Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
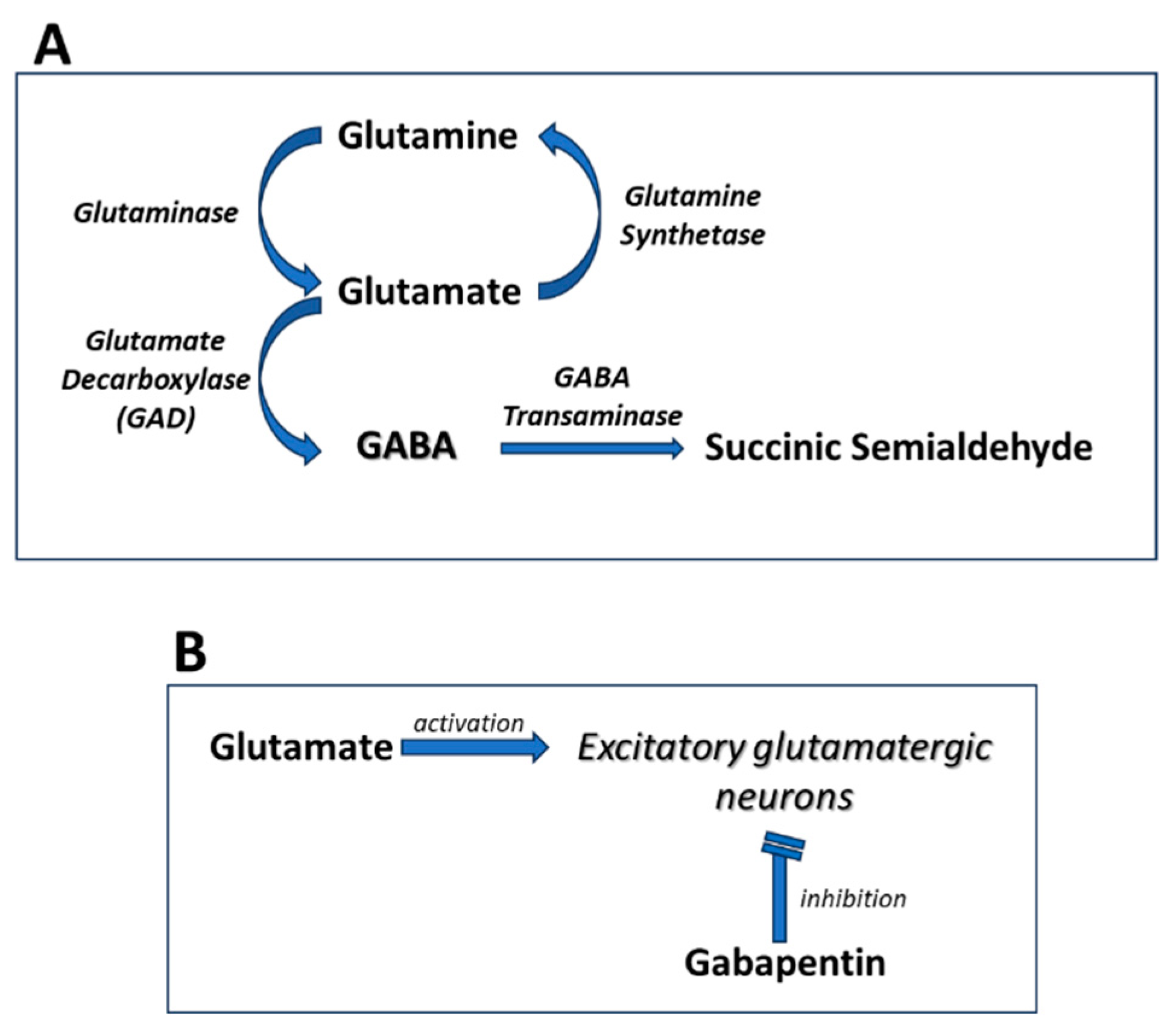
Gabapentin prevents neuronal death in several models including those designed to mimic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This may occur by inhibition of glutamate synthesis by branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase (BCAA-t). 1. Introduction. Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental pain. The effects of gabapentinoids may be attributed to depression of dorsal horn sensitivity through a multitude of mechanisms. The general mechanism of pregabalin physiological cellular action involves a decrease in the release of several types of neurotransmitters including glutamate, noradrenaline, and substance P (Fink et al., 2000; Dooley et al., 2007; Brawek et al., 2008). Research regarding gabapentin’s effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its They inhibit forward trafficking of α2δ-1 from the dorsal root ganglion, their recycling from endosomal compartments, thrombospondin mediated processes and stimulate glutamate uptake by excitatory amino acid transporters. Understanding its mechanism of action provides valuable insight into how it alleviates symptoms and aids in managing these conditions. First and foremost, gabapentin is structurally similar to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), although it does not directly affect GABA receptors the way other GABA analogs, like benzodiazepines In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. Gabapentin’s mechanism of action for anxiety management is not fully understood, but several theories exist: GABA Modulation: Gabapentin is believed to increase GABA levels in the brain, which can promote relaxation and reduce anxiety. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate nerve activity and calm the nervous system. Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. Gabapentinoids depress neuronal excitability through interactions with the a2d-1 calcium channel subunit, stimulate descending inhibition, inhibit descending serotonergic facilitation, inhibit inflammatory media-tors, and influence the affective component of pain. Mechanisms of action. Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ. Mechanism of Action. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. Since glutamate-mediated excitation is involved in the generation of seizure activity, some antiepileptics are targeting glutamatergic receptors--for instance, felbamate, phenobarbital, and topiramate. Besides, they also inhibit sodium currents. Zonisamide, apparently sharing this common mechanism, also reduces the concentration of free radicals. The current review targets the efficacy and mechanism of gabapentinoids in treating chronic pain. The discovery of interaction of α2/δ-1 with thrombospondins established this protein as a major synaptogenic neuronal receptor for thrombospondins. Several mechanisms of gabapentin have been proposed after neuropathy including an inhibition of NMDA receptors, inhibition of sodium currents and reducing β4a subunit mediated VGCC trafficking (Hara and Sata 2007; Mich and Horne 2008; Yang et al. 2009). Alternatively, gabapentin may reduce α2δ-1 interaction with thrombospondin, an astrocyte-secreted protein, and inhibit new synapse formation (but not already formed synapses) (Eroglu et al., 2009). Nevertheless, this action cannot fully account for the relatively rapid onset of gabapentinoid effects on pain hypersensitivity. pharmacokinetics of gabapentin: Absorption: Gabapentin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. However, its absorption is limited by an active transport mechanism, which can result in dose dependent absorption. Food intake does not significantly affect the extent of gabapentin As with many other agents, GBP was licensed for the treatment of epilepsy with little or no understanding of its mechanism of action. Continued research and the parallel development of PGB have contributed to a contemporary pharmacological view of GBP (and PGB) as drugs with multiple modest cellular effects at therapeutic concentrations, but with a single predominant mechanism of action that Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium As with many other agents, GBP was licensed for the treatment of epilepsy with little or no understanding of its mechanism of action. Continued research and the parallel development of PGB have contributed to a contemporary pharmacological view of GBP (and PGB) as drugs with multiple modest cellular effects at therapeutic concentrations, but with a single predominant mechanism of action that
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |