Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
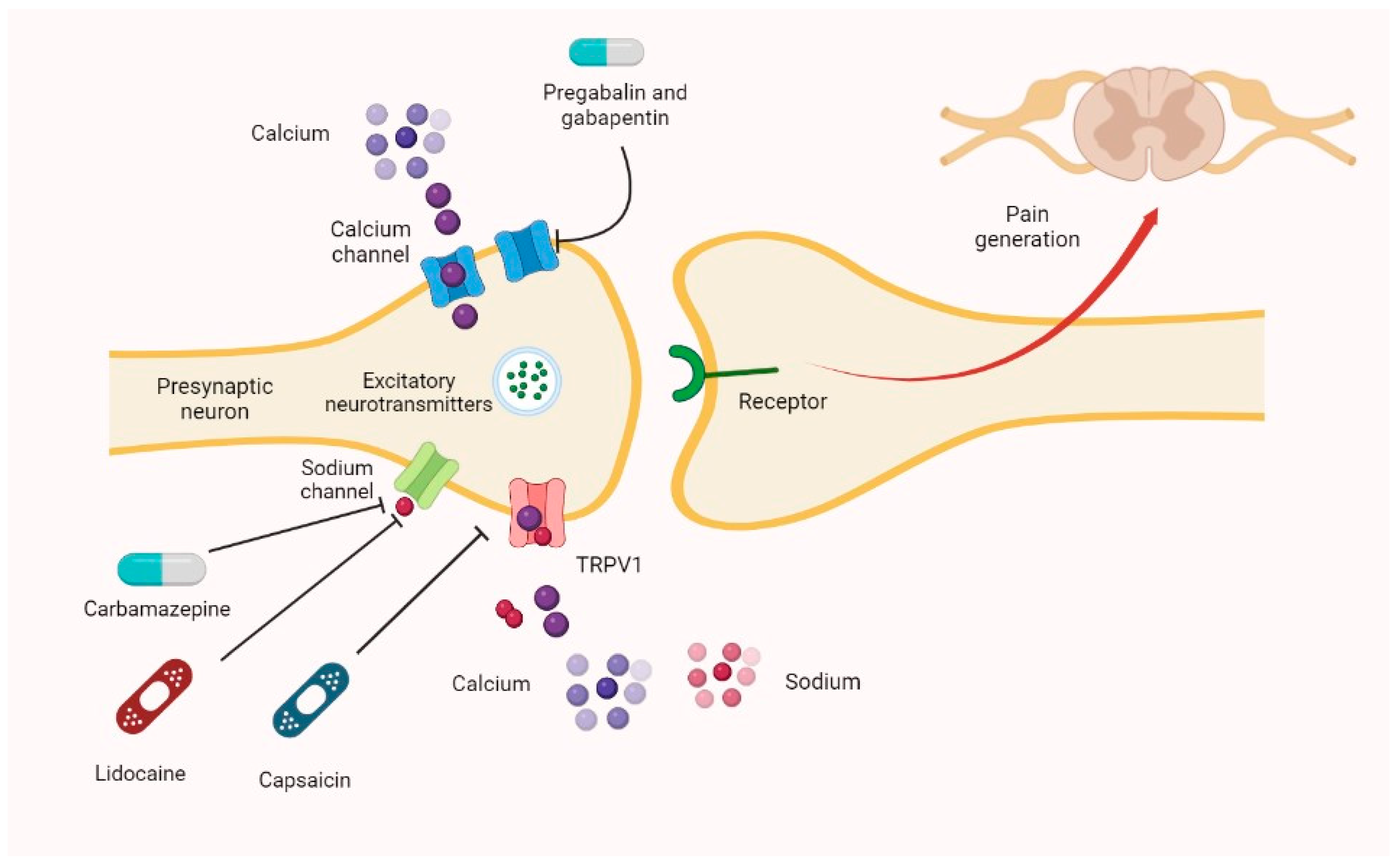 |  |
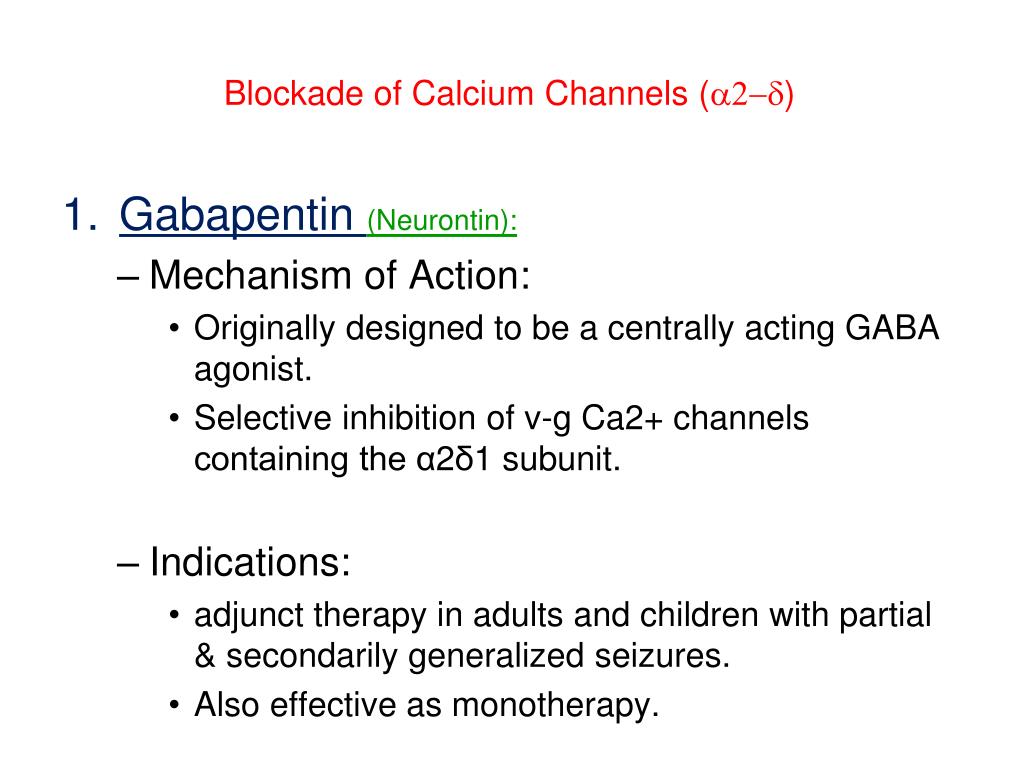
Mechanism of Action The mechanism by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic action is unknown, but in animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response As with many other agents, GBP was licensed for the treatment of epilepsy with little or no understanding of its mechanism of action. Continued research and the parallel development of PGB have contributed to a contemporary pharmacological view of GBP (and PGB) as drugs with multiple modest cellular effects at therapeutic concentrations, but with a single predominant mechanism of action that In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a Although the cellular mechanisms of pharmacological actions of gabapentin (Neurontin®) remain incompletely described, several hypotheses have been proposed. It is possible that different mechanisms account for anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anxiolytic and neuroprotective activity in animal models. Gabapentin is an amino acid, with a Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is Gabapentin's mechanism of action involves binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, modulating neurotransmitter release and dampening excessive neuronal excitability. Furthermore, gabapentin exhibits a favorable safety profile, with most adverse effects being mild to moderate in nature. Common Mechanisms of action of existing agents Sodium channels. Blockade of voltage-gated sodium channels is the most common mechanism of action among currently available AEDs. The established agents phenytoin and carbamazepine are archetypal sodium channel blockers, a mechanism they share with the This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, administration, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and characteristics of gabapentin toxicity. This activity also provides clinicians with the necessary skills and tools to treat various types of muscular, neurological, and psychiatric medical conditions The primary proposed mechanism of action for gabapentinoids involves their binding to the α 2-δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels on presynaptic neurons. orders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. The gabapentinoids share similar mechanisms of action but differ considerably in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. This article dis-cusses the differences in these characteristics. In this review, we summarized the recent progress in the findings proposed for the antinociceptive action mechanisms of gabapentin and suggest that the alpha(2)delta subunit of spinal N-type Ca(2 Gabapentin MECHANISM OF ACTION: * Main binding site: alpha2delta subunit of L type voltage gated calcium channels. * Binding results in inhibition of high voltage activated calcium currents —> resulting in decreased synaptic transmission —> reduced neurotransmission . * Structurally similar to GABA, but has no effect in GABA PHARMACOKINETICS: Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce different actions responsible for pain attenuation Mechanism of Action Gabapentin is designed as GABA analog (similar to pregabalin ), which means it binds to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels (VSCCs), and block the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate. Mechanisms of action Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium Mechanism of Action. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. Although gabapentinoids are classed as calcium channel blockers, their mechanisms of action are poorly understood. The analgesic effect in neuropathic pain is well evidenced but the role in postoperative pain is less certain. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. Request PDF | Gabapentin: mechanisms of action | Gabapentin (Neurontin or 1-[aminomethyl ]cyclohexa- neacetic acid)is a novel amino acid derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the chemical
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |