Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
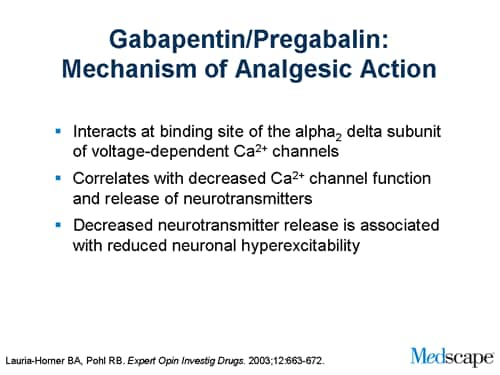
Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. The mode by which this medication works as an anticonvulsant and treats pain is not entirely clear, though there are theorized mechanisms of action. It is known, however, that gabapentin inhibits high voltage-gated Ca<sup>2+</sup> channels, leading to decreased levels of mono-amine neurotransmitters.Patients taking this drug often complain of Mechanism of Action. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. Mechanism of Action. The mechanism of action is not known, but it is believed to work through multiple mechanisms. Gabapentin primarily acts by binding to a specific subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Mechanism of Action. The exact anticonvulsant and analgesic action of gabapentin is unknown. What are the indications of gabapentin (Neurontin)? Gabapentin (Neurontin) indications include: to relieve neuropathic pain; to treat epilepsy (seizures) What are the contraindications of Gabapentin (Neurontin)? The mechanisms of the anti-allodynic effects of gabapentin proposed include: CNS effects (potentially at spinal cord or brain level) due to either enhanced inhibitory input of GABA-mediated pathways (and thus reducing excitatory input levels); antagonism of NMDA receptors; and antagonism of calcium channels in the CNS and inhibition of Adjunctive Therapy for Seizure Disorder Adult/Child (12 y or older): PO Start 300 mg on day 1, 300 mg b.i.d. on day 2, 300 mg t.i.d. on day 3, and continue to increase over a week to an initial total dose of 400 mg t.i.d. (1200 mg/day); may increase to 1800-2400 mg/ day depending on response (most patients receive 900-1800 mg/ day in 3 divided doses) 400 mg t.i.d. (1200 mg/day) Post-Herpetic Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Seizure patients should not resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. Mechanism of action: Gabapentin’s exact mechanism remains unclear. It is structurally similar to GABA but does not bind to GABA receptors. It is believed to bind to voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Grab our free cheatsheet covering the 50 most commonly prescribed medications right here: to all the episodes at: Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA but is neither a GABA agonist nor antagonist. Gabapentin-binding sites have been identified throughout the brain tissues e.g. neocortex and hippocampus. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. While gabapentin's mechanism of action is generally understood, it appears to be a pharmacologic option for treating issues involving the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor system. Gabapentin is a relatively safe, readily available, and effective drug for alcohol-use disorder treatment, specifically for the abstinence maintenance phase. As needed, open gabapentin capsules and mx contents with water, fruit juice, apple sauce or pudding before administration. Give drug at least 2 hours after an antacid. Be aware that routine monitoring of blood gabapentin level isn't needed. Monitor renal function test results, and expect to adjust dosage, if needed. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the presence of voltage-gated calcium channels Its mechanism of action as an antiepileptic agent likely involves its inhibition of the alpha 2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. -GABAPENTIN may be ordered by a physician for management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults. adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with and without secondary generalization. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |