Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
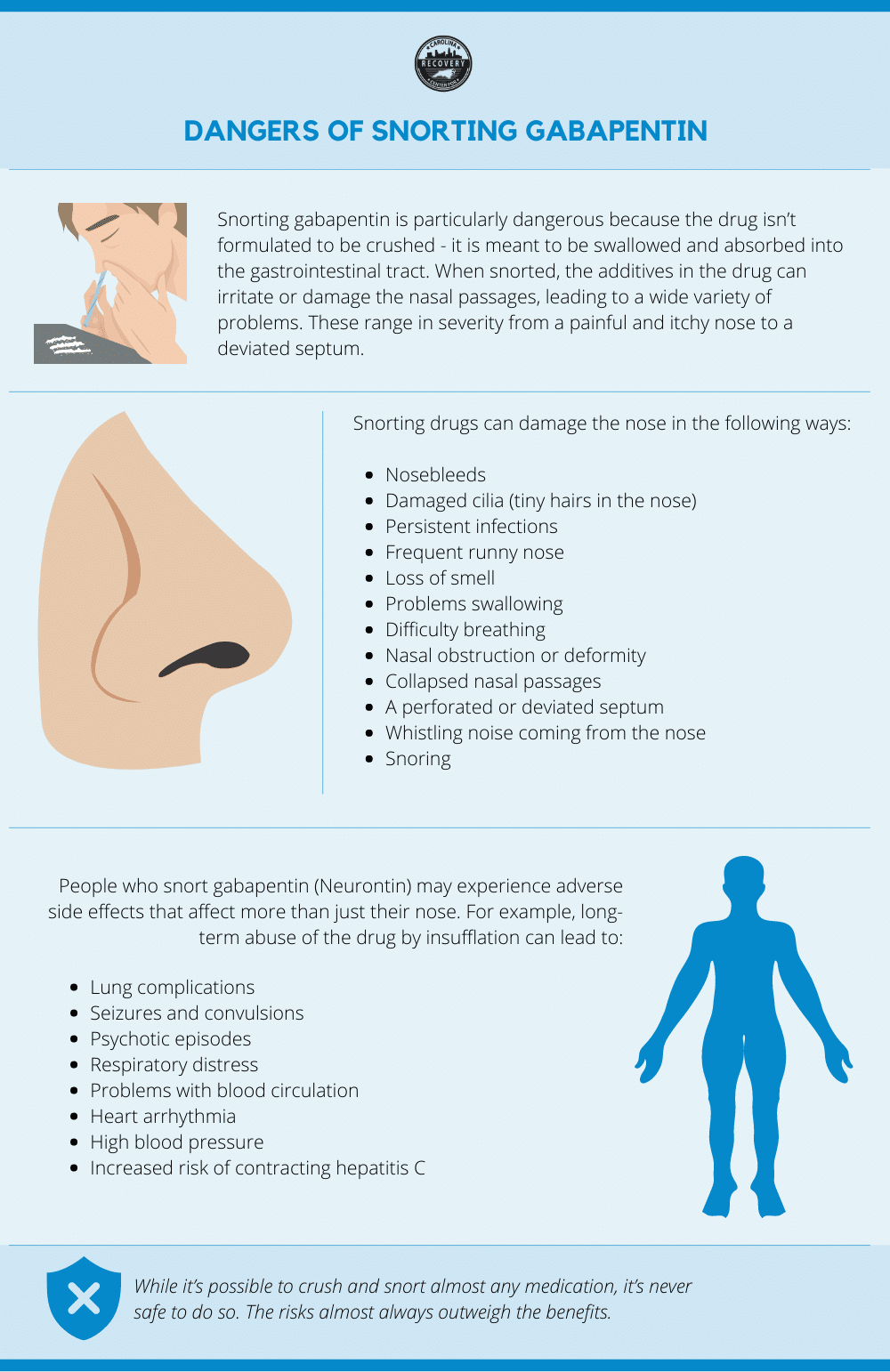
Generally, it is recommended to take gabapentin for at least four to six weeks or at the highest tolerated dose for at least two weeks. However, nerve pain can be a long-term issue, lasting for three or more months. If gabapentin provides relief, your healthcare provider may have you continue taking it daily. The only medicine I take is gabapentin for peripheral neuropathy that was caused by the chemotherapy drugs I received during the cancer treatment. One or more of these drugs caused neuropathy in Using gabapentin over a long period can lead to more dramatic health risks. While it can be effective for managing pain or seizures, prolonged use increases the chance of developing serious side effects. Some of the most common Gabapentin long-term side effects include: Memory loss: Long-term gabapentin use has been linked to problems with About Gabapentin Long-Term Use Side Effects. Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly prescribed to treat various conditions such as epilepsy, nerve pain, and restless leg syndrome. It belongs to a class of drugs known as anticonvulsants, which work by affecting certain chemicals in the brain. The only medicine I take is gabapentin for peripheral neuropathy that was caused by the chemotherapy drugs I received during the cancer treatment. One or more of these drugs caused neuropathy in While these studies suggest a connection between gabapentin and memory problems, more research is needed to know for sure. Still, talk to your prescriber about gabapentin’s long-term effects on the brain, especially if you’re over 65 and take other medications that affect the brain. 12. Withdrawal symptoms Some potential risks and side effects of long-term gabapentin use may include: Kidney problems – Gabapentin is eliminated by the kidneys, so prolonged use could potentially impact kidney function. Respiratory depression – High doses may affect breathing rate and depth. In a seminal trial on pain following shingles (post-herpetic neuralgia), the target dose of gabapentin was 900 mg four times daily. It often takes weeks or months to build up to this dose so that Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication approved for seizures, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome. It may also be prescribed off-label for other conditions, but it can have serious side effects and risks of abuse and overdose. A further effect of long-term gabapentin use arises when a person who has been taking the medication for a long period of time tries to abruptly discontinue use. This places a lot of stress on the brain because it has gotten used to relying on the augmented GABA neurotransmitter production for improved functioning in the central nervous system. Risks of Long-Term Use. While gabapentin is generally safe when taken as directed, there are some risks associated with long-term use to be aware of: Dependence – Gabapentin does have the potential to cause physical and psychological dependence. This risk increases the longer it is taken. Learn about the possible side effects of gabapentin, a drug used to treat nerve pain and seizures. Find out how gabapentin can cause serious problems such as respiratory depression, hypersensitivity syndrome, and withdrawal symptoms. Horizant is a long-acting prodrug of gabapentin that only requires once-daily dosing. It is usually taken once daily around 5 pm. Gabapentin is available as a generic; however, not all generics are interchangeable with some branded versions of gabapentin. In order to maintain appropriate access for those patients who do obtain substantial pain relief and to minimise misuse and abuse there is a need for a comprehensive understanding of the safety and harms of gabapentinoids. This review considers serious side effects and harms that have been reported with gabapentinoids. Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that doctors often prescribe to manage seizures related to epilepsy. It is not a cure for epilepsy, but it can help people manage the condition. In this Gabapentin can be a valuable tool in managing various health conditions, but long-term use comes with potential risks. From physical side effects like weight gain and fatigue to cognitive and emotional challenges, it’s essential to be aware of how this medication may affect you over time. In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. Side Effects of Gabapentin. The use of any medication, including gabapentin, can create a number of various side effects. Both short-term and long-term use of gabapentin can cause physical and psychological complications. Misusing it may cause you to experience a greater number of symptoms or experience them with greater severity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |