Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) | |
 |  |
 |  |
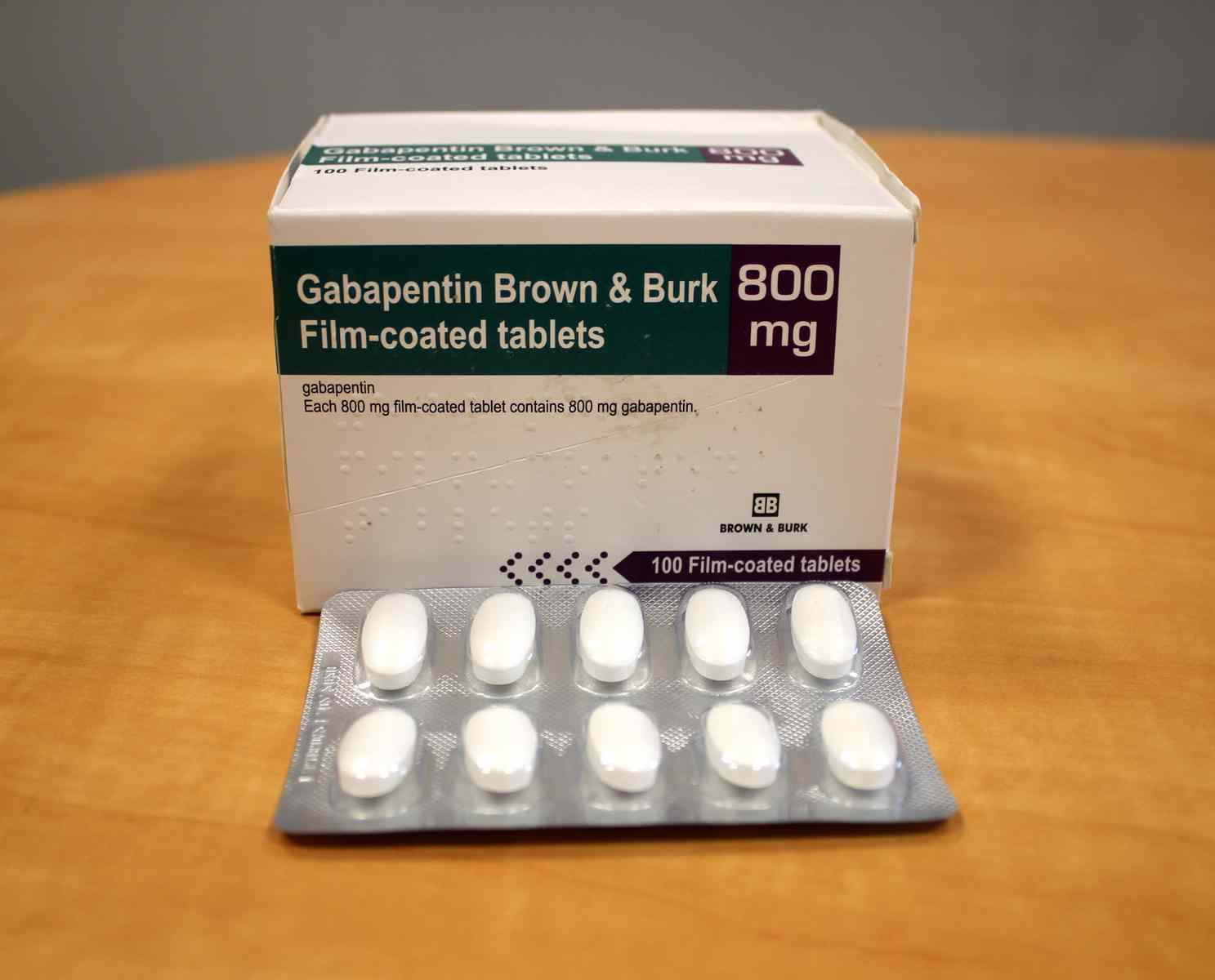 |  |
Some studies suggest gabapentin has muscle relaxant properties and can treat muscle pain and spasticity, while other studies indicate it does not significantly affect muscle strength or pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of gabapentin in increasing muscle strength of patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).Background: Preclinical data in experimental models of motor neuron disease suggest a neuroprotective effect of gabapentin. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Muscle weakness associated with gabapentin can occur due to several factors. The primary mechanism involves its effect on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin inhibits excitatory neurotransmission while enhancing inhibitory pathways. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin can be used for certain movement disorders, such as essential tremors and RLS. In 1996, Miller et al treated 152 ALS patients randomly assigned to receive 2400 mg gabapentin daily compared to a placebo group. Results showed a slower decline in muscle strength in the treatment group. Muscle Cramps (Off-label) 100-300mg PO qHS; may titrate to 300-400mg q8hr PRN; Anxiety (Off-label) 300mg PO qHS initially, THEN 300mg PO q8h; may further increase as tolerated; Diabetic Neuropthy (Off-label) 900mg/day PO initially; may increase gradually q3Days to 1800-3600mg/day; Neuropathic Pain. 600mg PO load in ED Skeletal Muscle Relaxants Table 1. Skeletal Muscle Relaxants (Antispasmodic Agents) Drug Recommended dosage Most common adverse effects Comments Monthly cost* Gabapentin can be used for certain movement disorders, such as essential tremors and RLS. In 1996, Miller et al treated 152 ALS patients randomly assigned to receive 2400 mg gabapentin daily compared to a placebo group. Results showed a slower decline in muscle strength in the treatment group. Muscle relaxers are drugs that can help relieve muscle cramps and spasticity. Learn about the different options. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant drug typically used to relieve Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Long-term use of gabapentinoids is associated with detrimental musculoskeletal outcomes, including increased fracture risk. Therefore, understanding potential complications is essential for clinicians to guide appropriate treatments. Keywords: Gabapentin, Pregabalin, α 2 δ 1, Bone, Muscle, Cartilage. Using nocturnal splint along with exercise and gabapentin significantly improved VAS, pinch and grip strength in moderate CTS compared to control group that only used nocturnal splint. However in mild CTS, grip strength was not significantly higher compared to control group (P =0.048). Muscle relaxer side effects: Find out more about what you can expect when taking muscle relaxers, including the most common side effects. Alcohol and muscle relaxers don’t mix. Learn why this can be a dangerous combination that should be avoided. Common muscle relaxer dosing: Wondering if you’re on a low dose? Key Takeaways: Gabapentin and Muscle Relaxation Primary Use: Gabapentin is mainly prescribed for managing nerve pain. Indirect Muscle Relaxation: It may help relax muscles by alleviating discomfort. Mechanism of Action: Gabapentin inhibits neurotransmitter release, reducing pain. How Skeletal Muscle Contracts. A single α-motor neuron can innervate up to 200 muscle fibers, forming a complex called motor unit (Figure 1).¹⁰ With movement, an action potential originates from the UMN in the motor cortex.⁹ This action potential depolarizes the motor neuron terminal, resulting in the opening of voltage-gated calcium (Ca²⁺) channels and the subsequent release of the Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of gabapentin in increasing muscle strength of patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Background: Preclinical data in experimental models of motor neuron disease suggest a neuroprotective effect of gabapentin. Other side effects from gabapentin include:. Clumsiness or unsteadiness. Constipation. Dizziness. Headaches. Memory loss. Nausea or vomiting. Weight gain. What Is Tylenol? Acetaminophen is a pain We recently reported that the neuropathic pain medication, gabapentin (GBP; Neurontin), significantly attenuated both noxious colorectal distension (CRD)-induced autonomic dysreflexia (AD) and tail pinch-induced spasticity compared to saline-treated cohorts 2–3 weeks after complete high thoracic (T4) spinal cord injury (SCI).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |