Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
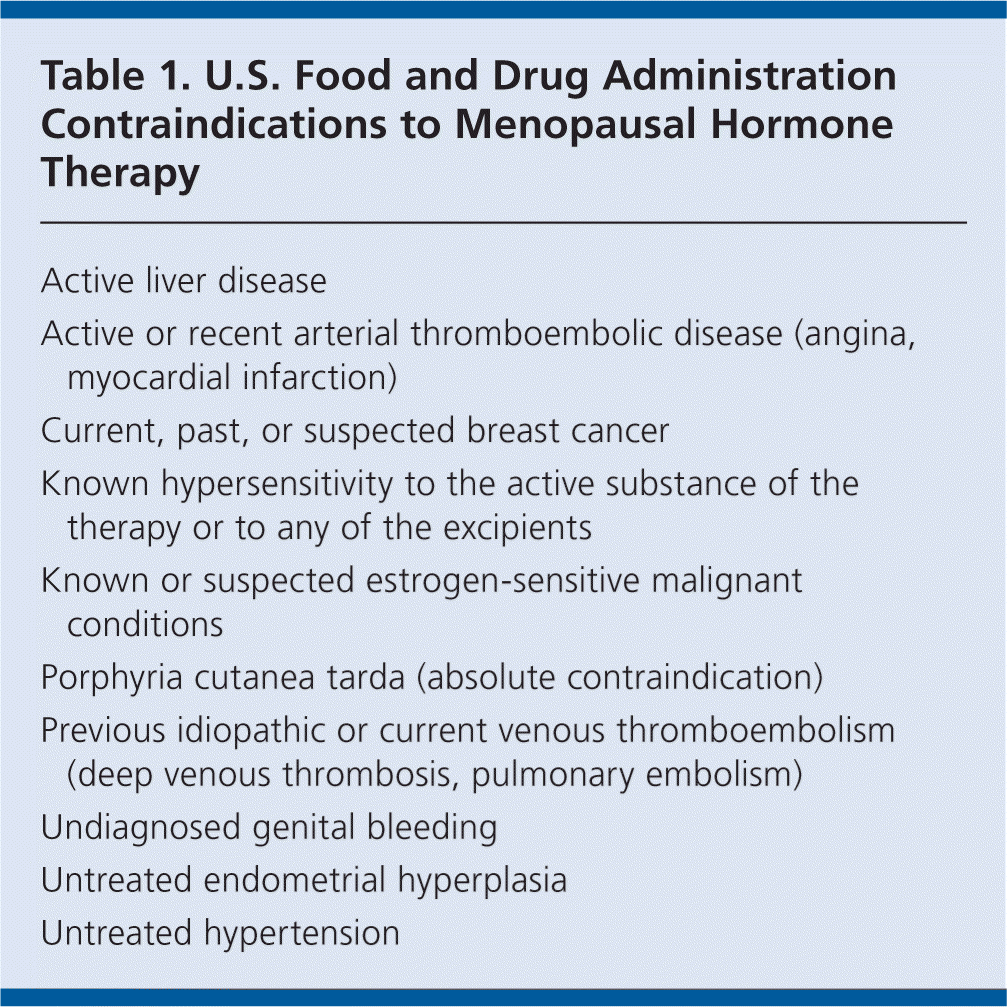 |  |
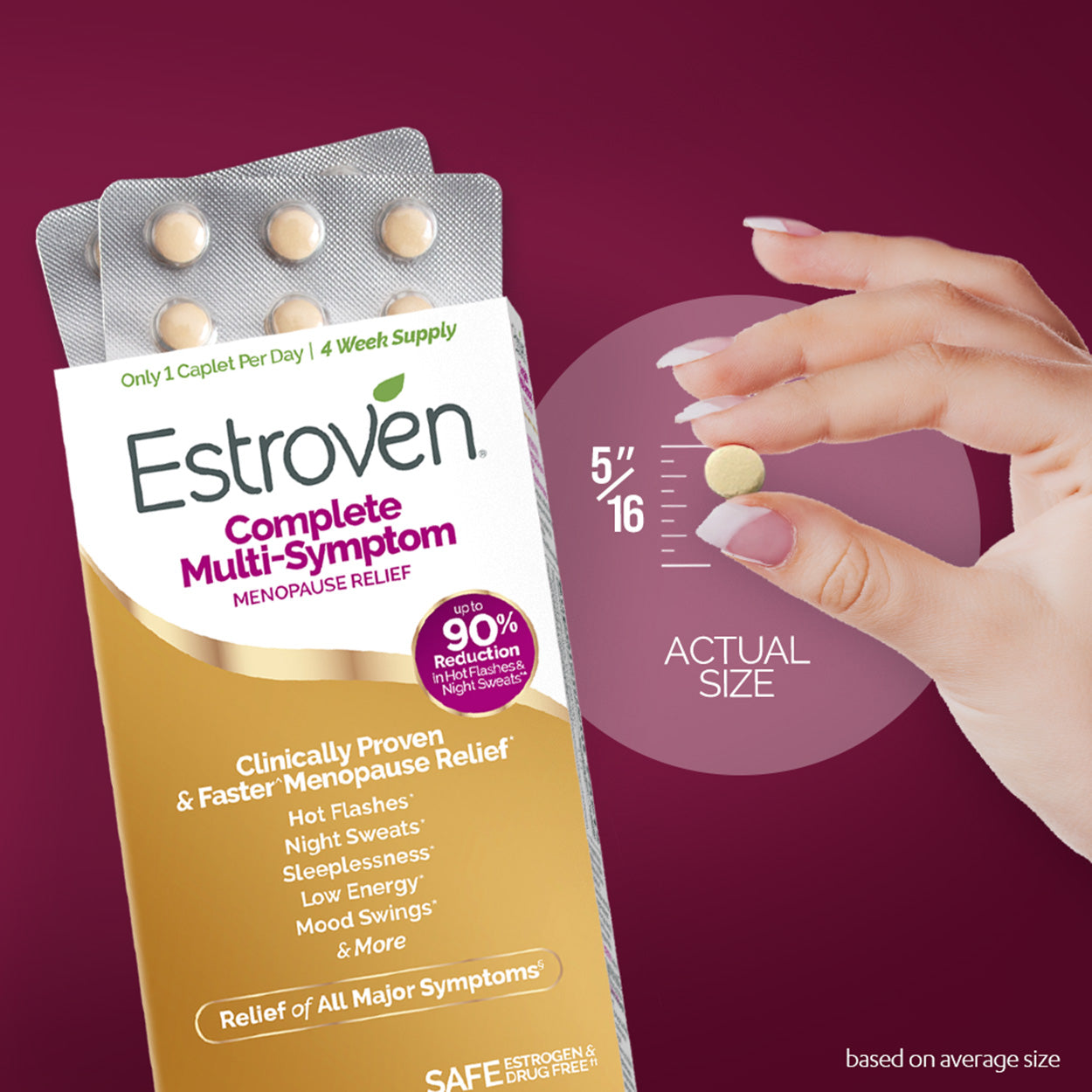
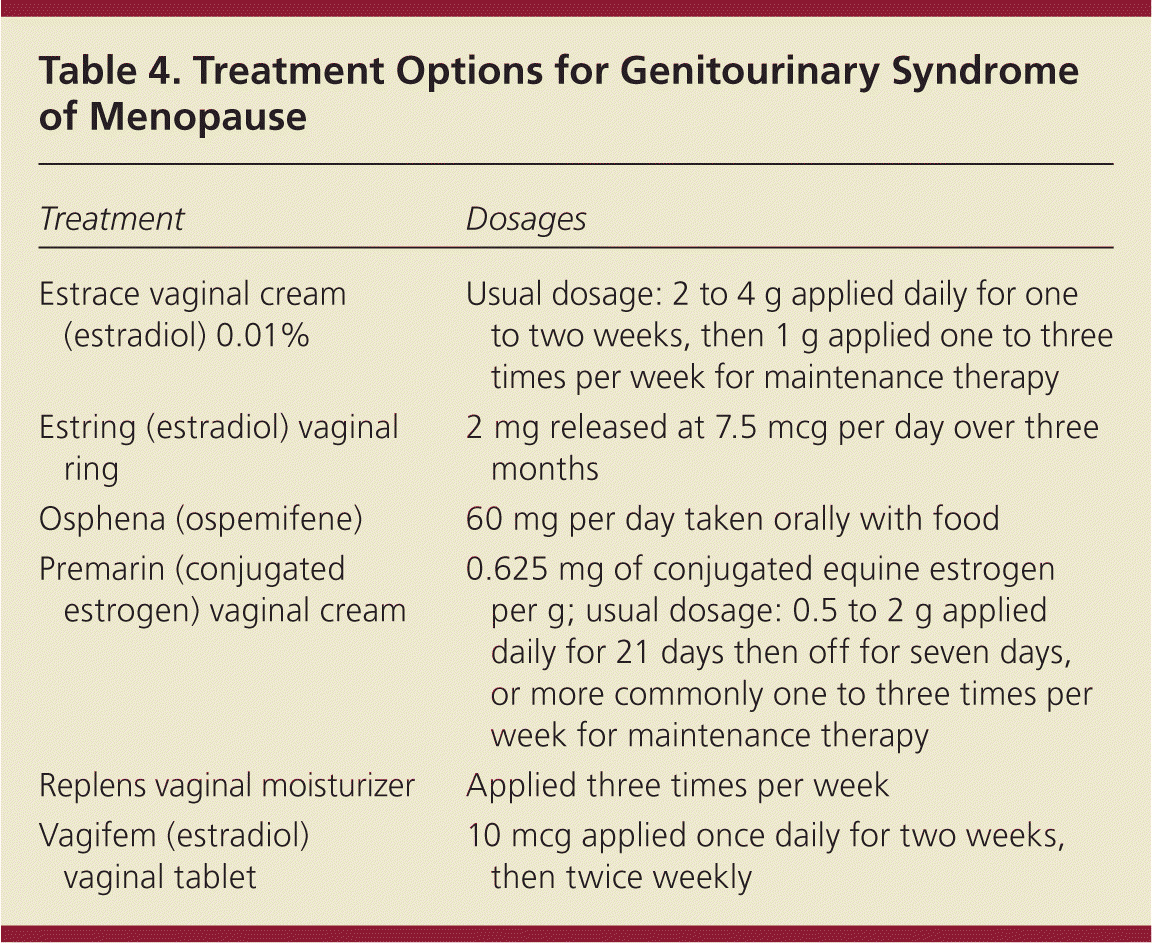
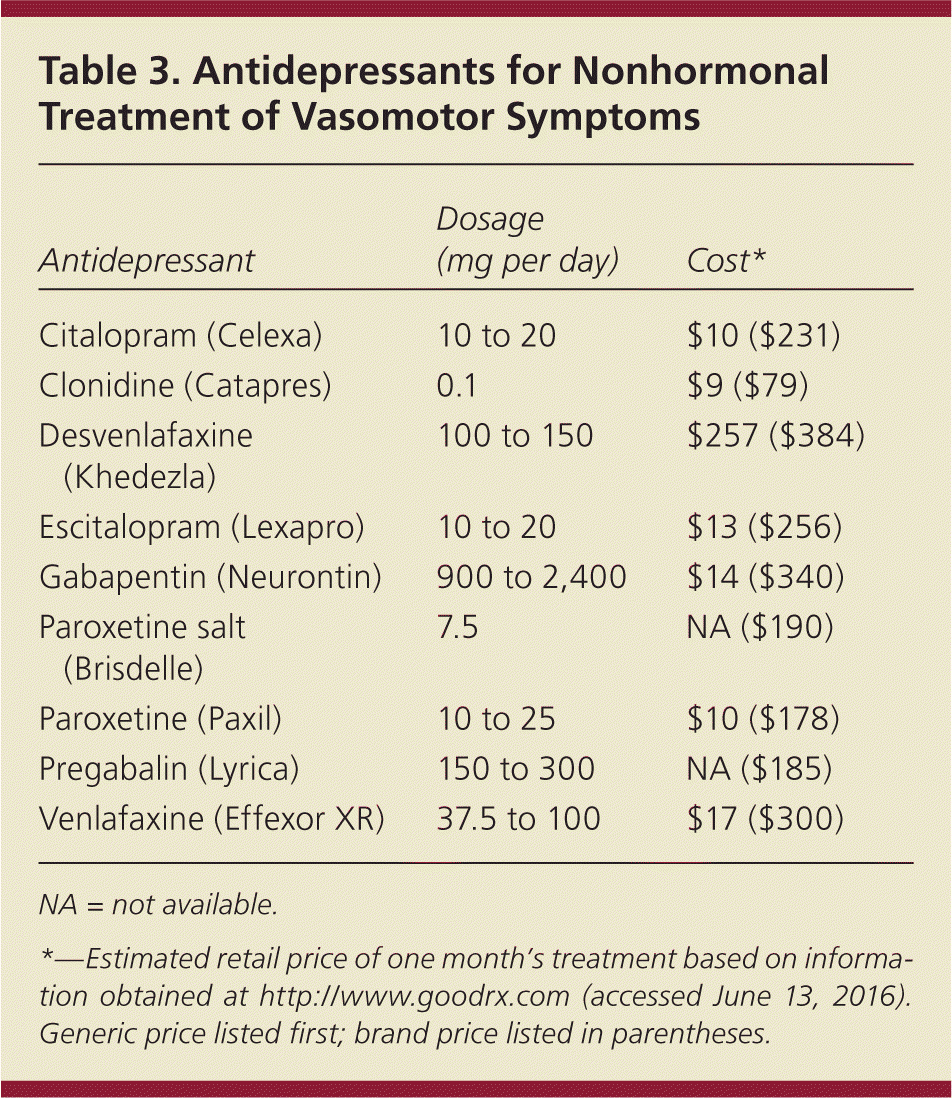
Gabapentin 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses may be a viable option for treating hot flashes in menopausal women who do not want to use hormone replacement therapy. An investigational nonhormonal drug, extended-release gabapentin, effectively improved sleep and reduced hot flashes in menopausal women. Since then, data has shown its efficacy in the treatment of neuropathic pain, tremors, restless leg syndrome, migraine prophylaxis and various mood disorders. 27 It was not until 2000 that gabapentin was first revealed as an option for the treatment of hot flushes and hypothermia through a series of anecdotal case studies in both men and women Overall, gabapentin was found to reduce the frequency of hot flushes at both 4 and 12 weeks (mean difference: -1.62 [95% CI: -1.98 to -1.26], and -2.77 [95% CI: -4.29 to -1.24], respectively). 28 Among the two crossover studies reported in the meta-analysis, there was no statistically significant difference between the use of gabapentin and anti Objective: To compare the effectiveness and tolerability of gabapentin with placebo for the treatment of hot flashes in women who enter menopause naturally. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others). This antiseizure medicine helps ease hot flashes. Side effects can include being drowsy, dizzy or tired and swelling in the arms and legs, called edema. Menopause typically begins 12 months after a woman's last menstrual cycle. During this time, hormone levels start to fluctuate, and the onset of menopause symptoms begins. Symptoms of menopause can include: • Sleep disturbances • Hot flashes • Night sweats • Fatigue • Weight gain • Thinning hair • Dry skin • Urinary changes The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of the North American menopause society. Menopause. 2017;24:728–53. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000921. [Google Scholar] 40. Stuenkel CA, Davis SR, Gompel A, Lumsden MA, Murad MH, Pinkerton JV, et al. Treatment of symptoms of the menopause: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. The first-line treatment option for hot flashes due to menopause is usually hormone therapy (HT). Topical options, such as creams, gels, sprays, or patches, may have fewer side effects than Low-dose vaginal estrogen is a very effective treatment for vaginal dryness or pain with intercourse due to menopause. This is a treatment that can be continued for many years after menopause because only minimal amounts get into the bloodstream. There are many alternatives to HRT for managing menopause symptoms. These include lifestyle changes, SSRIs, gabapentin, and complementary treatments. Adverse effects of gabapentin include dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. are not effective for the treatment of menopause-related vaginal symptoms; evidence does not indicate a earched the PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases for English-language articles published until June, 2018. The following search terms were used: “menopause,” “hot flushes,” “vasomotor symptoms,” “gabapentin,” and “non-hormonal therapy.” Primary outcomes were frequency, duration, and composite score of hot flushes. Secondary outcomes were adverse effects and Gabapentin presents a promising option for managing hot flashes, particularly for those who haven’t found relief through other treatments. By understanding its benefits, potential side effects, and proper administration, you can make informed decisions about its use. Objective: Gabapentin is used to treat vasomotor symptoms (VMS) in postmenopausal women with contraindications to hormonal therapy or who prefer alternatives. We investigated the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin for treating menopausal hot flushes via a meta-analysis. Several studies have shown that gabapentin (Neurontin) at 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses is effective for treating hot flashes in menopausal women. HRT is the current go-to treatment for menopausal hot flashes. Gabapentin offers non-hormonal relief and reduction in hot flashes and night sweats. Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® available as 100mg, 300mg, 400mg, 600mg and 800mg capsules. Also available in generic brands. Gabapentin is usually used to control epilepsy or chronic nerve (neuropathic) pain. It is also a non-hormonal medicine that has been shown to be effective in reducing menopausal hot flushes. Gabapentin appears to be Various non-hormonal agents have been used for the treatment of hot flashes in women with menopause. Some studies have reported that gabapentin appears to be an effective and well-tolerated treatment modality. AMS Nonhormonal Treatments for Menopausal Symptoms 251.06 KB. Many women seek non-hormonal treatments for menopausal symptoms. This information sheet addresses the evidence concerning safety and efficacy of currently available non-hormonal treatments for menopausal symptoms. These treatments are largely prescribed “off-label”.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |