Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 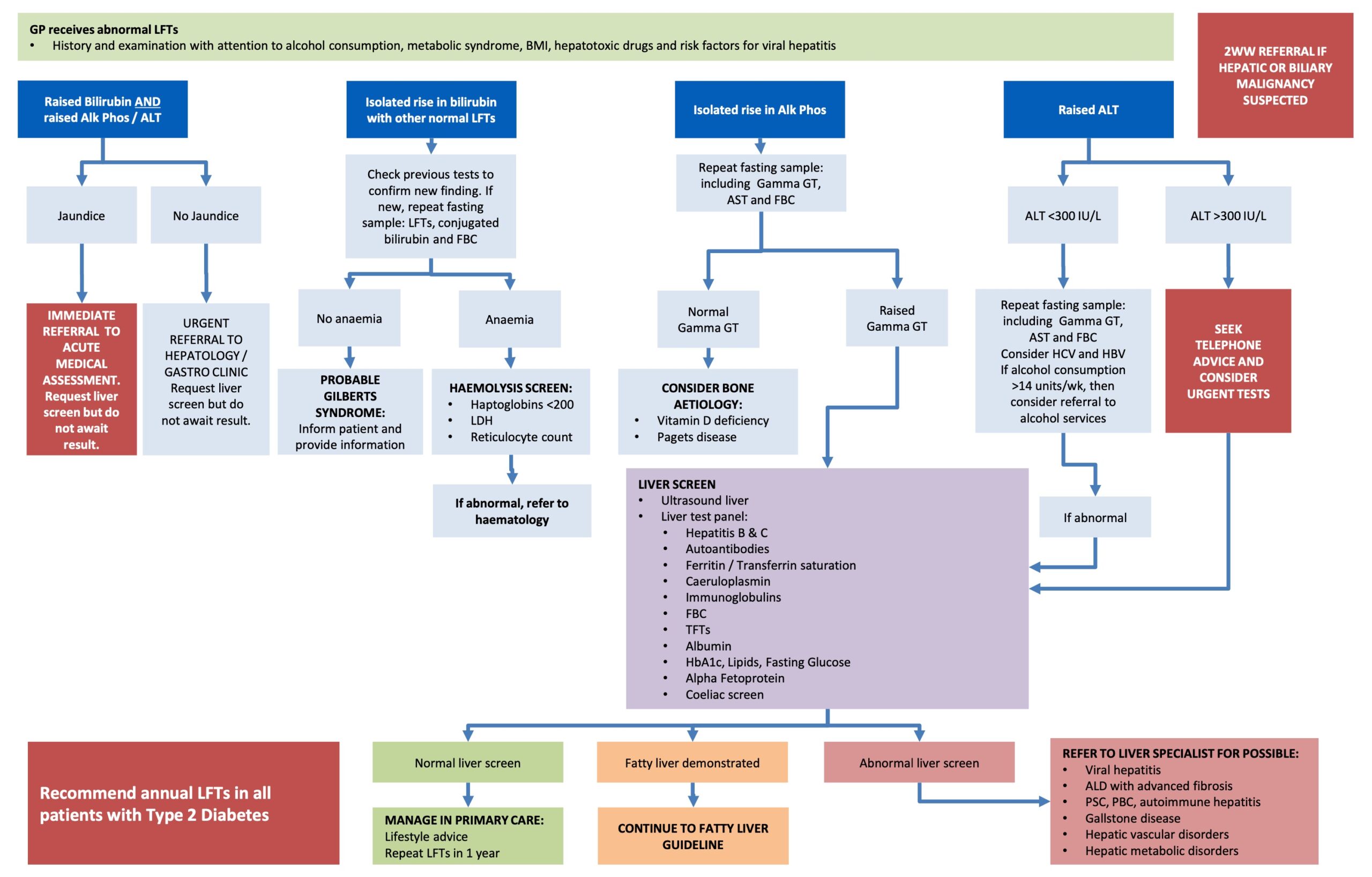 |
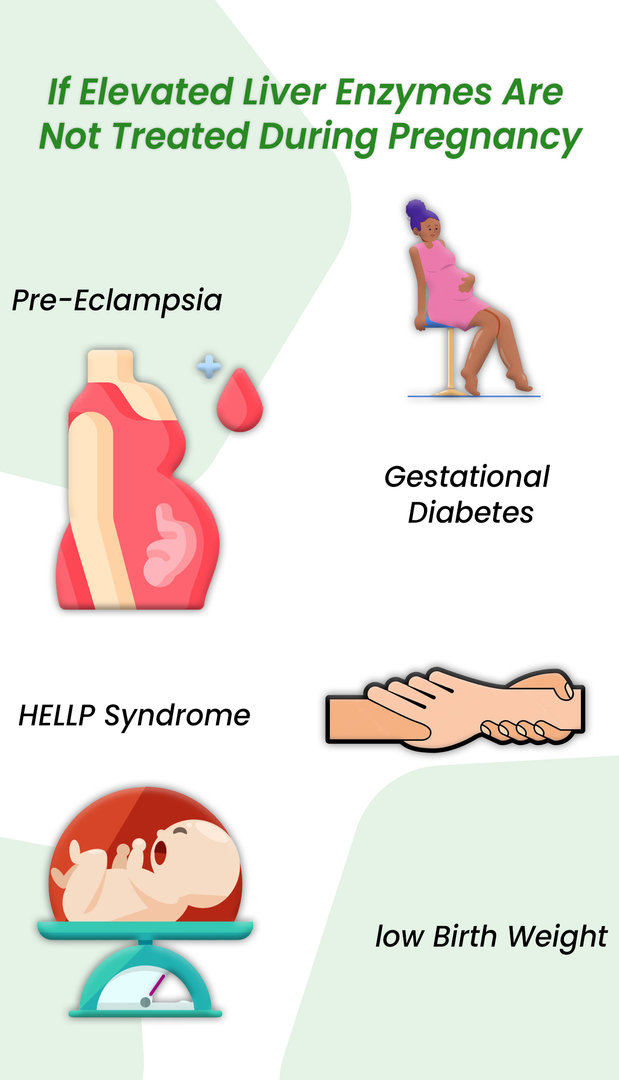
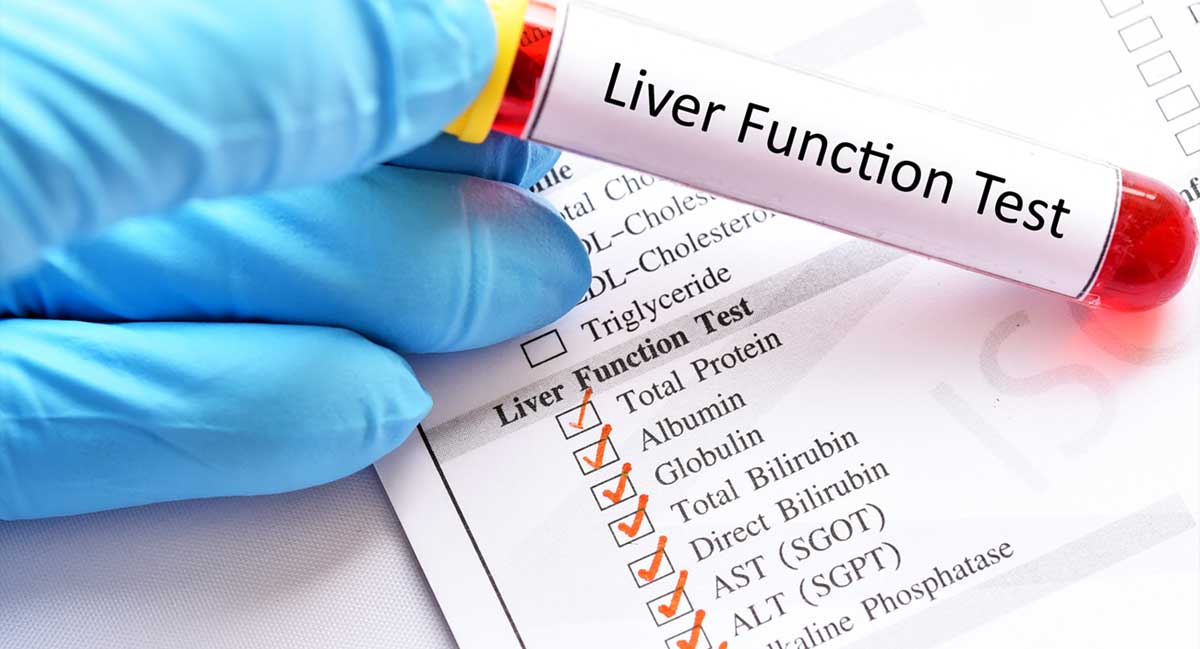
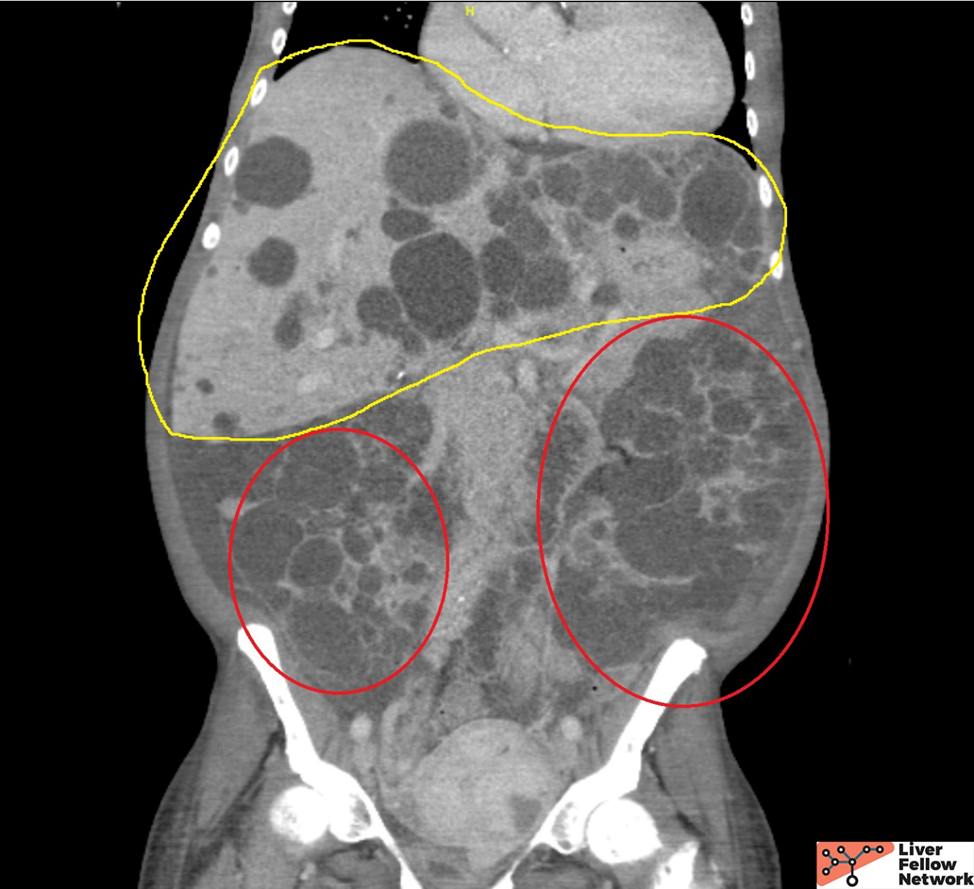
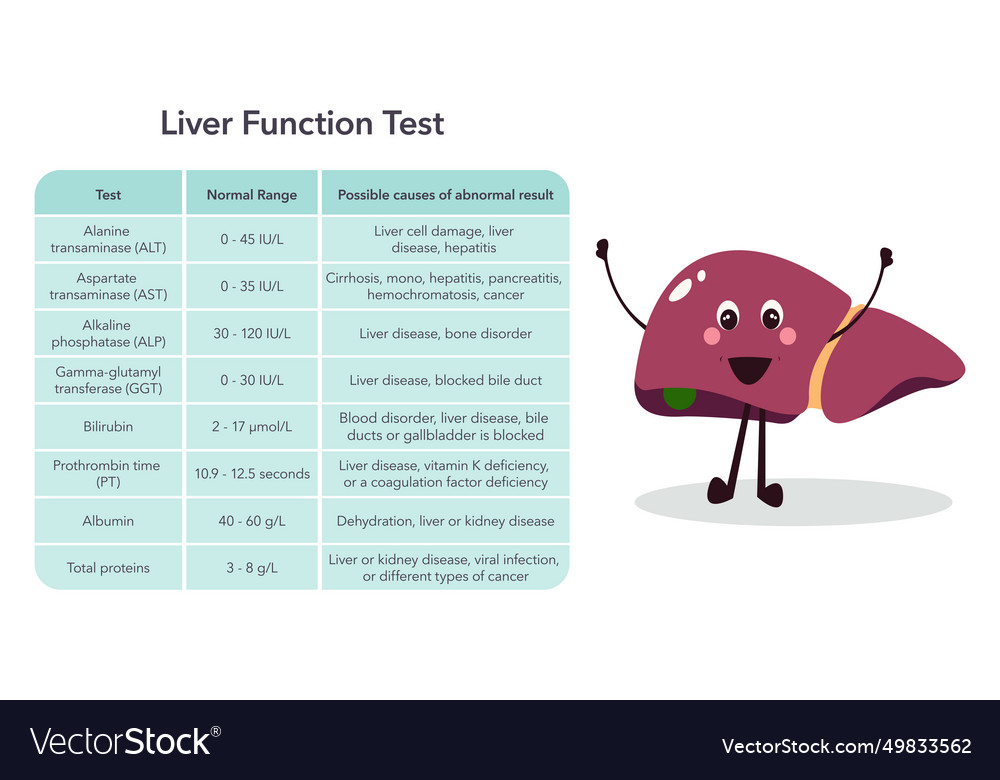
RETRACTED: Vitamin E protects against gabapentin-induced chronic hepatic and renal damage associated with the inhibition of apoptosis and tissue injury in rats Author links open overlay panel Nermeen N. Welson a , Remon R. Rofaeil b c , Sabreen Mahmoud Ahmed d , Shereen S. Gaber e , Gaber El-Saber Batiha f , Mary Girgis Shahataa g Liver function tests at this stage showed aspartate transaminase 104 U/l (reference range 10-40 U/l), bilirubin 199 μmol/l (5-20 μmol/l), alkaline phosphatase 210 U/l (25-115 U/l), and γ-glutamyltransferase 839 U/l (<85 U/l). Changes in liver function may be attributed to free radical damage induced by gabapentin, as documented in this study, where the drug enhanced antioxidant defense systems and elevated liver NO In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Can administration of gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia dramatically increase liver function tests? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. The discontinuation of gabapentin leads to an improvement in liver test abnormalities. The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Therefore this study was undertaken to find out the possibility of liver damage by this drug. Adult male (Wistar) rats of 180-220 g were administered intraperitoneally with GPN (20 or 100 mg/kg) for 45 days. After the experimental period, the liver function tests were carried out in control and experimental groups. Effect of gabapentin on liver function tests To examine the protective effect of Gabapentin on a liver injury during CLP-induced sepsis, serum ALT, AST, and ALP levels were determined. As depicted in Fig. 1 , the CLP group showed significant elevation (p < 0.001) in ALT, AST, and ALP levels compared to the sham group. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin induced cholestasis was thought likely and the drug was stopped. After this, clinical symptoms and liver function tests improved gradually (figure). A liver biopsy showed normal liver architecture with evidence of portal tract expansion by a chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate that incorporated eosinophils and neutrophils. Drug manufacturer Pfizer classifies abnormal liver function tests as an infrequent side effect for gabapentin 5. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer. Therefore this study was undertaken to find out the possibility of liver damage by this drug. Adult male (Wistar) rats of 180-220 g were administered intraperitoneally with GPN (20 or 100 mg/kg) for 45 days. After the experimental period, the liver function tests were carried out in control and experimental groups. Does gabapentin affect liver function tests? Gabapentin is excreted unchanged in the urine. It does not affect the liver enzymes and has not been associated with hepatotoxicity. When your liver is damaged, these enzymes leak out into your blood and can be measured with blood testing called liver function testing. There are several liver enzymes, but the ones that show liver damage from medications are aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT). Lab work revealed abnormal liver function tests, with ALP 1,232 IU/L, AST 291 IU/L, and ALT 188 IU/L, and normal total bilirubin of .8 mg/dL. Prior records revealed completely normal liver function tests 6 months prior to presentation. Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term treatment with GPN is not yet clear. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Gabapentin was held. Thereafter, the man's liver function tests improved and remained stable. He discontinued gabapentin. He was advised to follow up outpatient. However, he was lost to follow-up. Based on clinical presentation and investigational findings, he was diagnosed with drug-induced liver injury attributed to gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |