Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 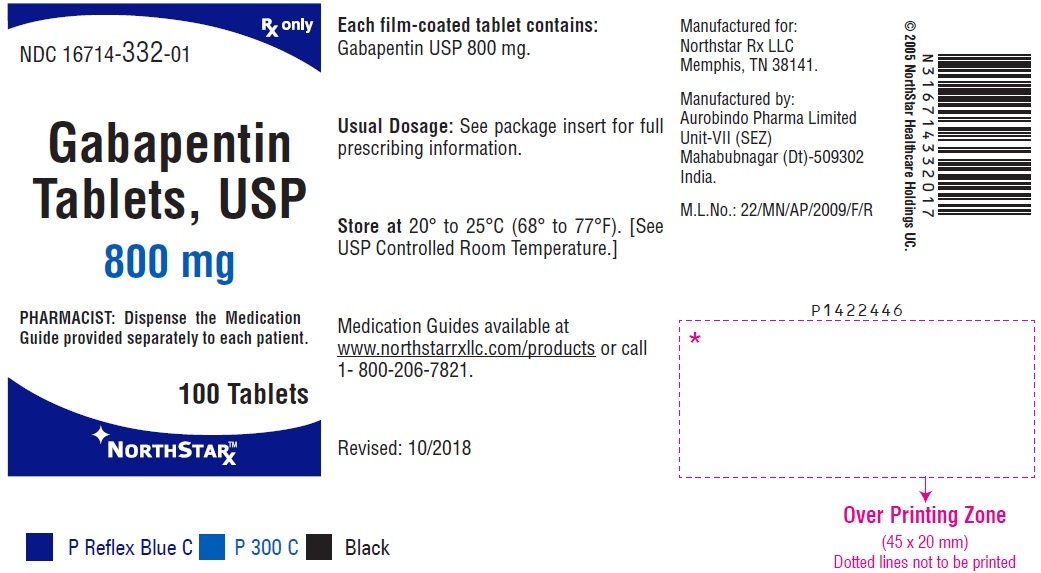 |
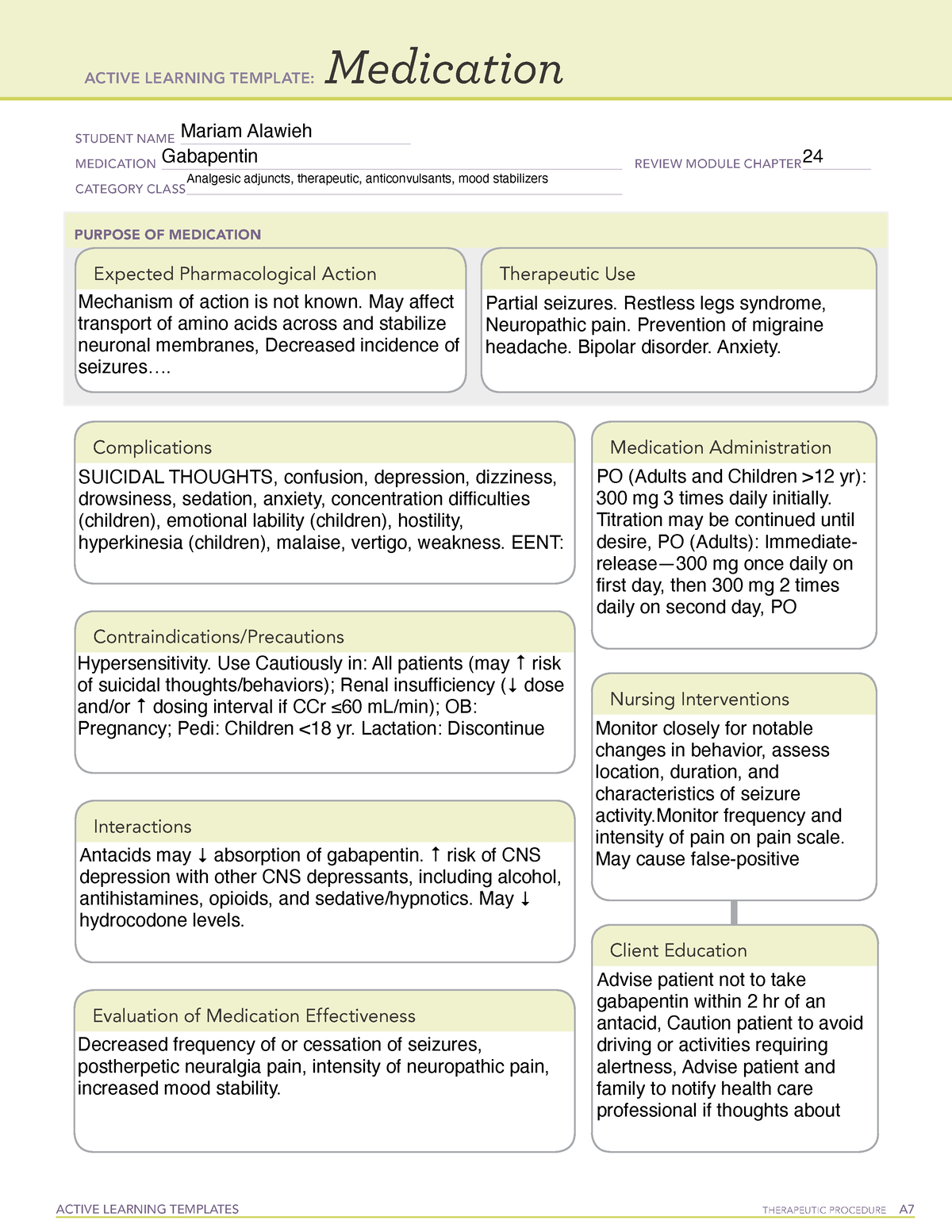
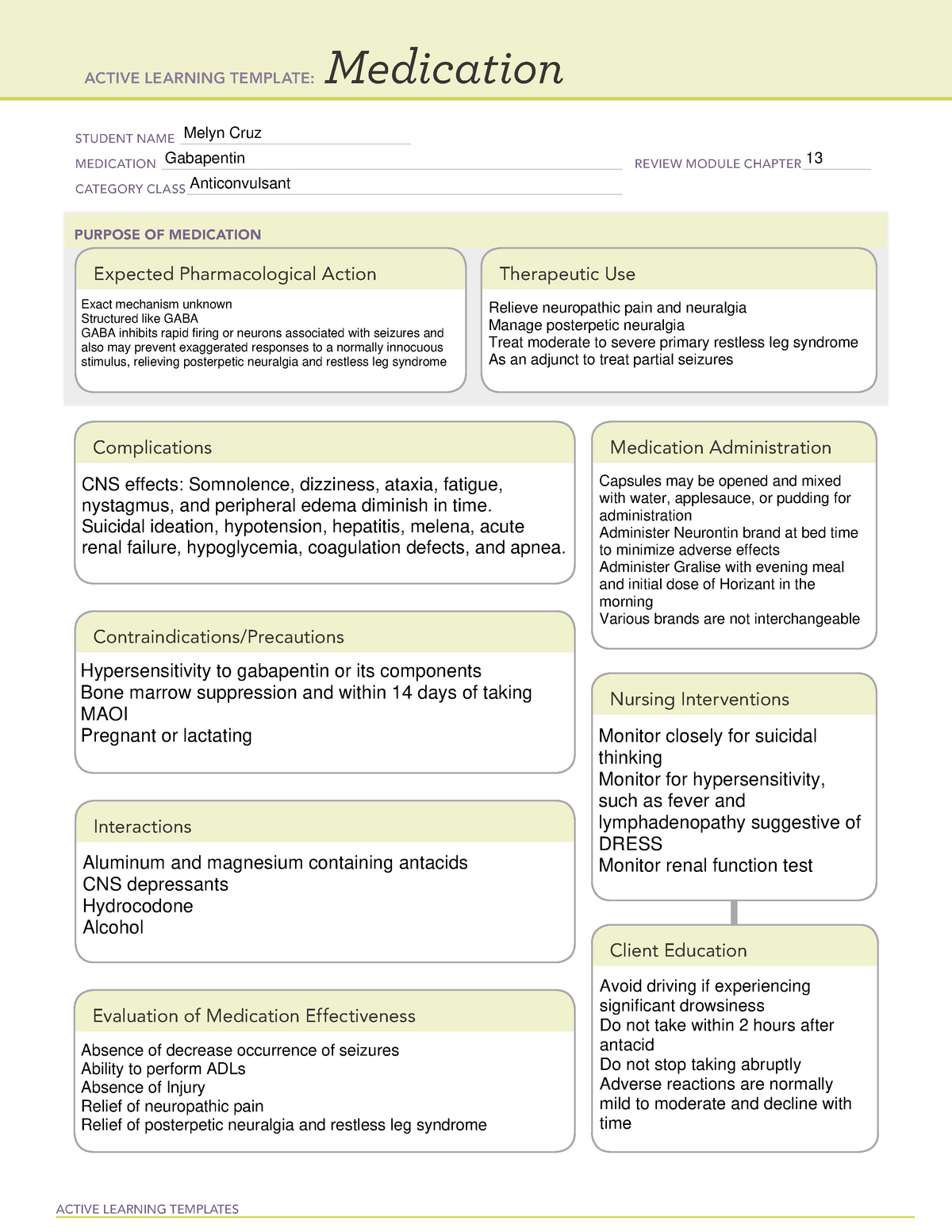
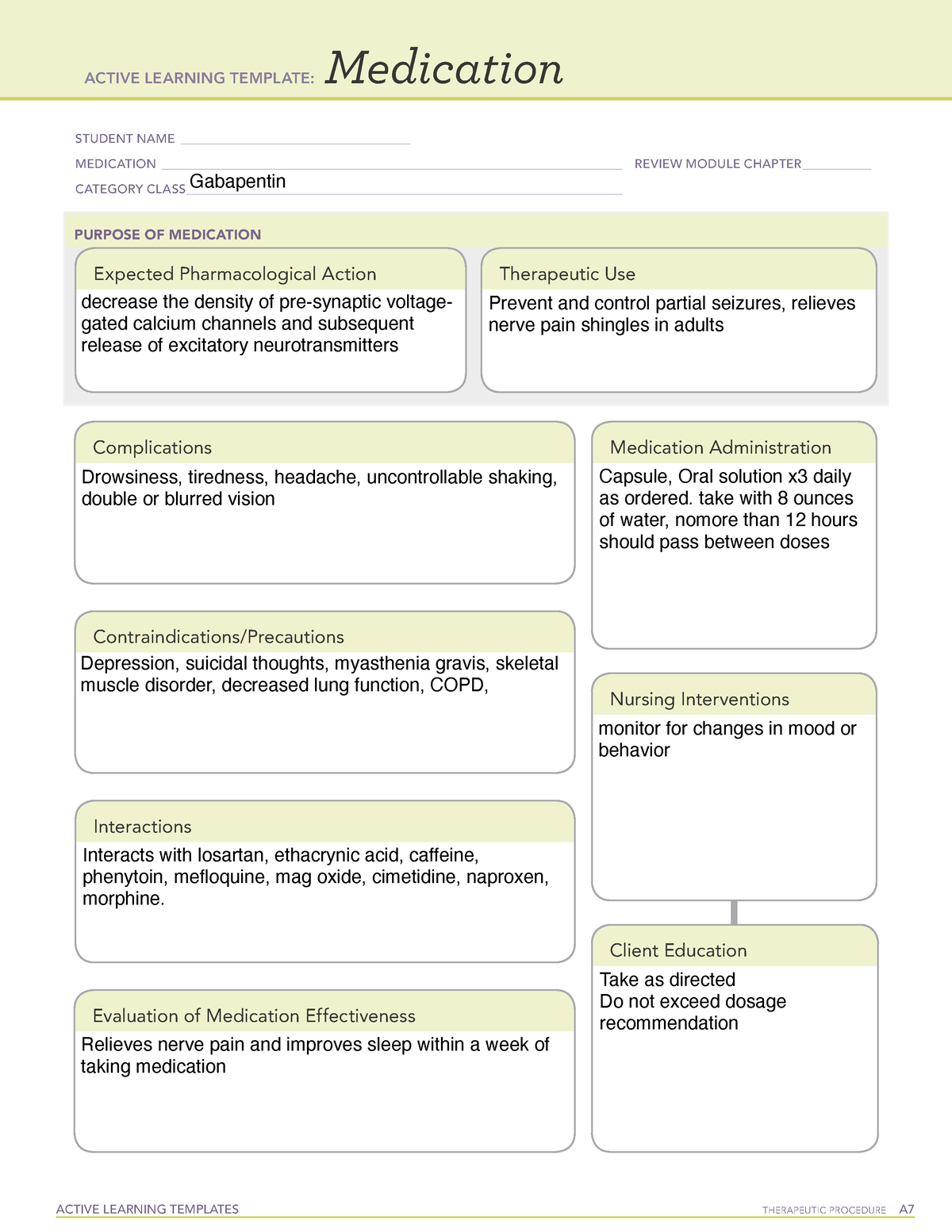
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gaba Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Then take this Neurontin medication at evenly spaced times throughout the day and night to ensure a constant level of Neurontin/gabapentin in your body. Follow the Neurontin directions on your Neurontin prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or Neurontin pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Pharmacodynamics. Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism . All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Oral Bioavailability: Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. Administer NEURONTIN three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules, or 600 mg or 800 mg tablets. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. 3 days. The Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. enteral administration could still result in tube blockage. Separate dose administration from feeds by at least 1 hour. Do not used extended release capsules or tablets. *Potential for increased side effects or loss of efficacy with GJ/JT administration; consider decreasing dose and increasing frequency to avoid negative outcomes. If you suddenly stop taking gabapentin tablets, capsules, or oral solution, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, nausea, pain, and sweating. If you are taking gabapentin to treat seizures and you suddenly stop taking the medication, you may experience seizures more often. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. Patient Teaching Associated with Gabapentin. Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed, at evenly spaced intervals. Do not stop taking gabapentin abruptly; gradual discontinuation is required. Avoid alcohol while taking gabapentin. Take antacids at least 2 hours apart from gabapentin. Report any unusual changes in mood or thoughts of self-harm. Coadministration of gabapentin (125 mg to 500 mg; N=48) decreases hydrocodone (10 mg; N=50) C max and AUC values in a dose-dependent manner relative to administration of hydrocodone alone; C max and AUC values are 3% to 4% lower, respectively, after administration of 125 mg gabapentin and 21% to 22% lower, respectively, after administration of Peak Development for Medication Administration© Competency Assessment Tool Vol. 22 Issue 10 October 2021 Pain Management: Gabapentin Directions: Place the letter of the one best answer in the space provided. Gabapentin extended-release tablets (Horizant) are used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS; a condition that causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move the legs, especially at night and when sitting or lying down). Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Oral Bioavailability. Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. This product's label may have been updated. For current full prescribing information, please visit www.zydususa.com Manufactured by: Cadila Healthcare Ltd. Ahmedabad, India. For BluePoint Laboratories Rev.: 12/17 Store gabapentin tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to Evaluate the patient’s understanding of gabapentin, including its purpose, dosage regimen, potential side effects, and the importance of medication adherence. Assessing the patient’s compliance and educational needs allows for appropriate support and reinforcement of medication instructions. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |