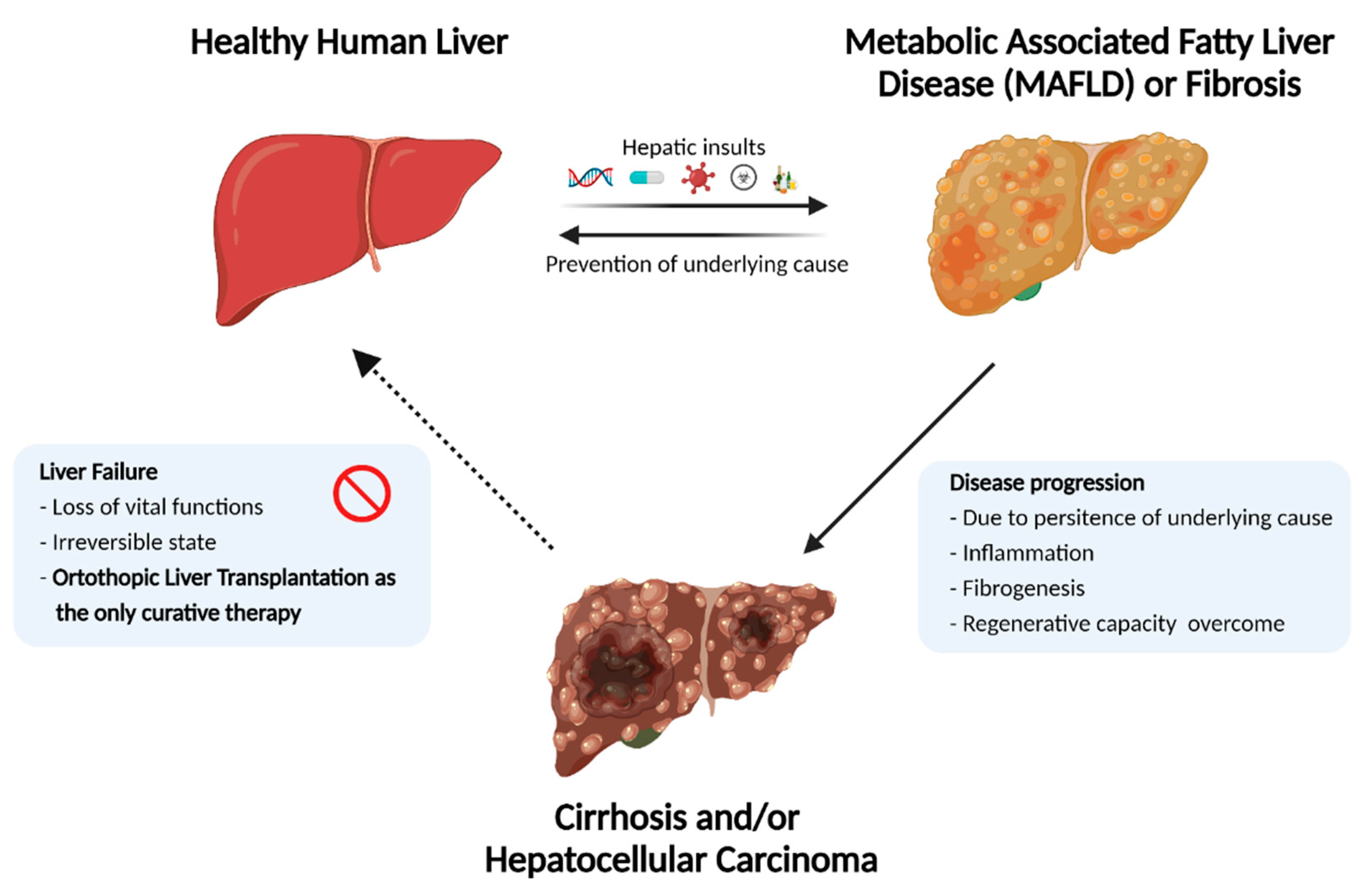
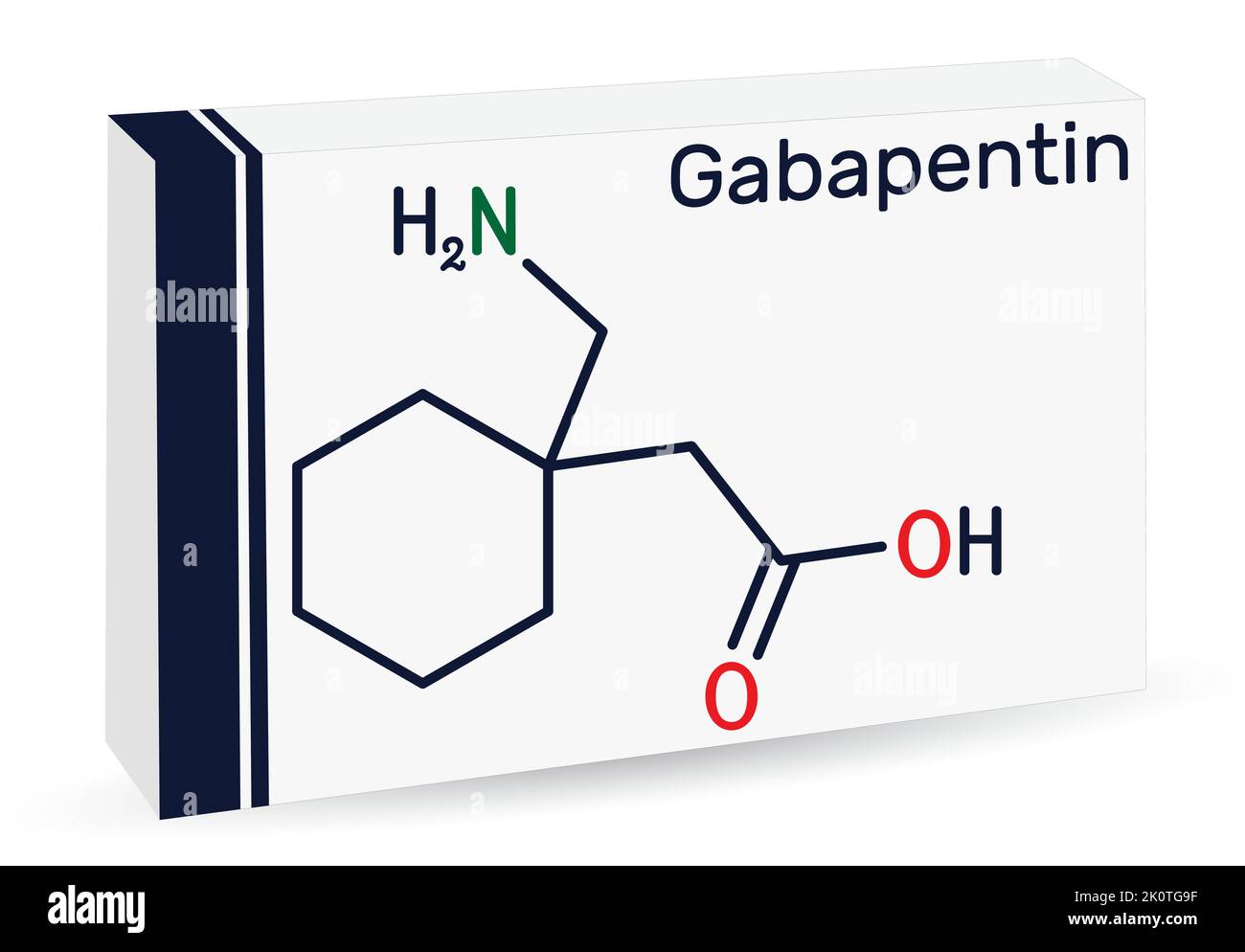
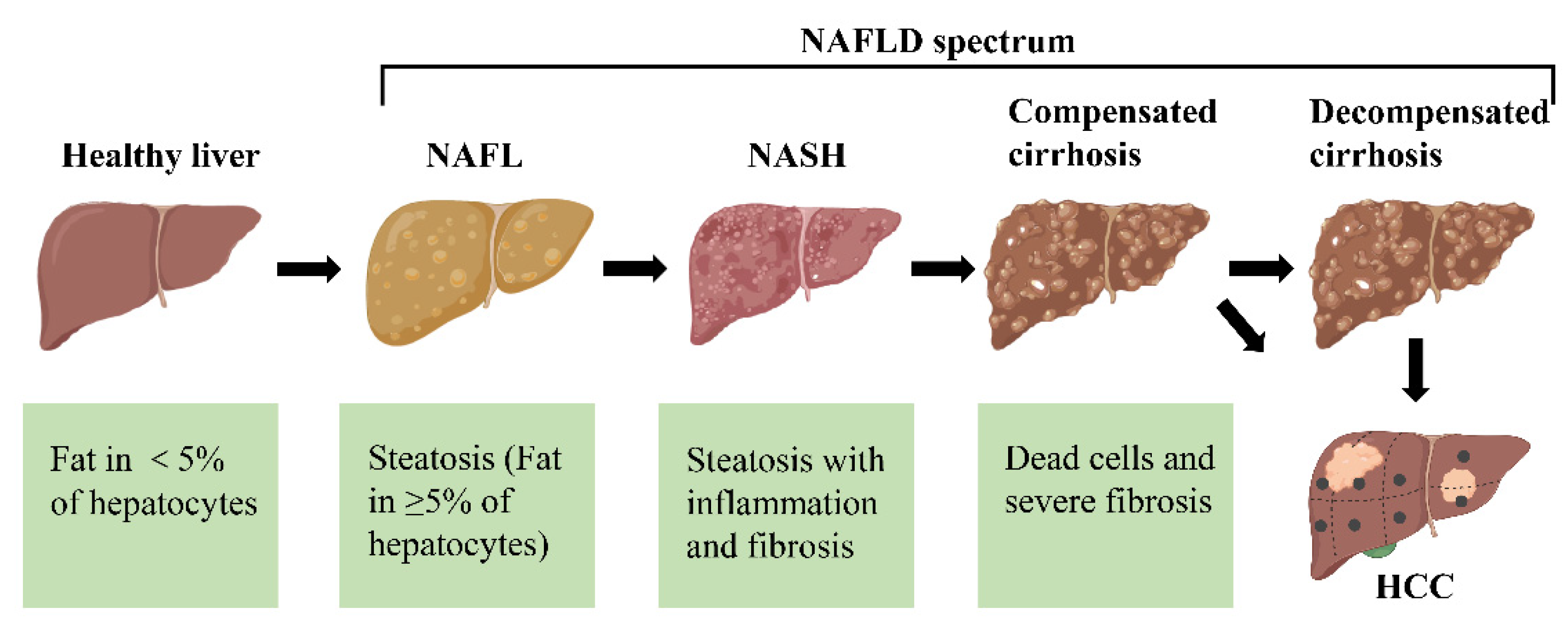
It seems likely that such susceptibility is related to genetic factors. We suggest that aromatic AEDs be avoided in treating African American patients for epilepsy or mood disorders, or if used, that they be followed closely and advised to stop the drug promptly at the first signs of skin or liver damage. Supplementary Material Gabapentin-Induced Liver Toxicity Am J Ther. 2022 Nov-Dec;29(6):e751-e752. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000001208. Gabapentin / adverse effects Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Prior lab review showed liver enzymes within normal limits until one month prior to admission, when his ALP was 851. He started taking gabapentin, without introduction of any other medications, one month prior to the initial rise in ALP . Evaluation for viral, inherited, and metabolic causes of liver disease were negative. The risk of liver damage is higher for people with other liver infections, like hepatitis B, who have alcohol use disorder or who take other medicines that can damage the liver. But one study found that long-term ART doesn’t increase the risk of liver damage. Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. However, there are a few descriptions of gabapentin-related Gabapentin and other adjuvant analgesics can be considered; consider side effect profile and tailor analgesic plan to specific liver disease complications (e.g. hepatic encephalopathy, fluctuating renal function, varices) In patients with liver disease, impaired hepatic function, reduced hepatic blood flow, and portosystemic shunting reduce first‐pass metabolism, thereby increasing the proportion of drug that is bioavailable and increasing the risk for toxicity. RETRACTED: Vitamin E protects against gabapentin-induced chronic hepatic and renal damage associated with the inhibition of apoptosis and tissue injury in rats Author links open overlay panel Nermeen N. Welson a , Remon R. Rofaeil b c , Sabreen Mahmoud Ahmed d , Shereen S. Gaber e , Gaber El-Saber Batiha f , Mary Girgis Shahataa g Purpose: Trazodone and gabapentin are commonly used treatments. We report a rare case of trazodone and gabapentin-induced liver injury. Case: A 40-year-old woman with a history of depression presented jaundice. She had no other complaints. The patient denied risk factors for acute and chronic liver disease. Gabapentin-Induced Liver Toxicity. Chahal, Japjot MD 1; Arif, Muhammad Osman MD 2; Achufusi, Ted George MD 1. Author Information . 1 Internal Medicine, SUNY Upstate (Review of spontaneous reports of adverse events attributed to gabapentin from a French registry [Fuzier 2013] identified 90 cases of liver damage, gabapentin being the only suspect drug in 10 cases of "hepatitis", one of which was fatal). Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Gabapentin was held and patient’s liver function tests improved, with ALP 1058 IU/L, AST 158 IU/L, and ALT 149 IU/L, and remained stable. Patient discontinued gabapentin and was advised to follow up outpatient, unfortunately he was lost to follow-up. Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease Changes in liver function may be attributed to free radical damage induced by gabapentin, as documented in this study, where the drug enhanced antioxidant defense systems and elevated liver NO Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. Keywords: gabapentin, hepatotoxicity, drug-induced liver injury. To minimize the risk of liver damage while taking Gabapentin, it is important to follow these guidelines: Inform your healthcare provider about any pre-existing liver conditions or medications you are taking. Regularly monitor liver function through blood tests as recommended by your doctor. Gabapentin is a prescription drug for seizures and nerve pain. It usually doesn’t harm the liver, but it can cause a severe allergic reaction called DRESS syndrome that can affect the liver and kidneys. Learn more about gabapentin and its effects on your liver and kidneys.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |