Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
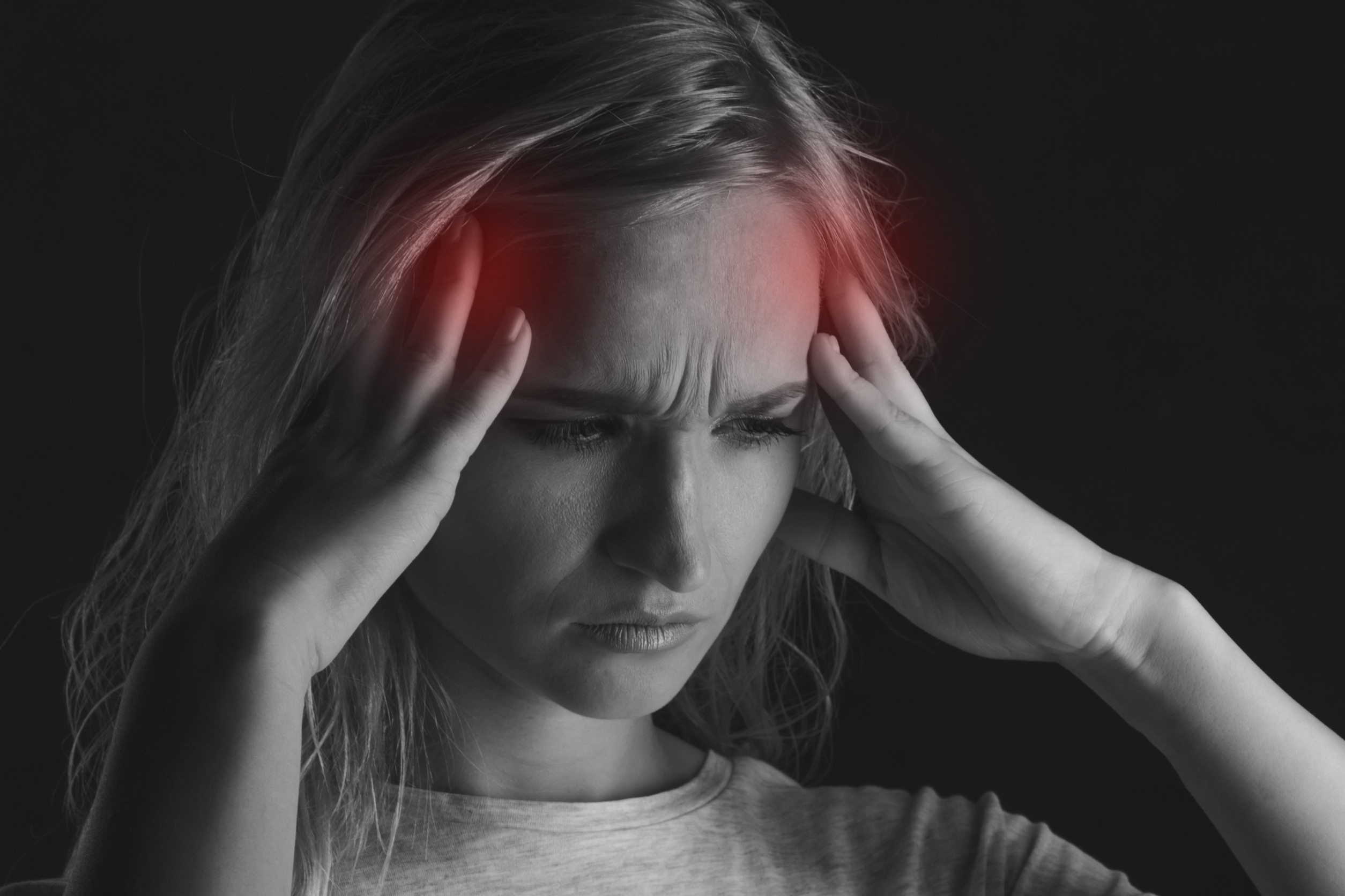
Amitriptyline is effective at preventing tension-type headaches after three months of treatment. • Triptans, ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin, and high-dose acetaminophen are effective treatments for There are some people who only need a rescue or an acute treatment for migraine because they have infrequent migraine attacks. But there are other people who are having frequent migraine attacks, maybe two or three times a week. If they used rescue treatments for every attack, it could potentially lead to other complications. Types of Drug Treatment Options for Migraine Prevention. Your doctor will work with you to create a migraine prevention plan based on your specific needs. This means taking into account any other conditions for which you are currently taking medication and/or which may be impacted by certain preventive migraine treatments. Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. We found moderate certainty evidence that beta-blockers, valproate, and amitriptyline increase the proportion of patients who experience a 50% or more reduction in monthly migraine days, and low certainty evidence that gabapentin may not be different from placebo. Gabapentin shows to have an effective therapeutic action in the prophylactic treatment of migraine. Our observations indicate that gabapentin is well tolerated by patients and that reduces headache frequency and use of symptomatic drugs in both groups. ficacy as migraine preventive treatments including certain beta blockers (propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol), amitriptyline, and several anticonvulsants. (Kaniecki and Lucas. 2004; Ramadan et al., 2000) Among anticonvulsants, topiramate and valproic acid, for example, have received FDA-a. The recommendations on preventative treatment for migraine are based on the clinical guidelines National headache management system for adults , Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management , Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015] and Pharmacological management of migraine , the American Headache Society updated Preventive medication therapy reduces migraine frequency, severity, and headache-related distress. Preventive therapy may also improve quality of life and prevent the progression to chronic We conducted a targeted search of Google Scholar and PubMed to identify original research, review articles and clinical practice guidelines published through November of 2021, using search terms that included, but were not limited to, “migraine acute treatment,” “migraine preventive treatment,” “migraine CGRP monoclonal antibodies Objective: To compare gabapentin with placebo for use as a prophylactic agent in patients with migraine (with or without aura). STUDY DESIGN AND TREATMENT: After screening, a 4-week, single-blind, placebo baseline period was followed by a 12-week, double-blind, treatment period. A treatment plan should consider not only the patient’s diagnosis, symptoms, and coexistent or comorbid conditions, but also the patient’s expectations, needs, and goals.1 Effective migraine treatment begins with making an accurate diagnosis, ruling out alternate causes, ordering appropriate studies, and addressing the headache’s impact Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1 , 2 . Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used off-label to help prevent migraine attacks. Learn about why it’s used and how it works. Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Headache Society (AHS) do not list gabapentin as "effective" or "probably effective" for preventing migraines in their 2012 guidelines. Instead, gabapentin is given a level U rating, which means the evidence is conflicting or inadequate to support or refute its use for migraine prevention.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |