Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
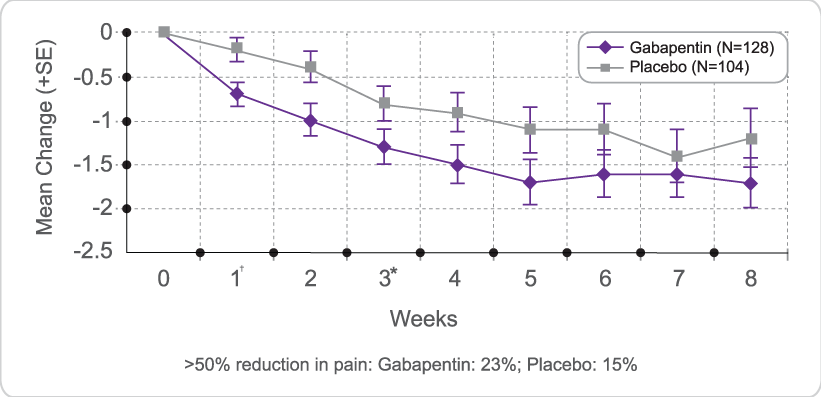 |  |
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more The recommended dose in cats is 0.5 to 1 mg/kg PO Q 24 H. 17 Always use prednisolone—while other species can convert prednisone to prednisolone in the liver, cats do not absorb or convert prednisone efficiently. 21 While there are no cures for the late-stage liver disease there are various treatment options including gabapentin and cirrhosis of the liver. One of the main goals of cirrhosis treatment is to ease the symptoms. Some options include avoiding alcohol, a low-salt diet, and weight loss. There is no specific dosage adjustment recommended for individuals with liver impairment. Dosage adjustments for renal and liver impairment. For individuals with impaired kidney function or undergoing hemodialysis, the gabapentin dosage may need to be adjusted. Based on limited safety and efficacy data, acetaminophen is the preferred analgesic in patients with liver disease who are not actively drinking, and it may be dosed up to 2 to 3 g/day. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided due to their adverse effects of renal impairment, fluid retention, and increased bleeding risk. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided A Cochrane review reported that 3 to 4 patients out of every 10 with either of these conditions experienced at least a 50% reduction in pain intensity when prescribed gabapentin at dosages of 1800mg-3600 mg/day (gabapentin encarbil: 1200mg-3600 mg/day). This compared with only 1 or 2 out of every 10 given a placebo (an inactive treatment). Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Gabapentin Dosage for Cats. The dosage for gabapentin may vary depending on a cat’s size, as well as whether it’s being used as a pain medication, as part of seizure management, or as a sedative before vet visits or travel. From a safety perspective, a gabapentin dosage for cats will typically not exceed 50-100mg per cat to address pain or Therapeutic dosing targets of both medications have been established in clinical trials for neuropathic pain (gabapentin 1800–3600 mg/day; pregabalin 150–600 mg/day). The recommended initial dose for adults is 300 mg three times daily increasing as needed to a maximum dose of 1800 mg daily. The most common side effects of gabapentin are dose related and include dizziness, somnolence, tremor, ataxia, blurred vision, anxiety, and gastrointestinal upset or nausea. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin is not extensively protein-bound with its bioavailability most pronounced at lower dose levels . Gabapentin has no appreciable liver metabolism, yet, suspected cases of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported. For gabapentin, start 300 mg daily and increase slowly over weeks. For pregabalin, start 50 mg bid for patients with normal renal function and increase slowly over weeks. Topical Anesthetics Dosage adjustment of GRALISE is necessary in patients with impaired renal function. GRALISE should not be administered in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min or in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Reductions in GRALISE dose should be made in patients with age-related compromised renal function. With a cautious approach including slow dose up-titration and careful monitoring, effective analgesia can be achieved in most cirrhotic patients without significant side effects or decompensation of their liver disease. Paracetamol is safe in patients with chronic liver disease but reduced doses of 2-3 grams daily is recommended for long-term use. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Suggested dosing schedule: Three or four times daily/ Two or three times daily: Usual dose: 900–3600 mg/day: 150–600 mg/day: Time to effective dose using recommended titrations: 14 days: 5–7 days: Gabapentin dosing in renal impairment (creatinine clearance, mL/min) 50–79: 600–1800 mg/day in three divided doses: 30–49 We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |