Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/GettyImages-1080011718-b7f22fa56b934a6b96c23e17458086c9.jpg) | 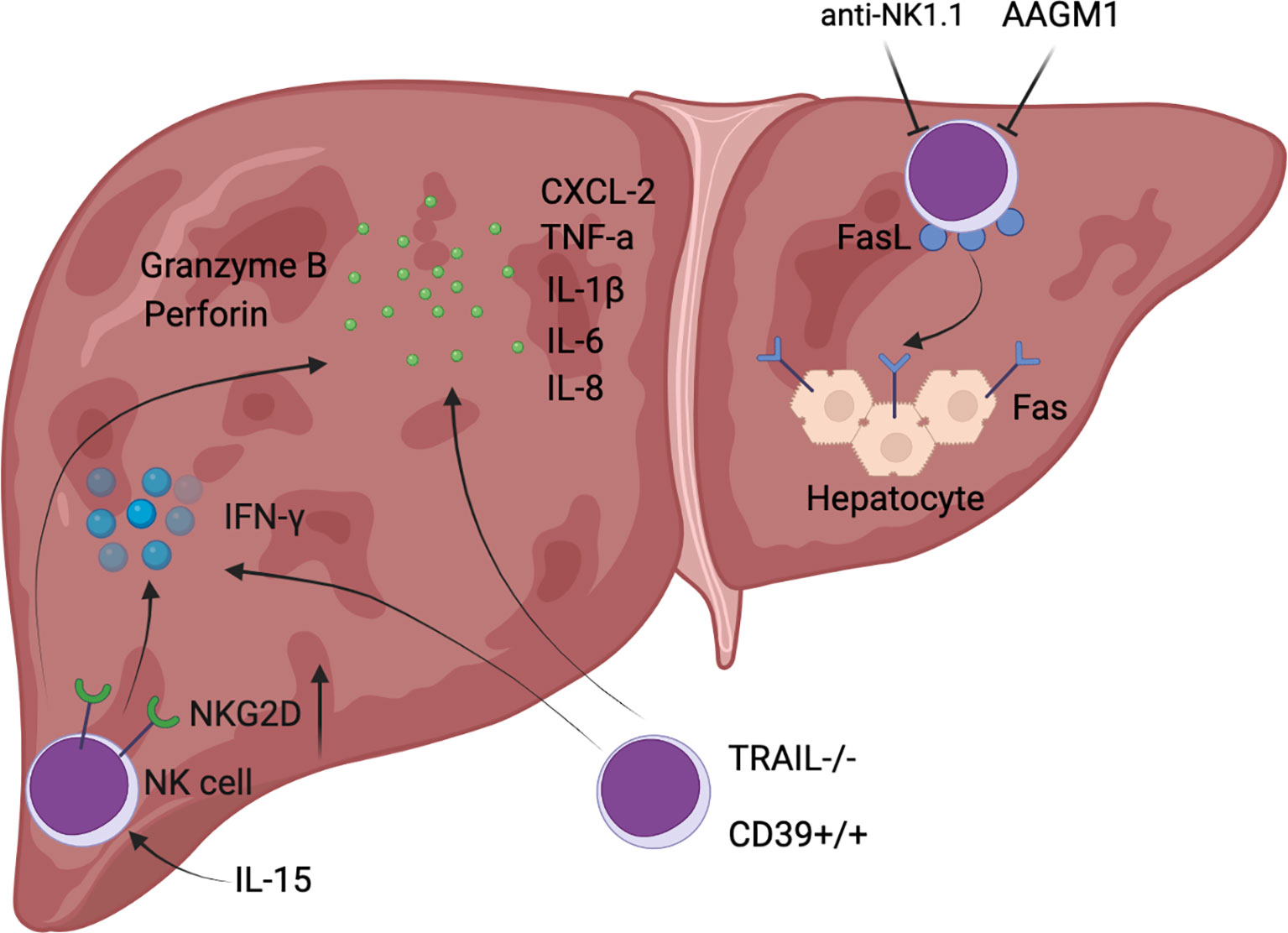 |
 |  |
 | 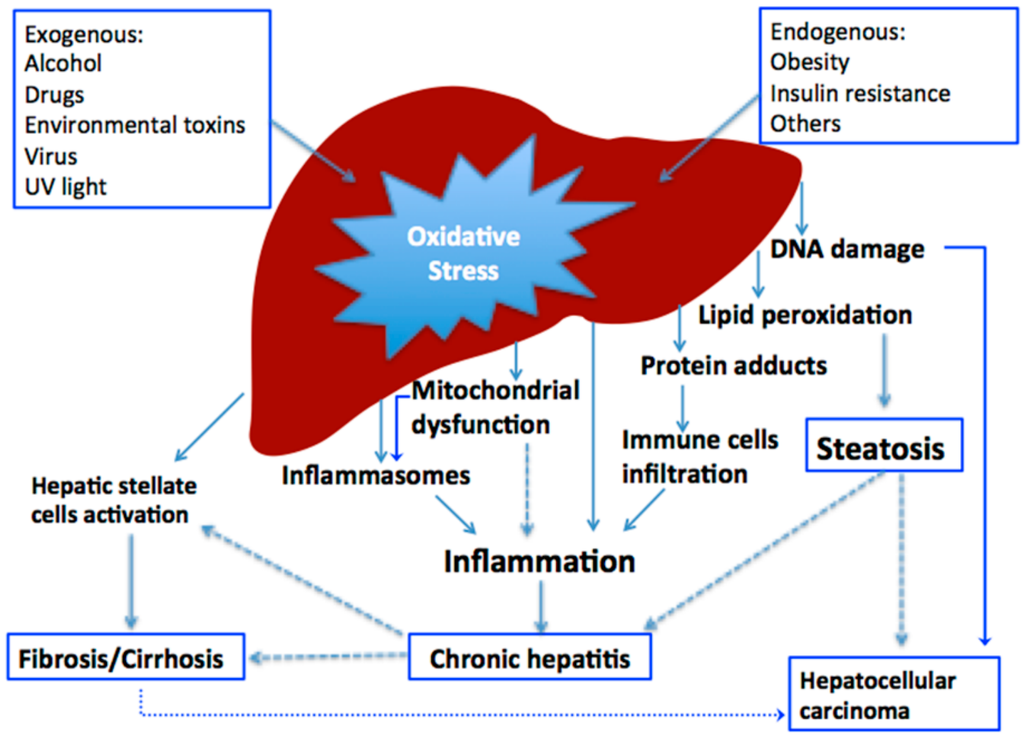 |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SymptomsLiverDamage_1943023_Final_1-ea70d54025564870bd9ac7aabbfca921.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 | 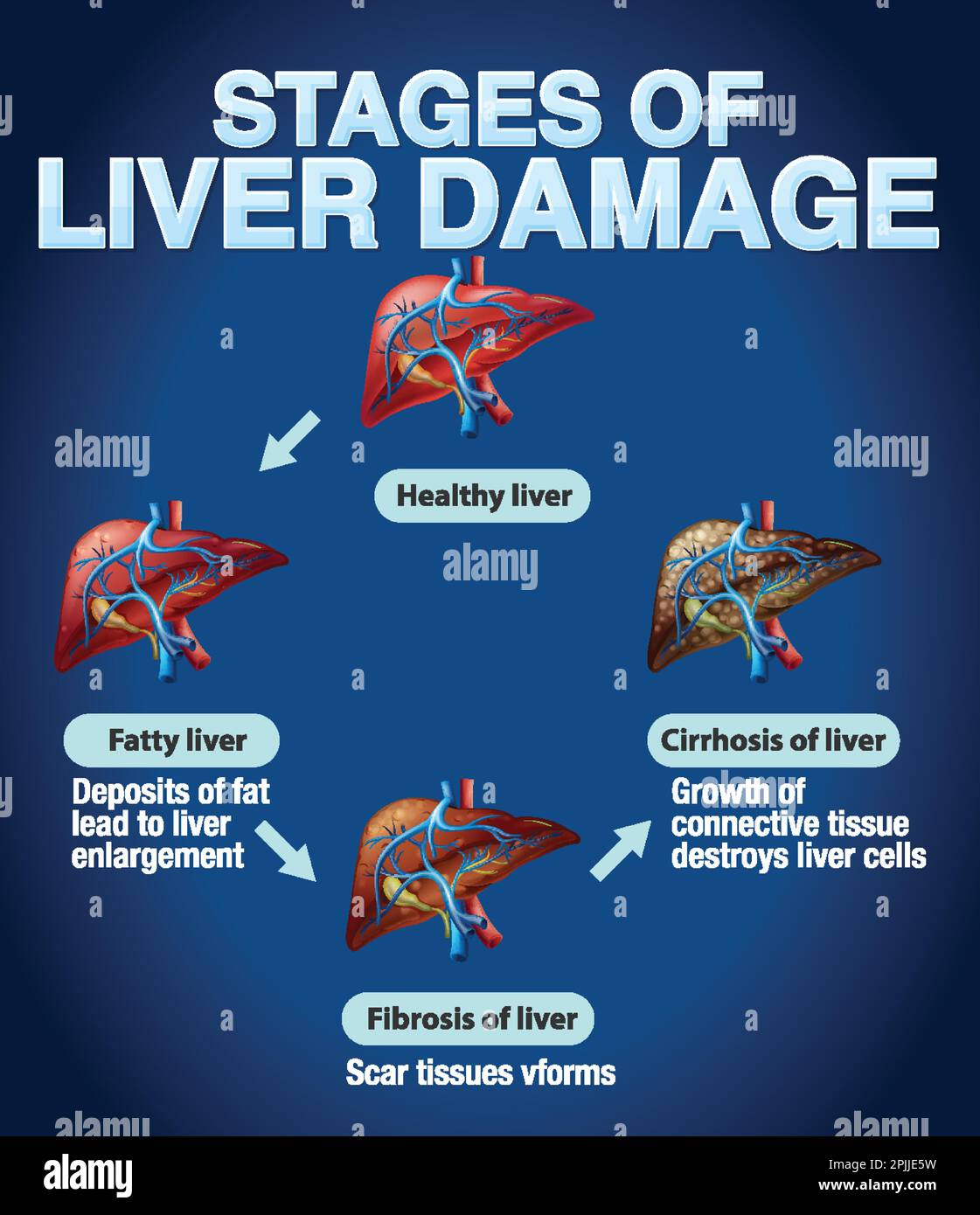 |
Question. I have a patient with trigeminal neuralgia who was taking 1600 mg of gabapentin and had serious elevations of liver function tests (aspartate transaminase 258 U/L, alanine transaminase However, rare individual case reports of liver injury from gabapentin have been published, with the causal relationship not always clear. The reported cases have been mild to moderate in severity and self-limited in course. Due to the wide-scale use of gabapentin, liver injury with symptoms or jaundice is quite rare. We are reporting a case of drug induced liver injury (DILI) secondary to gabapentin therapy with risk factors for underlying non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Gabapentin lacks liver metabolism; the mechanism by which it produces liver injury is still unknown; however, there are reports of hepatotoxicity associated with its administration, so its use must be individualized for each patient. 2. Liver disease is not a single disease entity, but rather ranges from acute liver injury, to chronic liver disease (e.g. nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, chronic hepatitis B) without significant fibrosis, to cirrhosis. Chronic administration of gabapentin causes hepatic and renal impairments, which is ameliorated by Vitamin E; possibly due to the inhibition of biomarkers of apoptosis and tissue injury. Vitamin E protects against gabapentin-induced chronic hepatic and renal damage associated with the inhibition of apoptosis and tissue injury in rats Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. This class, which includes gabapentin and pregabalin, is not metabolized by the liver. Therefore, risks in patients with advanced liver disease are not greatly increased. However, there are case reports of pregabalin‐induced hepatoxicity.4 Gabapentin and pregabalin are renally excreted, so dosages need to be adjusted for renal failure. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. DRESS was common with liver injury caused by lamotrigine, phenytoin, and carbamazepine, but not valproate or gabapentin. Liver injury severity was moderate to severe in the majority: 5 died, and 3 underwent orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). Gabapentin, a common over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer, has been linked to rare individual case reports of liver injury. The causal relationship between gabapentin and liver damage is unclear, with the latency to onset being 1 to 8 weeks. Rare individual case reports of liver injury from gabapentin have been published, although the causal relationship of gabapentin with the liver injury was not always clear. The latency to onset in these reports was 1 to 8 weeks and associated with cholestatic pattern of enzyme elevations. Other AEDs with rising and currently highest prescription rates were associated with few or no cases of liver injury including gabapentin (45.3 million), clonazepam (18.8 million), pregabalin (10.6 million), topiramate (9.3 million), and levetiracetam (7.7 million) and many of cases were judged as only “probable”. Daily treatment with gabapentin for four weeks elevated serum transaminases activities reflecting liver injury. These results are in line with the report of Daoud et al. (2004) and previous In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Purpose: Trazodone and gabapentin are commonly used treatments. We report a rare case of trazodone and gabapentin-induced liver injury. Case: A 40-year-old woman with a history of depression presented jaundice. She had no other complaints. The patient denied risk factors for acute and chronic liver disease. There have been very few cases of gabapentin induced liver injury. In our patient there was a clear temporal association of liver injury occurring after our patient began gabapentin therapy, and slight improvement after a few days of discontinuation. DRESS was common with liver injury caused by lamotrigine, phenytoin, and carbamazepine, but not valproate or gabapentin. Liver injury severity was moderate to severe in the majority: 5 died, and 3 underwent orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/GettyImages-1080011718-b7f22fa56b934a6b96c23e17458086c9.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SymptomsLiverDamage_1943023_Final_1-ea70d54025564870bd9ac7aabbfca921.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |