Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
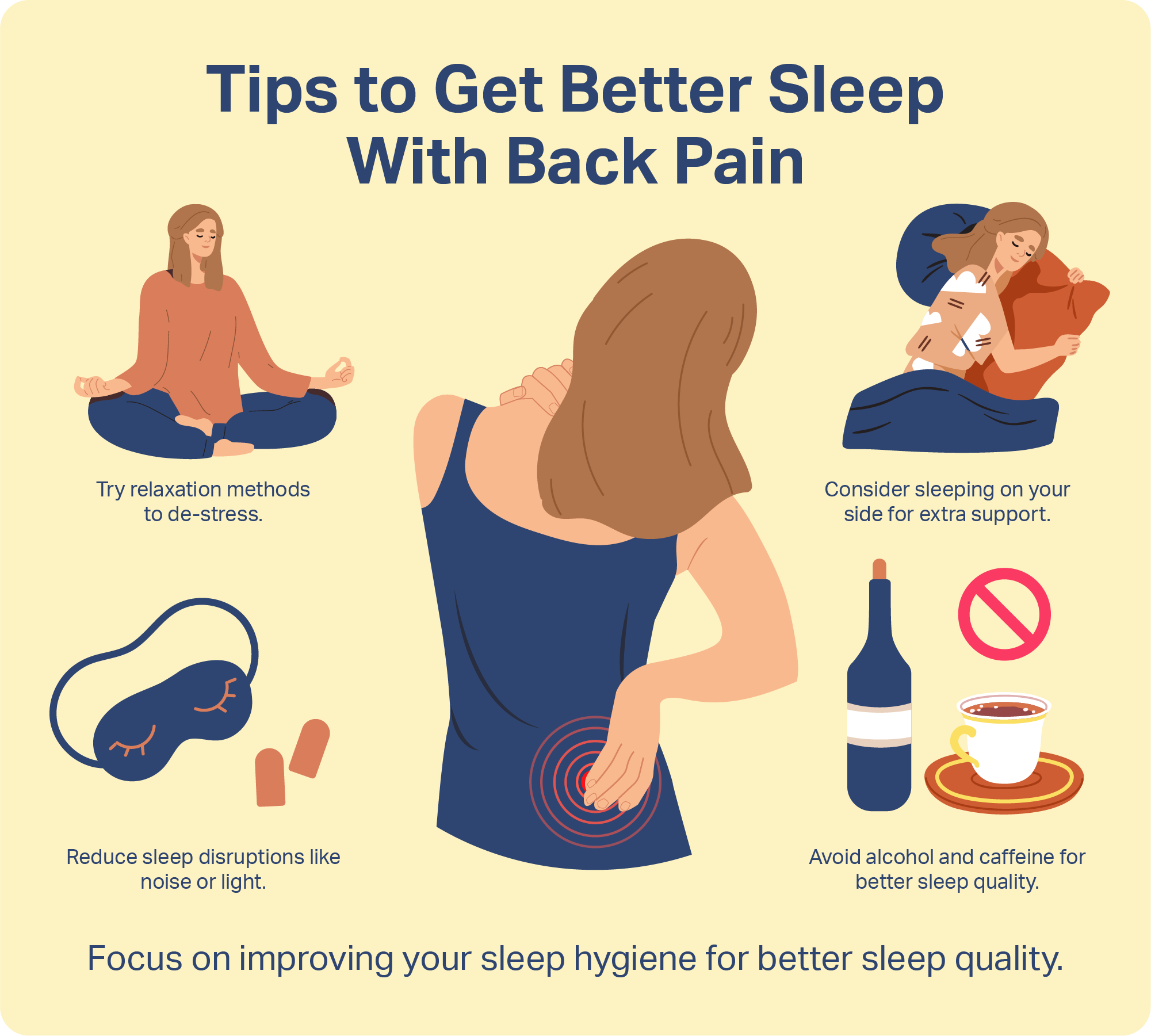
Management of patients with chronic liver disease and pain is particularly challenging in inpatients who may have acute pain or acute-on-chronic pain due to their acute medical illness, and may also have acute hepatic decompensation resulting in increased impairment in hepatic metabolism, further limiting analgesic options. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. One case involved a 60-year-old male taking 2400 milligrams of gabapentin for chronic pain, who developed DILI with a mixed hepatocellular and cholestatic pattern . The removal of gabapentin and the administration of steroids resulted in the normalization of liver test abnormalities. Gabapentin, a common over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer, has been linked to rare individual case reports of liver injury. The causal relationship between gabapentin and liver damage is unclear, with the latency to onset being 1 to 8 weeks. Other AEDs with rising and currently highest prescription rates were associated with few or no cases of liver injury including gabapentin (45.3 million), clonazepam (18.8 million), pregabalin (10.6 million), topiramate (9.3 million), and levetiracetam (7.7 million) and many of cases were judged as only “probable”. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. In an effort to facilitate safe pain control, this article will summarize the existing literature regarding impaired pharmacokinetics due to liver dysfunction and dosing recommendations for analgesic treatment in patients with cirrhosis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin has minimal impact on the liver because it is not extensively metabolized in the liver. Liver toxicity is not a common side effect of gabapentin. However, in rare cases, individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other liver-damaging medications may experience an increased risk of liver-related side effects. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Patients with liver disease can have pain that any person may have (eg, chronic back or knee pain) and are not immune to having other general conditions that cause pain, such as migraine headaches. Some liver conditions, especially cirrhosis and advanced liver disease, can exacerbate that pain. A recent case report from Sweden determined that pregabalin was a probable cause of acute liver failure in a 61-year-old healthy man with no previous liver disease. 47 Although this may have been an idiosyncratic event because no further case reports have been published in the literature, clinicians must be mindful of the increased risk of drug Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Question. I have a patient with trigeminal neuralgia who was taking 1600 mg of gabapentin and had serious elevations of liver function tests (aspartate transaminase 258 U/L, alanine transaminase as the liver metabolizes ketamine5. • If pain continues to be an issue, a consult to the acute pain service is warranted for further recommendations. • Of note, gabapentin and NSAIDS have not been clearly shown to be of benefit in liver transplantation and have been of concern to produce increased risk of reintubation and Pain management is often a challenge for healthcare professionals, but it remains a very important component of providing quality patient care and is a common factor in patient satisfaction. 5 A high prevalence of pain has been found among patients with chronic liver disease, reported between 32% and 77%. 6-8 Pain and opioid-based pain regimens
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |