Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 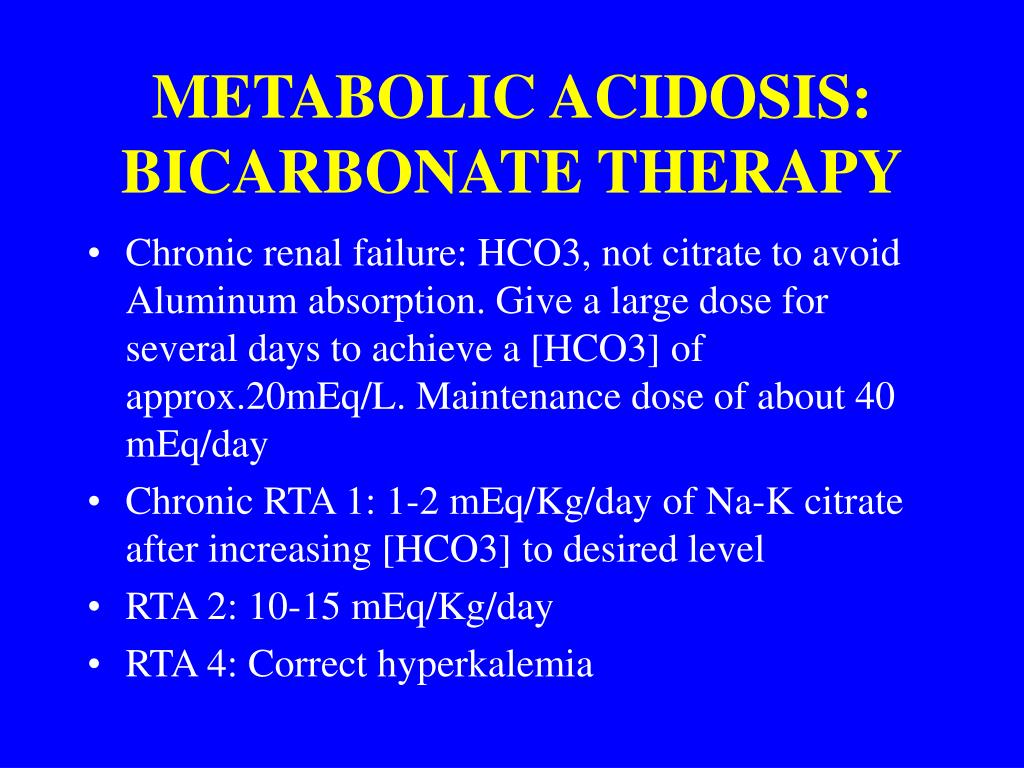 |
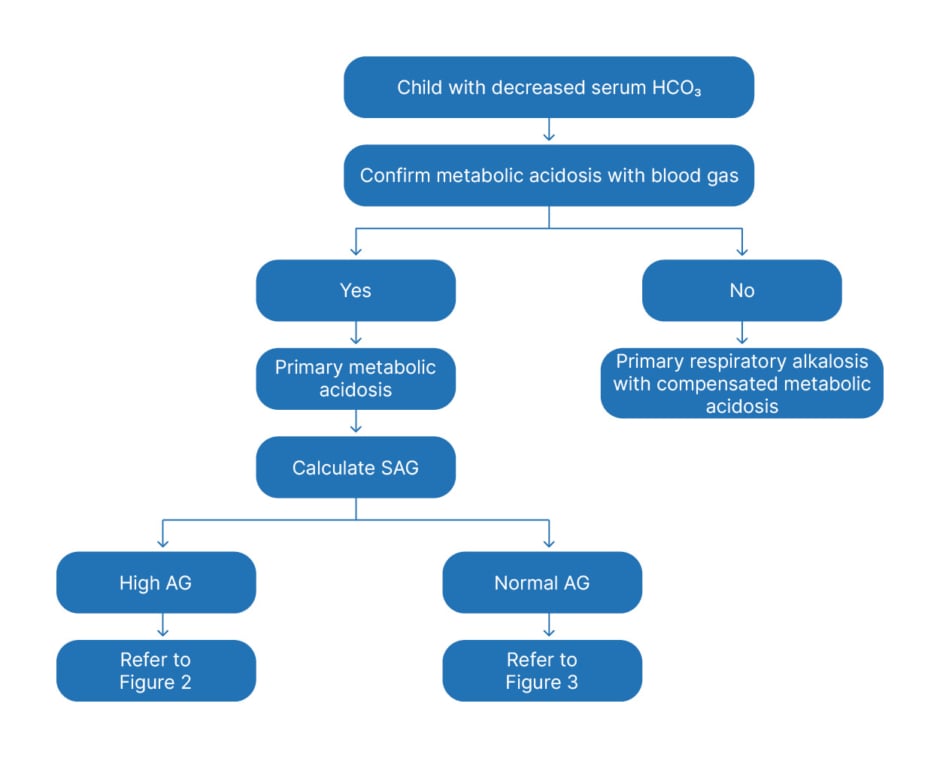
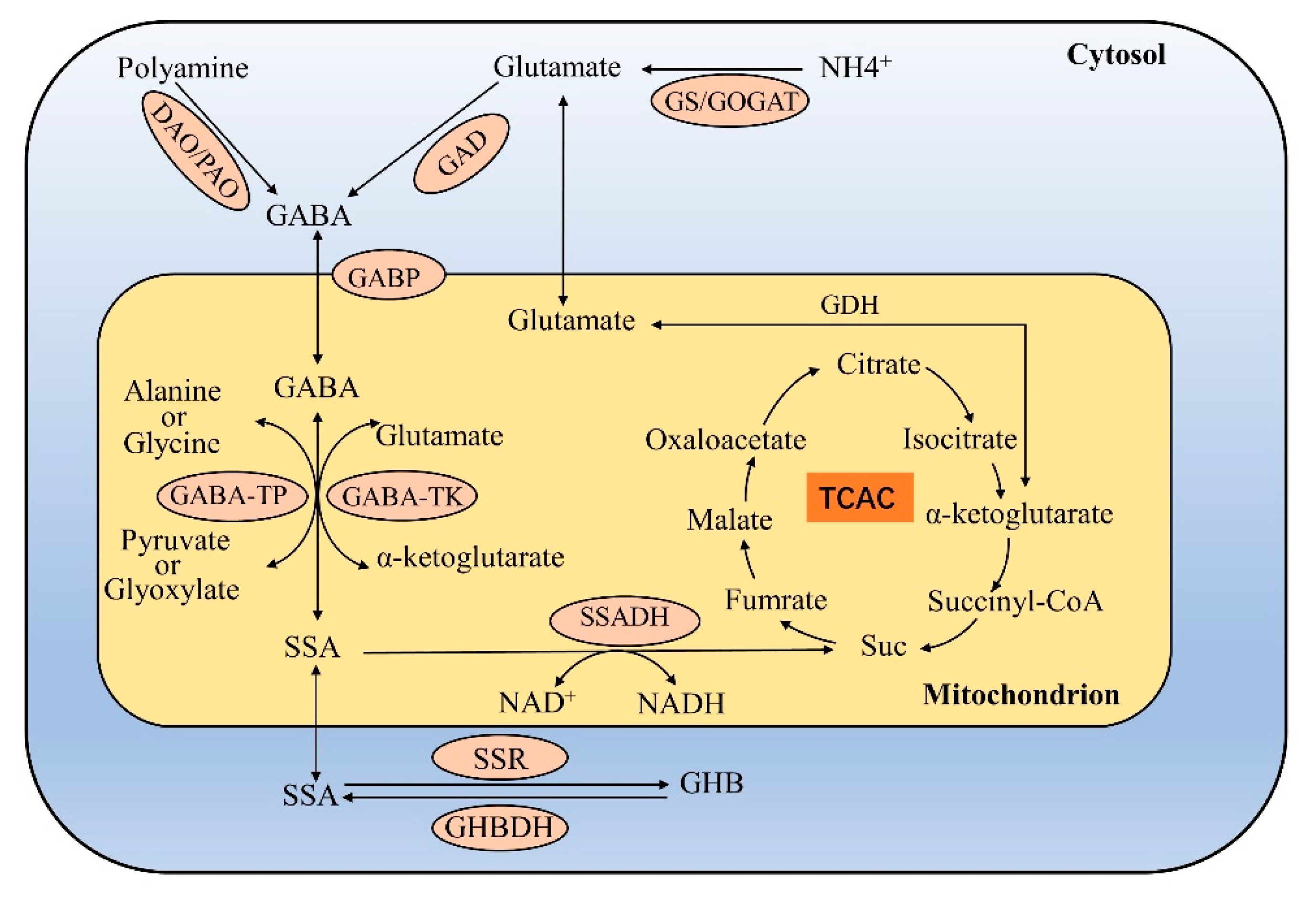
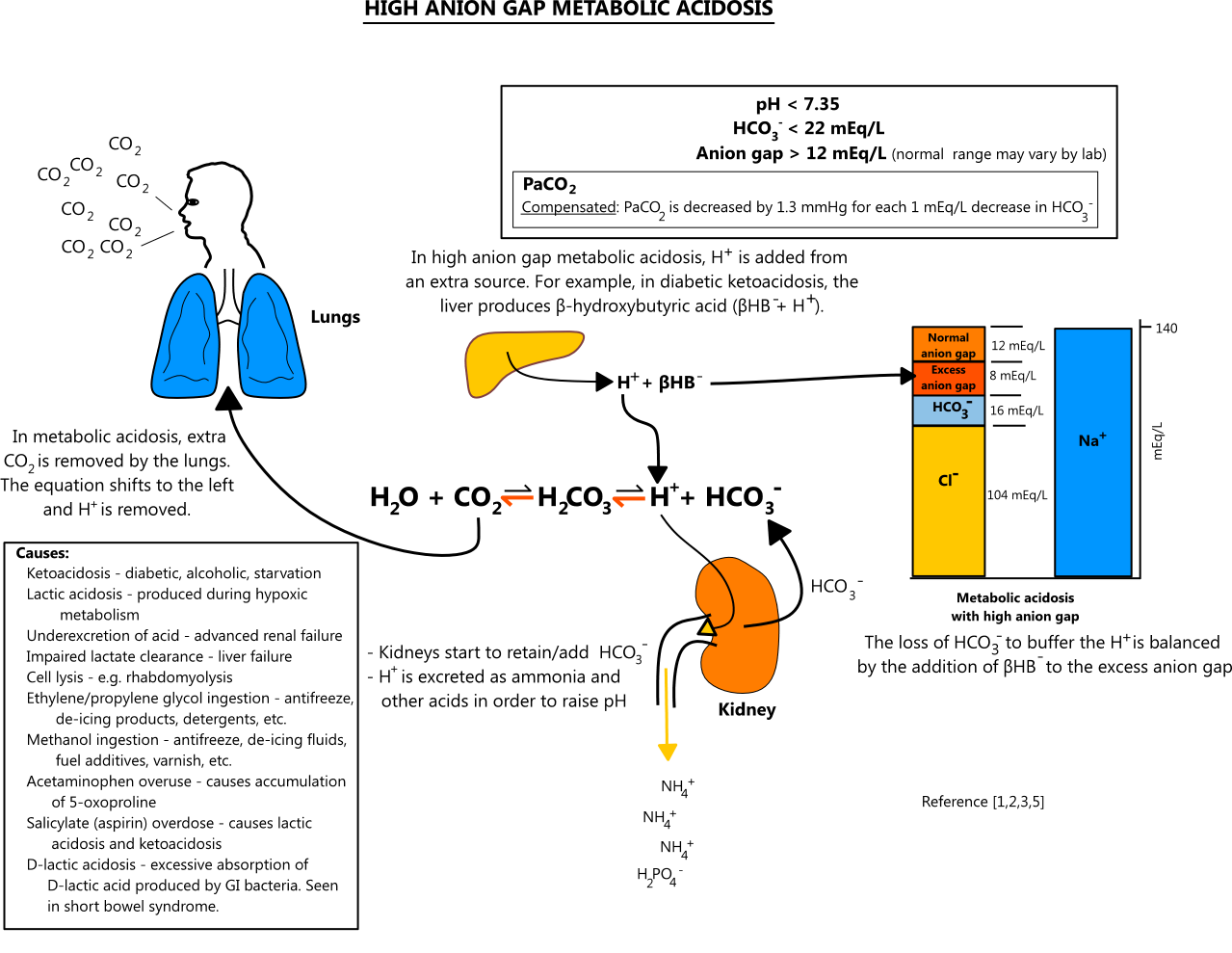
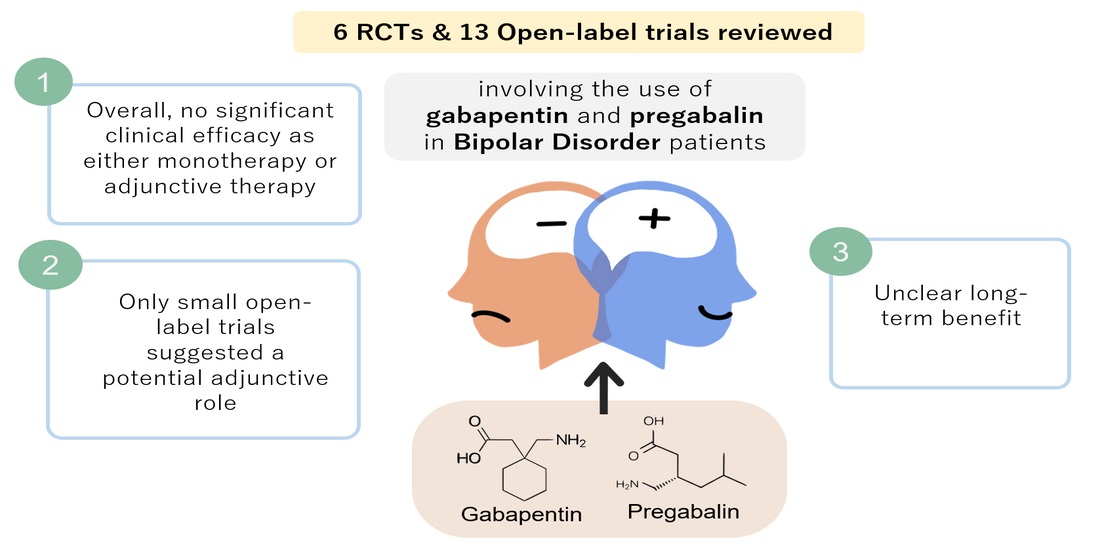
The delta anion gap/delta HCO3 ratio in patients with a high anion gap metabolic acidosis; Treatment of distal (type 1) and proximal (type 2) renal tubular acidosis; Treatment of severe hypovolemia or hypovolemic shock in adults; Venous blood gases and alternatives to arterial carbon dioxide measurement in adults Conclusions: Gabapentin is considered very safe, with failure to absorb more than 3600mg. Abuse is rarely reported, with one suicide described despite its use by psychiatric patients. PRES has not been described, and neurotoxicity, including metabolic encephalopathy is usually described in dialysis or renally-impaired patients. Electrolyte derangements are common in patients with persistent nausea and vomiting and should be corrected. A thyroid stimulating hormone level can be checked if hypothyroidism is a concern. Hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis may indicate adrenal insufficiency, which can be initially evaluated by measuring a fasting cortisol level. Metabolic acidosis is defined as a pathologic process that, when unopposed, increases the concentration of hydrogen ions in the body and reduces the HCO 3 concentration. Acidemia (as opposed to acidosis) is defined as a low arterial pH (<7.35), which can result from metabolic acidosis, respiratory acidosis, or both. The metabolic acidosis rate differed significantly below and above the best cut-off points for heart rate (60% vs. 31.9%) in patients with and without metabolic acidosis, respectively (P = 0.001). Furthermore, the rate of metabolic acidosis was higher in patients presented after 3 h of toxin ingestion (69.4%) compared to those presented after 3 Either way, the result is metabolic acidosis with hyperchloraemia. Since the fall in [HCO 3-] (either through losses or buffering) occurs in proportion to the rise in [Cl-], the anion gap remains normal. Drug causes of metabolic acidosis This review focuses on drugs that cause or exacerbate metabolic acidosis during therapeutic use (Table Do you take Gabapentin and have Metabolic acidosis? Check whether Metabolic acidosis is associated with a drug or a condition Biotinidase deficiency was only suspected when results from tests showed high anion gap metabolic acidosis with lactic acidosis, euglycemia, ketonuria and suggestive skin changes such as alopecia, despite having a normal plasma ammonia level. Author Information. An event is serious (based on the ICH definition) when the patient outcome is: * death * life-threatening * hospitalisation * disability The addition of carbonic anhydrase receptors may be responsible for the drug to potentiate a metabolic acidosis and calcium phosphate kidney stones. Vigabatrin: is an irreversible suicide inhibitor of GABA transaminase, the enzyme responsible for the catabolism of GABA. Drug causes of metabolic acidosis are numerous and their mechanisms are diverse. Broadly, they can cause metabolic acidosis with either a normal anion gap (e.g. drug-induced renal tubular acidosis) or an elevated anion gap (e.g. drug-induced lactic acidosis or pyroglutamic acidosis). Metabolic acidosis produced by drugs and/or chemicals can be conveniently divided into those with an increase in the anion gap (anion gap = Na- (Cl + HCO3)) and those with a normal anion gap. The increase in the anion gap is due to the accumulation of unmeasured organic anions, such as lactate or ac Metabolic acidosis with anion gap Hypernatremia Hypocarnitemia Gabapentin (Neurontin) • Available forms 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg tablets and A 42-year-old woman developed bradycardia, autonomic instability, acute renal failure, metabolic acidosis and anoxic brain injury following gabapentin overdose in suicidal attempt in 2013. The woman had no history of renal disease. She ingested 64 000mg of gabapentin in a suicidal attempt. Lactate levels greater than 2 mmol/L represent hyperlactatemia, whereas lactic acidosis is generally defined as a serum lactate concentration above 4 mmol/L. Lactic acidosis is the most common cause of metabolic acidosis in hospitalized patients. Metabolic acidosis is a condition in which acids build up in your body. Causes include untreated diabetes, the loss of bicarbonate in your body and kidney conditions. Symptoms include an accelerated heartbeat, confusion and fatigue. Blood and urine tests can help diagnose it. Treatment may include sodium bicarbonate, IV fluids and insulin. Hyperlactatemia and lactic acidosis are two syndromes that are associated with morbidity and mortality. Medication-induced hyperlactatemia and lactic acidosis are diagnoses of exclusion and have the potential to be overlooked. Metabolic acidosis could emerge from diseases disrupting acid-base equilibrium or from drugs that induce similar derangements. Occurrences are usually accompanied by comorbid conditions of drug-induced metabolic acidosis, and clinical outcomes may range from mild to fatal. Metabolic acidosis characterized by the accumulation of lactate in the body. It is caused by tissue hypoxia. Pathologic condition resulting from accumulation of acid or depletion of the alkaline reserve (bicarbonate) content of the blood and body tissues, and characterized by an increase in hydrogen ion concentration (decrease in ph). Unpredictably, patients have presented with a severe metabolic acidosis, with or without seizure activity [57, 62]. The metabolic abnormalities have been reported to persist after neurological improvement, 72 h from ingestion (Grade III).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |