Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
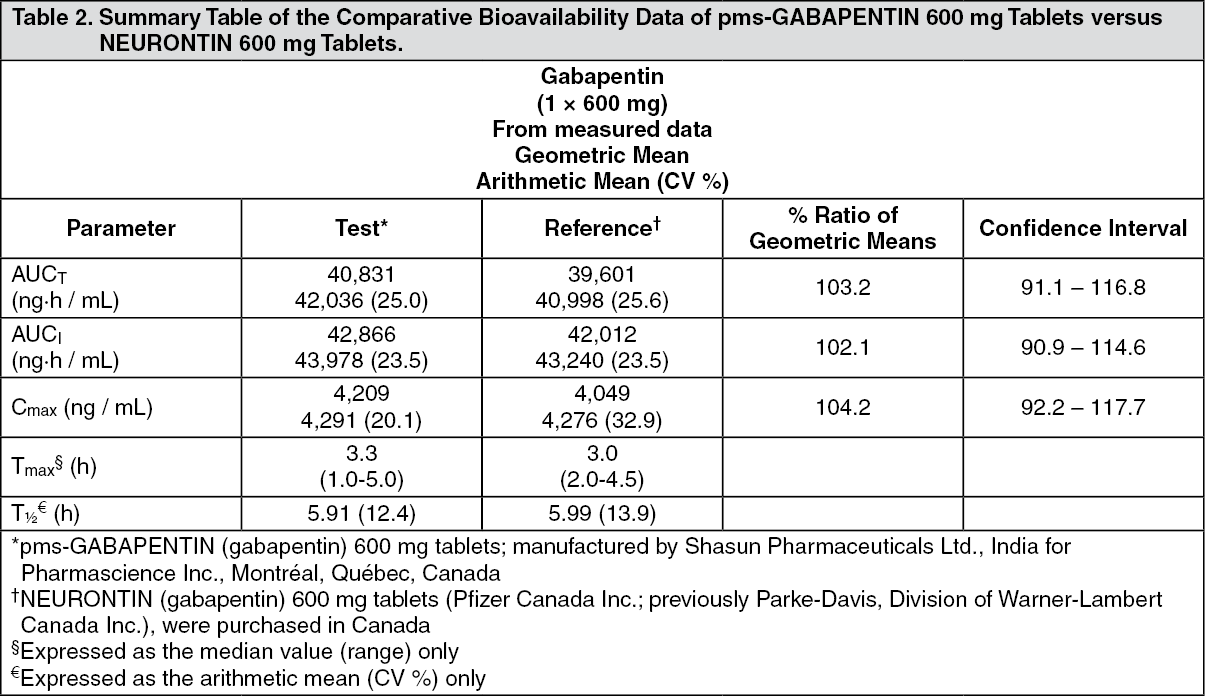
Gabapentin has become popular as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain because of its efficacy as an antineuropathic agent and relatively benign side-effect profile. However, its mechanism of action is far from clear. This review discusses the available evidence for the postulated mechanisms of action of gabapentin. Mechanism of Action Gabapentin is designed as GABA analog (similar to pregabalin ), which means it binds to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels (VSCCs), and block the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. One of the primary mechanisms of gabapentin involves its interaction with voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). Specifically, gabapentin binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of these channels. VGCCs play a crucial role in the release of neurotransmitters by regulating calcium influx into neurons. I appreciate the comments of Gazulla et al. regarding my focused review on the mechanisms of action and side effects of gabapentinoids. 1 I cited the article by Yu et al., as they found that gabapentin increases expression of delta subunit-containing GABAA receptors. 2 I am also aware of the placebo-controlled pilot study of Gazulla et al. regarding the potential benefit of pregabalin for orders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. The gabapentinoids share similar mechanisms of action but differ considerably in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. This article dis-cusses the differences in these characteristics. Mechanism of Action Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin; Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue; Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures. Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. The mode by which this medication works as an anticonvulsant and treats pain is not entirely clear, though there are theorized mechanisms of action. It is known, however, that gabapentin inhibits high voltage-gated Ca<sup>2+</sup> channels, leading to decreased levels of mono-amine neurotransmitters.Patients taking this drug often complain of Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is Mechanism of action of gabapentinoids Site of action The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake.21 They were originallydesigned as g aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogues but do not have any effects on GABA receptors. Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental pain. The effects of gabapentinoids may be attributed to depression of dorsal horn sensitivity through a multitude of mechanisms. Gabapentin mechanism of action. Researchers know that gabapentin operates on neurotransmitters and traverses the blood-brain barrier readily, but the specific mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unclear. A cyclohexyl group is attached to the molecular structure of the neurotransmitter GABA in gabapentin. Mechanism of action: By inhibiting the voltage-gated calcium channels in the CNS, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (mostly noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin), and therefore decreases epileptogenesis. Clinical effects Mechanisms of action. Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Gabapentin MECHANISM OF ACTION: * Main binding site: alpha2delta subunit of L type voltage gated calcium channels. * Binding results in inhibition of high voltage activated calcium currents —> resulting in decreased synaptic transmission —> reduced neurotransmission . * Structurally similar to GABA, but has no effect in GABA PHARMACOKINETICS: Herein we review the current understanding of the state‐dependent mechanisms of the gabapentinoids, the pathophysiological role of their molecular target, the α 2 δ calcium channel subunit, and the implications for clinical usage. Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental pain. The effects of gabapentinoids may be attributed to depression of dorsal horn sensitivity through a multitude of mechanisms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |