Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 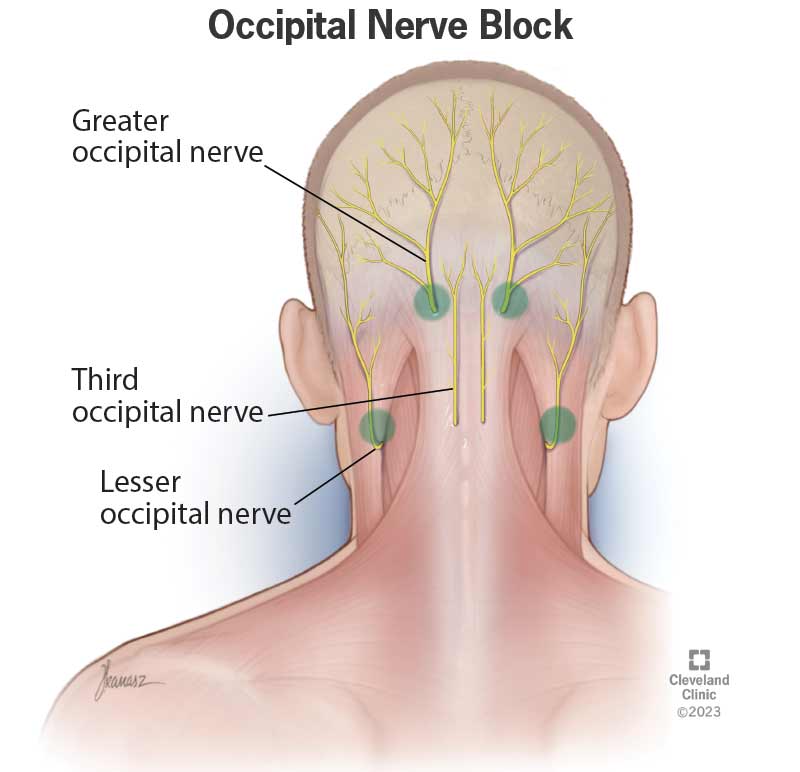 |
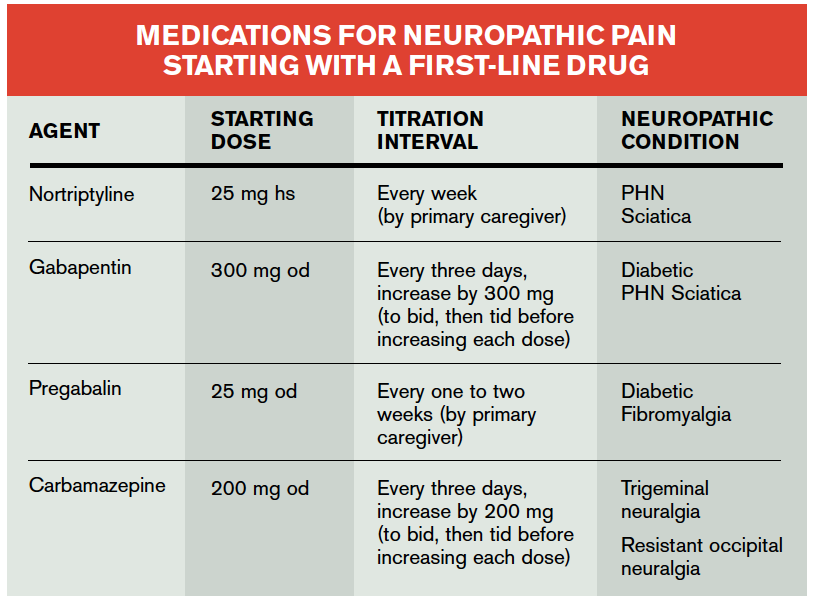
Is Gabapentin a Long-Term Solution for Back Pain? Gabapentin as a long-term solution for back pain involves considering the nature of the underlying conditions: In cases of nerve pain, the duration of gabapentin usage is contingent on alleviating pain. Continuing gabapentin for several months or longer after the pain stops aims to prevent its Keywords: Low Back Pain, Back Pain, Chronic Pain, Pregabalin, Gabapentin, Systematic Review. Resumo. Antecedentes Dor lombar crônica (DLC) é um problema de saúde global, e a gabapentina e a pregabalina são frequentemente utilizadas no tratamento de pacientes sem radiculopatia ou neuropatia associada. Por isso, determinar sua eficácia e Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally with the evening meal Day 2: 600 mg orally with the evening meal In short, gabapentin’s action for back pain involves a multifaceted approach, including modulation of neurotransmitter release, prevention of pain responses, neuroprotection, alteration of nerve function, and a specific effect on voltage-dependent calcium ion channels. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. If your back pain is nerve-related, then the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin may be a good choice for you. This article will explain how gabapentin works, detail its uses, and go over potential side effects, so that you can assess with your doctor whether this drug may be right for you. "The most important finding is that the widespread use of pregabalin or gabapentin for chronic non-specific low back pain, which is the most common chronic pain ailment today, is not supported by evidence," said study author Harsha Shanthanna, MD, MBBS, MSc, PhD, associate professor of anesthesiology and a chronic pain physician at St. Joseph's Healthcare, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Gabapentin is a versatile medication used to treat various conditions, including seizures, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome. It works by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain and calming overactive nerves. Dosage for nerve pain. The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. Changes to your dose. To prevent side effects, your doctor will prescribe a low dose to start with and then increase it over a few days. Once you find a dose that suits you, it will usually stay the same. How to take it Neuropathic pain is a chronic debilitating pain syndrome that is complex to treat. Current medication management for neuropathic pain includes select neuromodulating agents such as anticonvulsants, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and certain opioids. 1,2 Gabapentin remains among the most commonly used anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain. Doctors often prescribe gabapentin off-label to treat conditions such as: pain from diabetic neuropathy, which is numbness or uncomfortable tingling caused by nerve damage from diabetes; nerve pain in the neck and back from conditions such as sciatica, a painful compression of the sciatic nerve Nerve pain can be recurring and persistent, sometimes lasting three months or longer. Many people stay on gabapentin for long-term management of their nerve pain and take it daily. Talk to your healthcare provider if you don't have pain relief within a couple of weeks after starting treatment. Yes, I have. I take Gabapentin for back pain. I was also taking Cymbalta which I've been weaning off of slowly. I've had 2 surgeries. A decompression and disc replacement on my cervical spine and also a spinal fusion in my lumbar spine. I have back pain with most lifting activities that the Gabapentin helps with. Despite its many uses, Gabapentin is particularly effective at treating neuropathic (nerve-related) pain. According to research, Gabapentin can often alleviate back problems caused by a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. Spinal herniation occurs when a disc between adjacent spinal vertebrae slips out of place and pinches a nerve. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for sciatica. But the evidence supporting its use for sciatic nerve pain is weak. Sciatica is a very common condition that’s also known as lumbosacral radiculopathy. Up to 40% of people will have sciatica within their lifetime. Nerve pain due to diabetic neuropathy: 50–100 mg three times daily; maximum dosage of 600 mg daily; Fibromyalgia: 75–150 mg twice daily; maximum 450 mg daily; Nerve pain due to spinal cord injury: 75–300 mg two times daily; maximum 600 mg daily Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |