Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
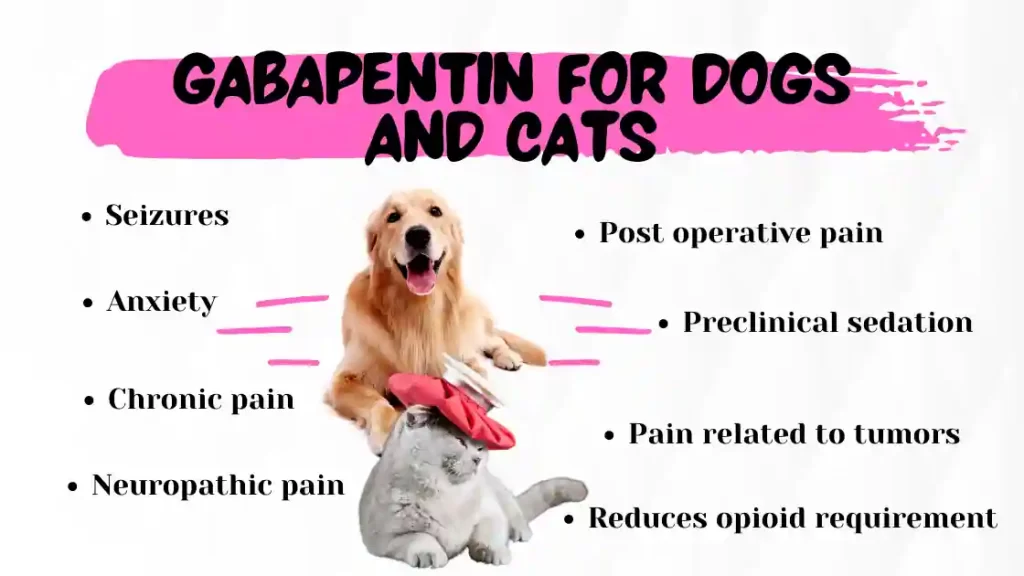
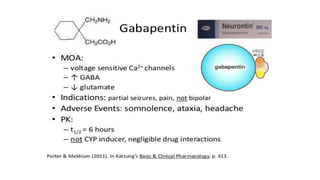
In dogs, gabapentin was useful in the treatment of epilepsy, as well as chronic, neuropathic, and post-operative pain and anxiety. In cats, it was effective in post-ovariohysterectomy-related pain and in the management of anxiety. In horses, it has been administered as an analgesic for chronic pain. Gabapentin is primarily an anticonvulsant medication used in people for treating neuropathic and chronic pain, and it has been introduced to veterinary medicine, but as an off-label drug in most countries and states. Its mechanism of action is not entirely clear but is likely related to inhibition of calcium and, possibly, sodium channels. 1. Gabapentin is excreted unchanged in humans but is metabolized to N-methyl-gabapentin in dogs. Results in faster elimination and ability for shorter dose intervals in dogs as compared with humans 2 Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin's mode of action is not fully understood. However, it is thought to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. In dogs suffering from epilepsy, gabapentin is thought to stop seizures by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The short answer is: Gabapentin is not a primary painkiller for dogs, but it can play a valuable role in pain management, especially for neuropathic pain (nerve pain) and when used in combination with other pain relief medications. Several case reports note analgesia when gabapentin was used for treatment of chronic pain. 14,15 And in a clinical study on postoperative pain in dogs undergoing mastectomy, although pain scores did not differ, dogs receiving NSAIDs plus gabapentin required fewer opioid rescue doses than dogs receiving NSAIDs alone; thus, the gabapentin did Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Mechanism of Action. Understanding the mechanism of action of gabapentin is critical when evaluating the role that gabapentin may have as an analgesic for veterinary patients. As mentioned, gabapentin was initially intended to be a centrally acting agonist at the GABA receptor. Considering the mechanism of action of gabapentin and its impact on pain signaling, it is unlikely that gabapentin will be an effective analgesic in this context. Inflammation is the most common component of acute post-operative pain, and while gabapentin modulates pain signals from the periphery, it does not treat inflammation directly. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the presence of voltage-gated calcium channels Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug, which presents an established clinical efficacy in human patients for the management of refractory partial seizures, secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and for the control of chronic neuropathic pain. Gabapentin was synthesized as a structural analog Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug, which presents an established clinical efficacy in human patients for the management of refractory partial seizures, secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and for the control of chronic neuropathic pain. Gabapentin was synthesized as a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, with GABA-mimetic effects, able to cross the blood Vets use gabapentin in dogs to treat a number of conditions, including situational anxiety, chronic pain, and (less commonly) seizures or muscle tremors. This medication is very affordable and low in side effects, making it a low-risk option for many dogs. Gabapentin. Gabapentin is a lipophilic structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. This drug was initially developed as an anticonvulsant and is now indicated for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain. The mechanism of action of gabapentin remains to be elucidated. What Is Gabapentin for Dogs? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug that is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. How gabapentin works is not completely understood; however, it is thought to block stimulation of the nerve cells. This article delves into the various uses of gabapentin for dogs, exploring its mechanism of action, potential benefits, side effects, and important considerations for pet owners. Is it safe for dogs? And how is it used? In this article, we will answer these questions and talk about Gabapentin for dogs. In veterinary medicine, Gabapentin is used “off-label” and in conjunction with other meds to prevent neuropathic pain and manage pets with seizures. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about Gabapentin
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |