Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
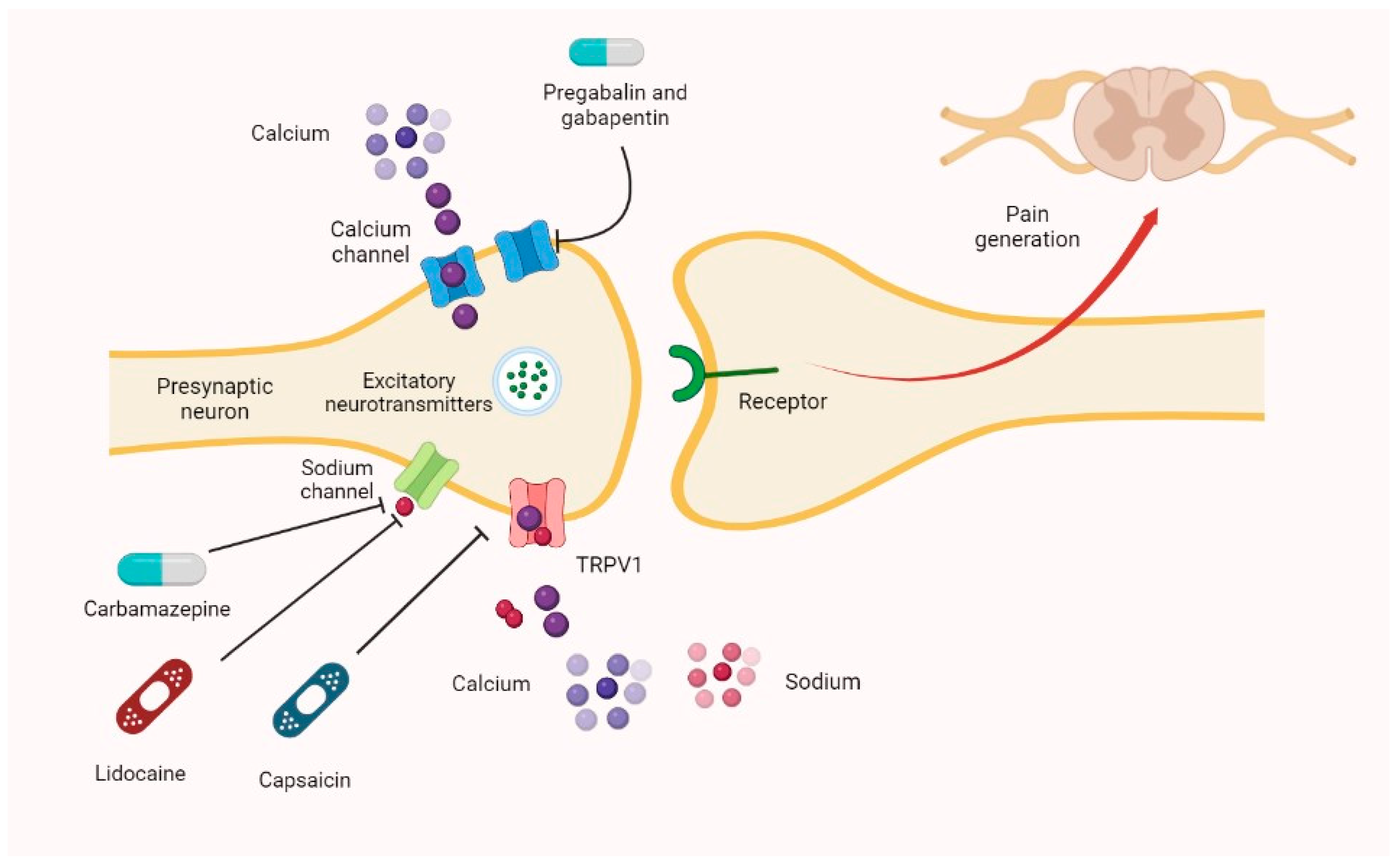 |  |
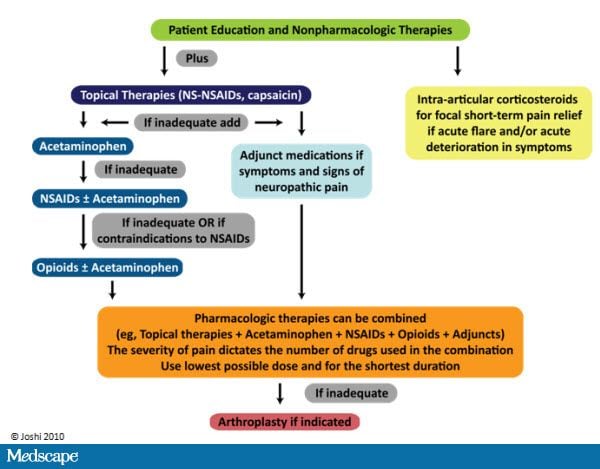
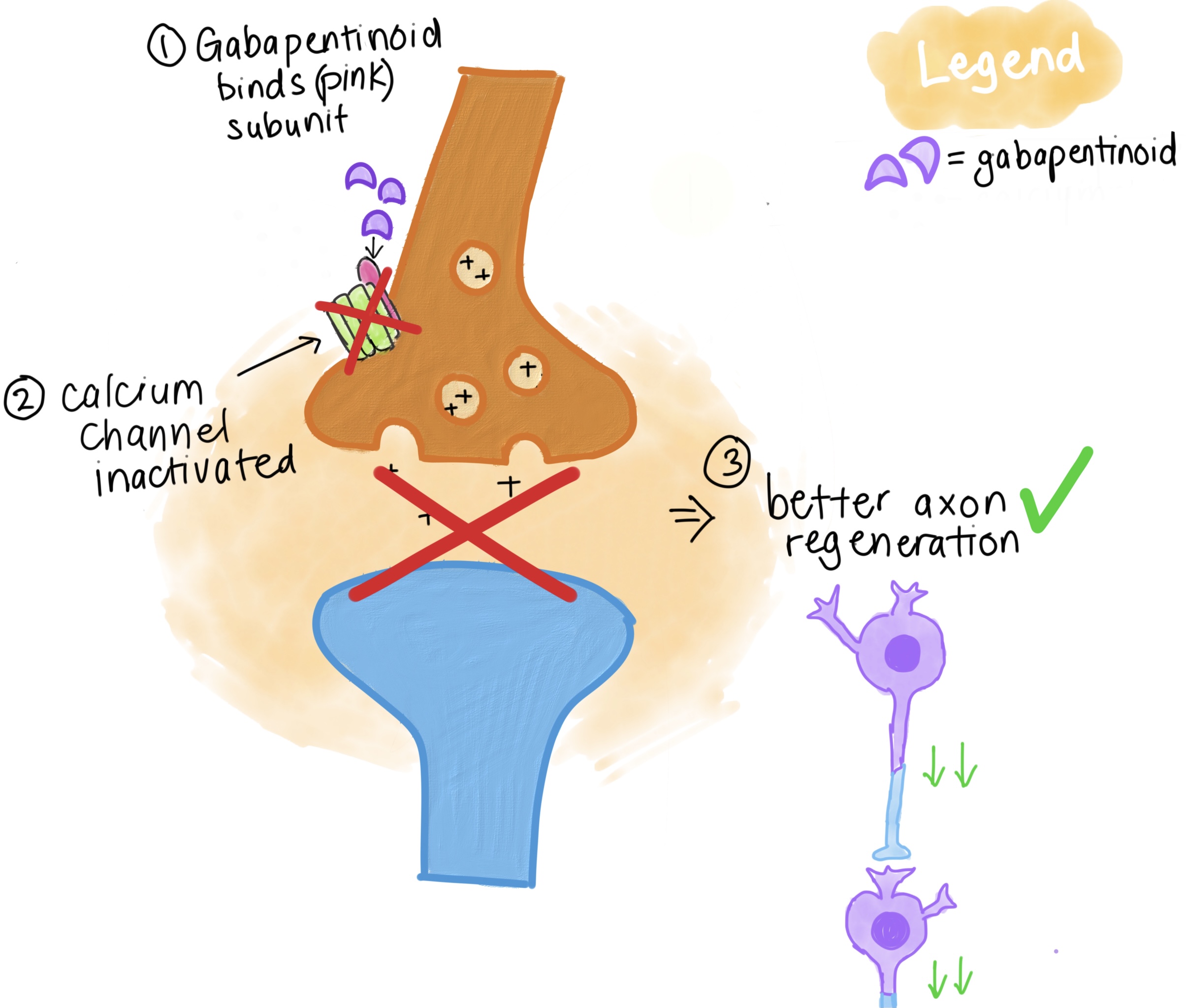
Gabapentin has become popular as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain because of its efficacy as an antineuropathic agent and relatively benign side-effect profile. However, its mechanism of action is far from clear. Gabapentin or an α2δ-1 C terminus-interfering peptide normalizes NMDAR synaptic targeting and activity increased by nerve injury. Thus, α2δ-1 is an NMDAR-interacting protein that increases NMDAR synaptic delivery in neuropathic pain. Gabapentinoids reduce neuropathic pain by inhibiting forward trafficking of α2δ-1-NMDAR complexes. Neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has proved to be efficacious in the treatment of neuropathic pain and is now approved for this indication in patients over 18 years of age. Evidence for its efficacy is discussed below. Dosage and administration. Oral doses of gabapentin are administered three times a day (tds) because of its short half-life. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. The analgesic effect in neuropathic pain is well evidenced but the role in postoperative pain is less certain. Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental pain. Although gabapentinoids are classed as calcium channel blockers, their mechanisms of action are poorly understood. The analgesic effect in neuropathic pain is well evidenced but the role in postoperative pain is less certain. Beside the implication of the noradrenergic system, it has also been suggested that descending serotonergic transmission could be important for acute gabapentinoid action in a neuropathic pain context (Suzuki et al., 2005, Bee and Dickenson, 2008), and it has been shown that pain relieving action of a high dose of gabapentin in rats with spinal Understanding how gabapentin works for pain is crucial for those exploring treatment options for conditions like neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and even post-surgical discomfort. The Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's primary mechanism revolves around its interaction with calcium channels in the nervous system. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce Neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has proved to be efficacious in the treatment of neuropathic pain and is now approved for this indication in patients over 18 years of age. Evidence for its efficacy is discussed below. Dosage and administration. Oral doses of gabapentin are administered three times a day (tds) because of its short half-life. Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the The focus of perioperative pain management should be to attempt to minimise the nociceptive input and reduce the risk of transition to central sensitisation. Gabapentinoids are being increasingly used as adjuncts for management of perioperative pain. Although gabapentinoids are classed as calcium channel blockers, their mechanisms of action are poorly understood. The analgesic effect in Numerous studies confirm that gabapentinoids do not perturb normal detection and pain thresholds (Attal et al. 1998; Dirks et al. 2002); the pathophysiological state‐dependent effects of pregabalin and gabapentin implies other factors influence efficacy in neuropathic conditions. A recent study has shown the effectiveness of gabapentin (5 or 50 mg/kg, i.p.) in attenuating neuropathic pain behavior in forelimb neuropathic pain model (due to partial injury to medial and ulner nerves) in a dose-dependent manner (Yi et al. 2011). The first case reports of treatment of refractory neuropathic pain conditions with gabapentin were presented in 1996. 9, 10 In 1998, confirmatory evidence was published for treatment of PHN, 11 for which it received FDA approval, as well as DPN. 12 The efficacy of pregabalin was demonstrated in several trials, gaining it approval for both Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Gabapentinoids can be effective in some patients with neuropathic pain but more than half of the patients fail to get worthwhile pain relief. Their efficacy in non-neuropathic pain is even less impressive. Although pregabalin has more favourable pharmacokinetics as compared to gabapentin, there is little evidence to support its preferential use. This paper reviews the pharmacology and clinical effectiveness of gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic properties but does not have significant actions as an anti-nociceptive agent. Because spinal plasticity and sensitization have been intensely studied in neuropathic pain, most laboratory studies have focused on actions of gabapentinoids in the spinal cord, where they reduce primary afferent traffic and excitation of spinal nociceptive neurons, via interaction with α2δ subunits of voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |