Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
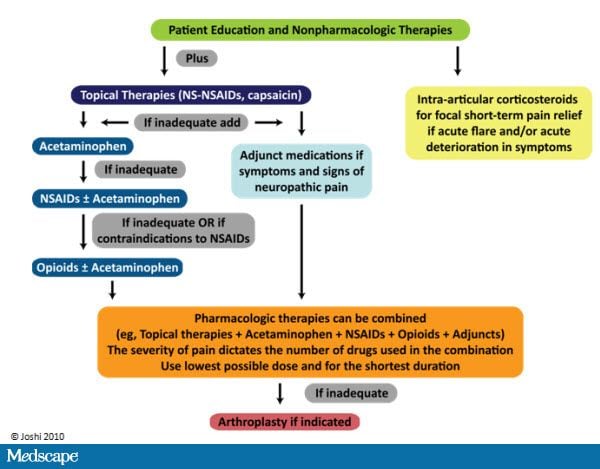
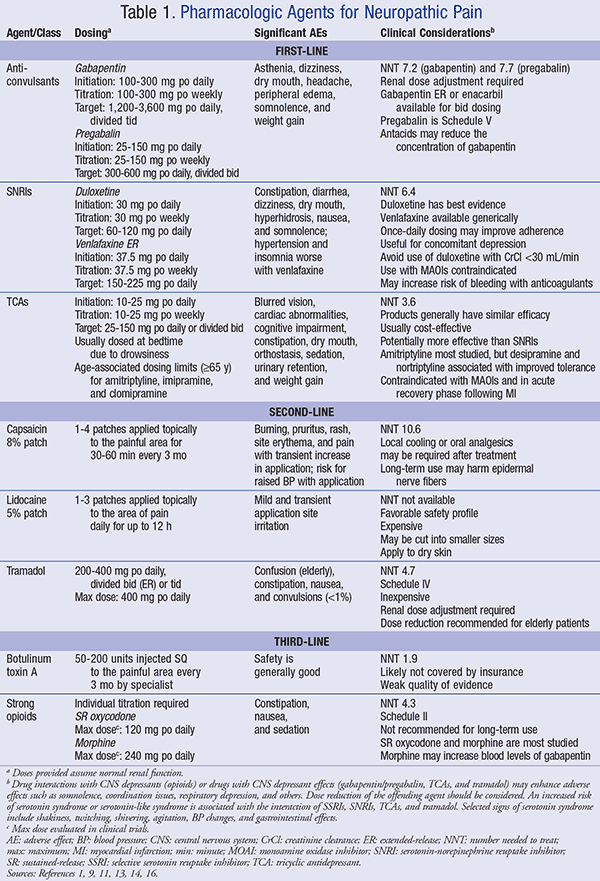
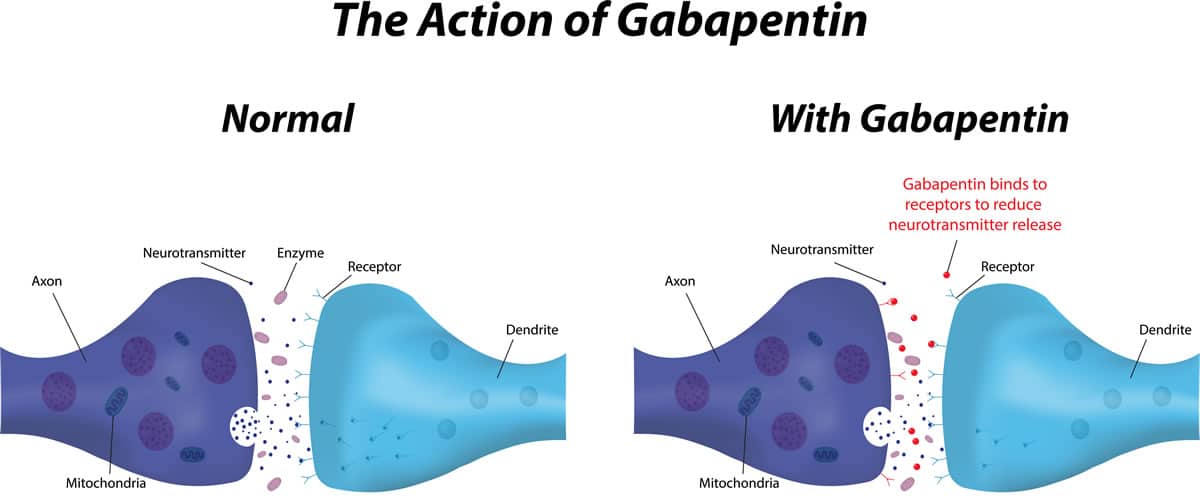
All types of neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) Initial treatment . To begin with, your doctor should offer you treatment with amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin or pregabalin. What if my pain doesn't improve? If your neuropathic pain is still causing you problems or if you are having side effects that Neuropathic pain definition and treatment goals Neuropathic pain is either pain of nerve origin or pain that has not resolved within the normal healing time for a condition (pain which has continued for three months or longer). The goal of neuropathic pain treatment is to support initial symptomatic relief such that patients are Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a]. However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided entinoids is usually 4-8 weeks. If found of little benefit to the patient, the dose should be tapered gradually. For gabapentin doses lower than 900mg a day reduce the to. al daily dose by 100mg every 4 days; for doses above 900m. A person with neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) should be offered a choice of amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, or pregabalin. The dosage should be titrated according to response and tolerability. Analgesic Tapering Guidelines for adult patients with persistent pain patients taking strong opioids and/or gabapentinoids. Prescribing of gabapentinoids for neuropathic pain should be reviewed in line with the criteria set out in NICE4 and should be gradually discontinued if ineffective. For detailed prescribing information on amitriptyline, capsaicin cream, duloxetine, gabapentin, pregabalin, and tramadol, please see the CKS topic on Neuropathic pain - drug treatment. Note that since 1 April 2019, pregabalin and gabapentin are controlled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 as Class C substances and scheduled under the Misuse of Is gabapentin licensed for neuropathic pain?Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a Covers the management of neuropathic pain. The recommendation to manage any treatable causes of neuropathic pain is based on a textbook on symptom relief in palliative care [Regnard, 2022], a textbook of symptom management in advanced cancer [Twycross, 2016], the Palliative Care Formulary [Wilcock, 2020], and a palliative care guideline [NHS Scotland, 2021]. • Botulinum toxin type A for focal neuropathic pain. Treatment only to be initiated in specialist care/pain clinic LIDOCAINE 5% (700mg) PLASTERS (AMBER 2) for treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia or *focal neuropathic pain with allodynia. primary care should involve an individual management plan. The specialist must specify For a person with sciatica, see the CKS topic on Sciatica (lumbar radiculopathy). Offer a choice of amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, or pregabalin. Titrate the dosage according to response and tolerability. Neuropathic pain, which occurs as a result of damage to neural tissue, includes phantom limb pain, compression neuropathies, peripheral neuropathies (e.g. due to Diabetic complications, chronic excessive alcohol intake, HIV infection, chemotherapy, idiopathic neuropathy), trauma, central pain (e.g. pain following stroke, spinal cord injury, and syringomyelia), and postherpetic neuralgia This guideline covers managing neuropathic pain (nerve pain) with pharmacological treatments (drugs) in adults in non-specialist settings. It aims to improve quality of life for people with conditions such as neuralgia, shingles and diabetic neuropathy by reducing pain and promoting increased participation in all aspects of daily living. pain, and neuropathic cancer pain (such as chemotherapy-induced neuropathy, neuropathy secondary to tumour antigens, or caused by direct invasion or compression of neural structures). Examples of conditions that can cause central neuropathic pain include stroke, spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis. Ensure that gabapentin and pregabalin are prescribed at an appropriate place in therapy for neuropathic pain taking into consideration value for money. Ensure prescribed (and taken) doses of pregabalin and gabapentin are not outside the therapeutic dose range. Prescribing of pregabalin capsules should be optimised to the Use of gabapentin for central neuropathic pain is therefore off-label. However, gabapentin is recommended by NICE as a first-line treatment option for adults with all types of neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia). Important aspects of prescribing information relevant to primary healthcare are covered in this section specifically for the drugs recommended in this CKS topic. For further information on contraindications, cautions, drug interactions, and adverse effects, see the electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC), or the British National Formulary (BNF). A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak . Neuropathic pain (NeP) is defined as a pain arising as a direct consequence of a lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system. While nociceptive pain is produced by direct damage to the tissues involved, abnormally stimulated nerves are believed to play a key role in NeP.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |