Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
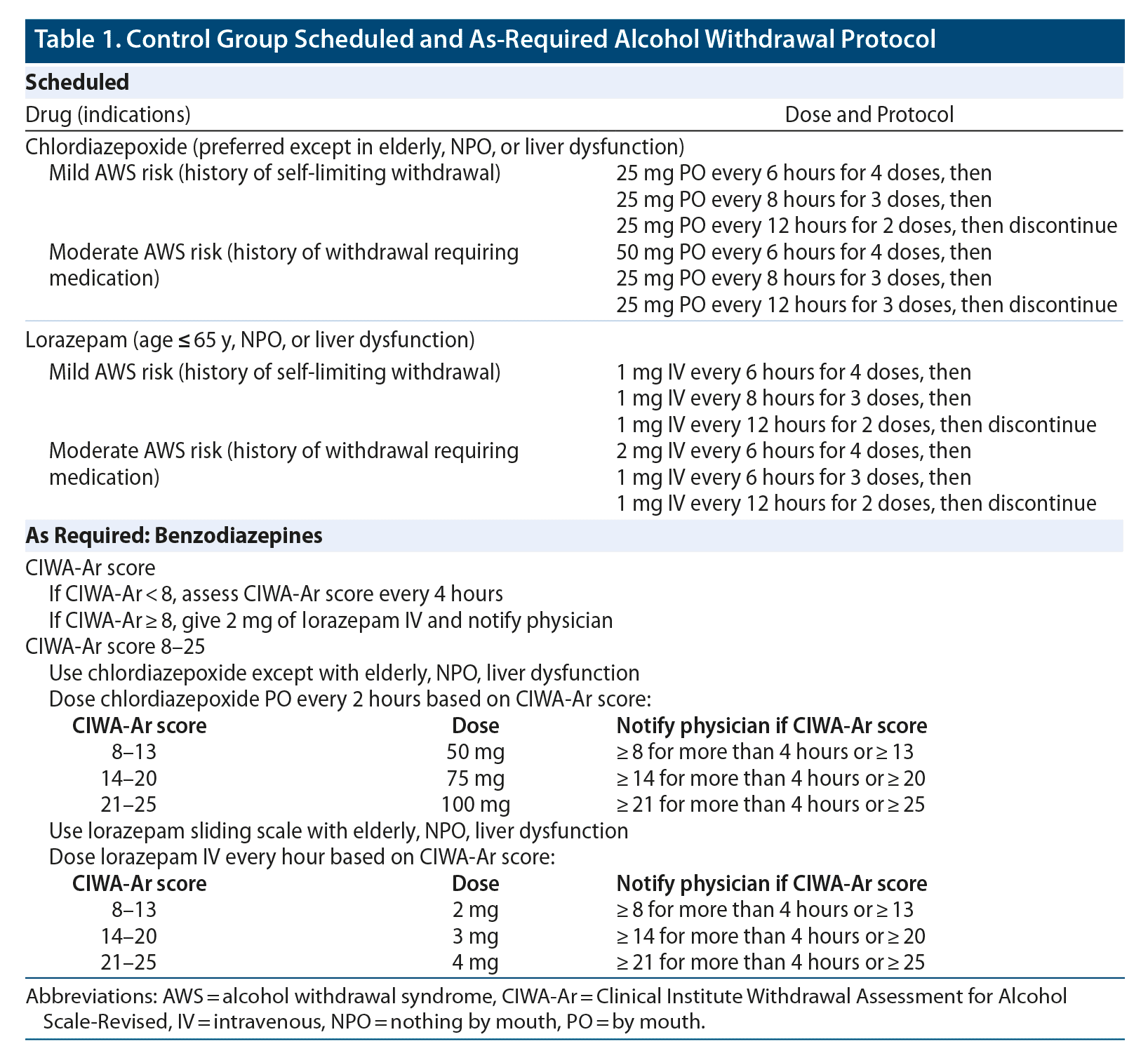 |
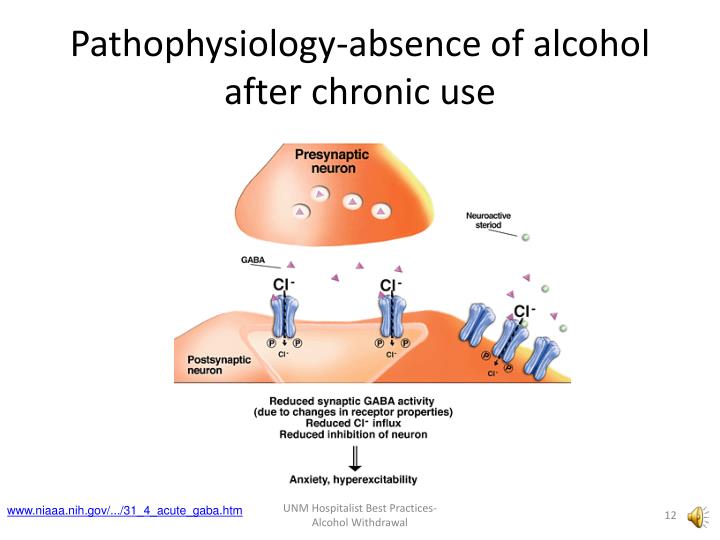
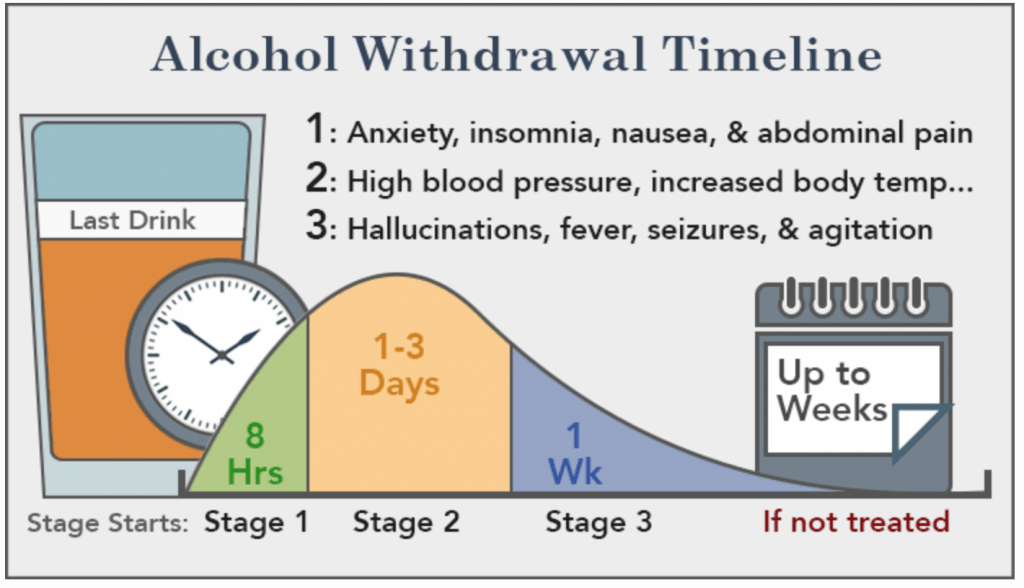
Objectives: Recent literature suggests that gabapentin may be an alternative treatment to standard management of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Study Objective. Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Future studies should evaluate sleep changes and mood during early recovery as mediators of gabapentin efficacy. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. The mechanism of action of gabapentin may also benefit patients suffering from acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to examine if gabapentin can effectively replace/reduce the use of benzodiazepines for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms in hospitalized patients. Treatment with gabapentin may benefit alcohol withdrawal inpatients based on its use in Alcohol Use Disorder outpatients and mechanism of action. Benzodiazepines are commonly used to treat hospitalized alcohol withdrawal syndrome patients, but are associated with several adverse drug events. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and pain-relieving medication that has several off-label uses, including the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Learn more here. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin: Class: Analgesics Mechanism of action: as a co-analgesic, and in alcohol withdrawal. Adverse effects are few, but do include Steven-Johnson A middle-aged man was admitted to the ICU for refractory alcohol withdrawal. mechanism of action is well matched 3200mg of gabapentin PO or via OG in the To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol for alcohol withdrawal in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively identified patients admitted to the hospital from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, for alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or 3.2 GABAPENTIN AND ITS ALCOHOL-RELATED MECHANISM OF ACTION. In animal models of alcohol dependence, gabapentin decreased the amplitudes of GABA receptor mediated inhibitory post synaptic currents (IPSCs) in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA), and decreased dependence-induced alcohol drinking. Treatment with gabapentin may benefit alcohol withdrawal inpatients based on its use in Alcohol Use Disorder outpatients and mechanism of action. Benzodiazepines are commonly used to treat hospitalized alcohol withdrawal syndrome patients, but are associated with several adverse drug events. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Researchers assess that 3.8% of worldwide deaths result from direct or indirect effects of alcohol misuse. While gabapentin's mechanism of action is generally understood, it appears to be a pharmacologic option for treating issues involving the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor system. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. The mechanism of action by which gabapentin mitigates AWS is likely related to increasing GABA concentrations through direct GABA synthesis and interaction with the α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels. 3, 10 Gabapentin has sedative and anxiolytic properties, as well as utility in the setting of chronic neuropathic pain. 11
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |