Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
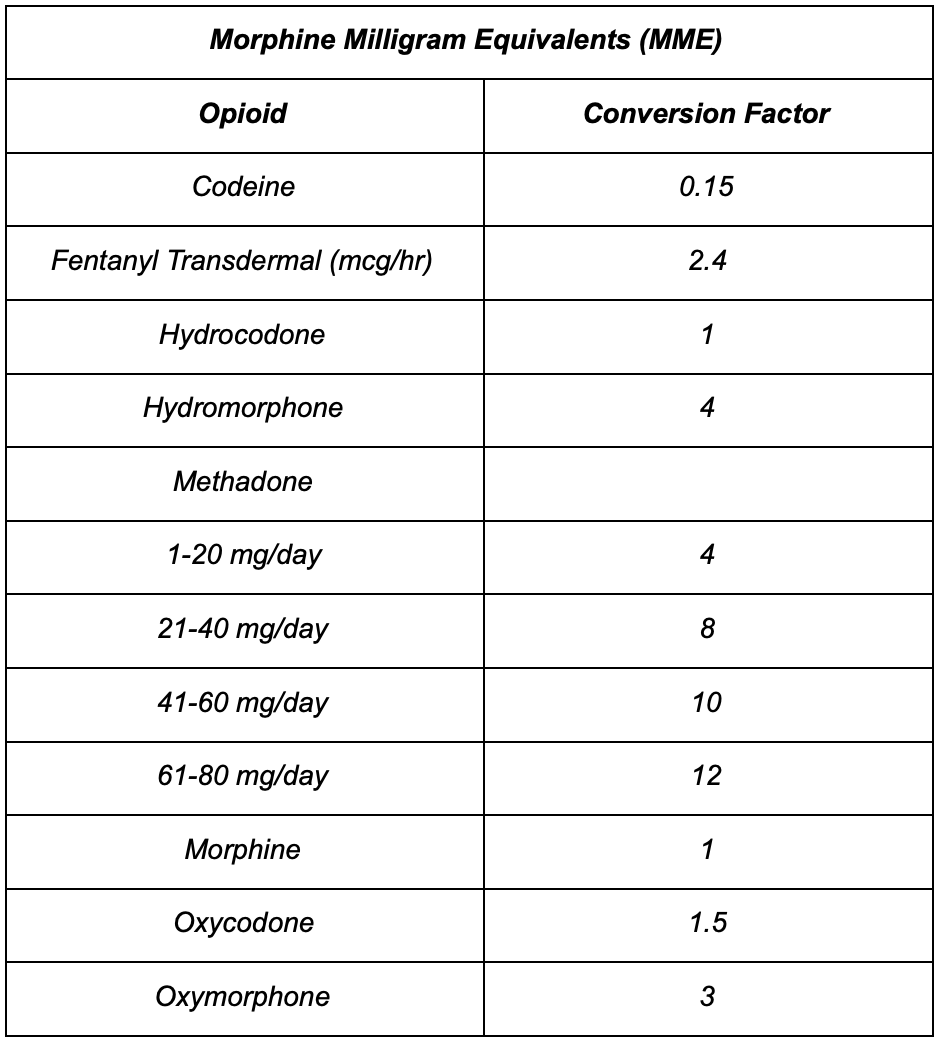
This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. Methods: Databases were searched for peer‐reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion.Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating The aim of this systematic review was to improve our understanding of the lived experiences of gabapentinoid misuse and symptoms of gabapentinoid dependence. Twenty-one qualitative studies from nine countries were located. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. Methods Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and Background: A 2017 systematic review (SR) identified 59 studies examining gabapentinoid (pregabalin and gabapentin) misuse/abuse. Evidence of gabapentinoid misuse/abuse has since grown substantially. Objective: Update previous SR and describe new insights regarding gabapentinoid abuse. Evidence suggests gabapentinoids possess potential for abuse, particularly in individuals with a history of opioid abuse, and reports of such abuse are increasingly being documented. Prescribers should be aware of high-risk populations and monitor for signs of abuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. METHODS Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion.METHODS: Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and A systematic review found that about 15%–22% of people with opioid use disorder also reported gabapentin misuse. 2 Although there are limited data evaluating co-consumption with illicit opioids, in a case–control study, coprescribed gabapentin and opioids significantly increased risk of death compared with prescribed opioids alone. 7 This This review summarizes current evidence on the abuse and misuse of the gabapentinoids pregabalin and gabapentin. Pharmacovigilance studies, register-based studies, surveys, clinical toxicology studies, and forensic toxicology studies were identified This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. Methods Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. Methods Databases were searched for peer‐reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and Epidemiological and case report evidence suggests that the anti-epileptic and analgesic medication gabapentin is being misused internationally, with substance abuse populations at special risk for misuse/abuse. Epidemiological and case report evidence suggests that the antiepileptic and analgesic medication gabapentin is being misused internationally at a rate of about 1%, with substance abuse populations at special risk for misuse/abuse. Keywords: gabapentin, prescription drug misuse, systematic review, diversion, substance abuse. Introduction Epidemiological and case report evidence suggests that the anti-epileptic and analgesic medication gabapentin is being misused internationally, with substance abuse populations at special risk for misuse/abuse. 11 This was con rmed by a third systematic review, which found a 1.6-percent prevalence of gabapentionoid abuse among the general public, compared to a 3-to 68-percent prevalence of gabapentinoid Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subse-quently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. Methods Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion. Methods: Databases were searched for peer-reviewed papers demonstrating gabapentin misuse, characterized by taking a larger dosage than prescribed or taking gabapentin without a prescription, and The risk of gabapentin misuse is higher in those with concurrent opioid use. A systematic review found that about 15%–22% of people with opioid use disorder also reported gabapentin misuse.2 Although there are limited data evaluating co-consumption with illicit opioids, in a case–control study, coprescribed gabapentin and opioids significantly increased risk of death compared with
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |