Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
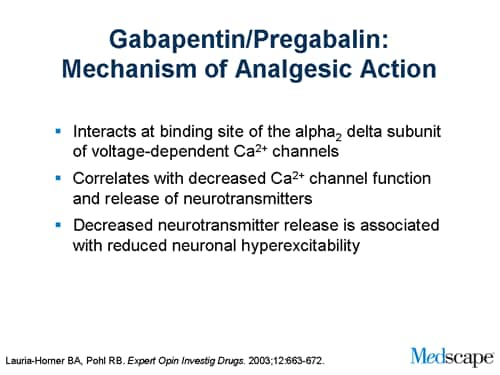
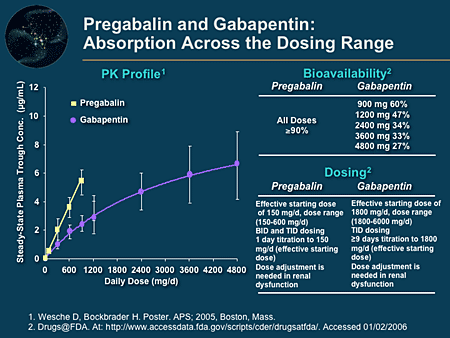
Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. The aims of this article are to review the pharmacology of gabapentin and its use in pain management. Chemistry. Gabapentin, a structural analogue of GABA, is a water-soluble, bitter-tasting, white crystalline substance with a structure resembling GABA with a cyclohexane ring incorporated . Introduction. The anticonvulsant gabapentin was first reported as providing pain relief 20 years ago (Mellick et al. 1995).The discovery that anticonvulsants could be used as analgesics started a scientific journey leading to the inclusion of gabapentinoids as key frontline therapy for various neuropathies. The National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines on the management of neuropathic pain recommend gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline or duloxetine as the initial choice of treatment for neuropathic pain with the exception of trigeminal neuralgia. 1 The guideline development group found that gabapentin was the most cost Gabapentin prevents pain responses in several animal models of hyperalgesia and prevents neuronal death in vitro and in vivo with models of the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Gabapentin is also active in models that detect anxiolytic activity. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. The analgesic effect in neuropathic pain is well evidenced but the role in postoperative pain is less certain. Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental pain. Mechanism of action of pregabalin and gabapentin. Reproduced with permission from []Brainstem structures, from which descending modulatory fibers originate, may be a key target of the analgesic action of gabapentinoids, because alpha-2/delta-1 expression is very high in these areas. Multiple dose gabapentin attenuates cutaneous pain and central sensitisation but not muscle pain in healthy volunteers. Pain 125: 158–164. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ] In a meta-analysis of trials evaluating the treatment of neuropathic pain, including painful polyneuropathy and spinal cord injury pain, gabapentin was shown to be safe and effective IASP [Finnerup 2015]. Data from meta-analyses support the use of IR gabapentin for reducing pain by more than 50% in diabetic neuropathy Moore 2014, Rudroju 2013. Targeted Use of Gabapentin. One of the most commonly cited uses of gabapentin in veterinary medicine is for treating acute post-operative pain. 5 Considering the mechanism of action of gabapentin and its impact on pain signaling, it is unlikely that gabapentin will be an effective analgesic in this context. Inflammation is the most common Gabapentin (GBP) is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy pain.1 Despite the widespread use in neuropathic pain, the precise mechanism of action is uncertain. The effect of gaba-pentinoids in pain are assumed to be because of direct inhibi-tion of voltage gated Ca2þ channels by binding to its a2d-1 subunit resulting in reduction of presynaptic Ca2þ influx and Neuropathic pain: The recommended gabapentin dosage ranges from 300 to 1200 mg taken orally 3 times daily, with a maximum daily dosage of 3600 mg. Fibromyalgia: The recommended gabapentin dosage is between 400 and 800 mg taken orally 3 times daily, with a maximum daily dosage of 2400 mg. In randomized open clinical trial, the combination of gabapentin with opioid analgesics was shown to provide better relief in neuropathic pain in cancer patients as compared to opioid analgesics alone in terms of reduction in pain intensity for burning and shooting pain at different days of the study. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. The interaction of gabapentin and pr Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy , postherpetic neuralgia , and central pain . [ 11 ] Gabapentin has become popular as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain because of its efficacy as an antineuropathic agent and relatively benign side-effect profile. However, its mechanism of action is far from clear. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |