Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
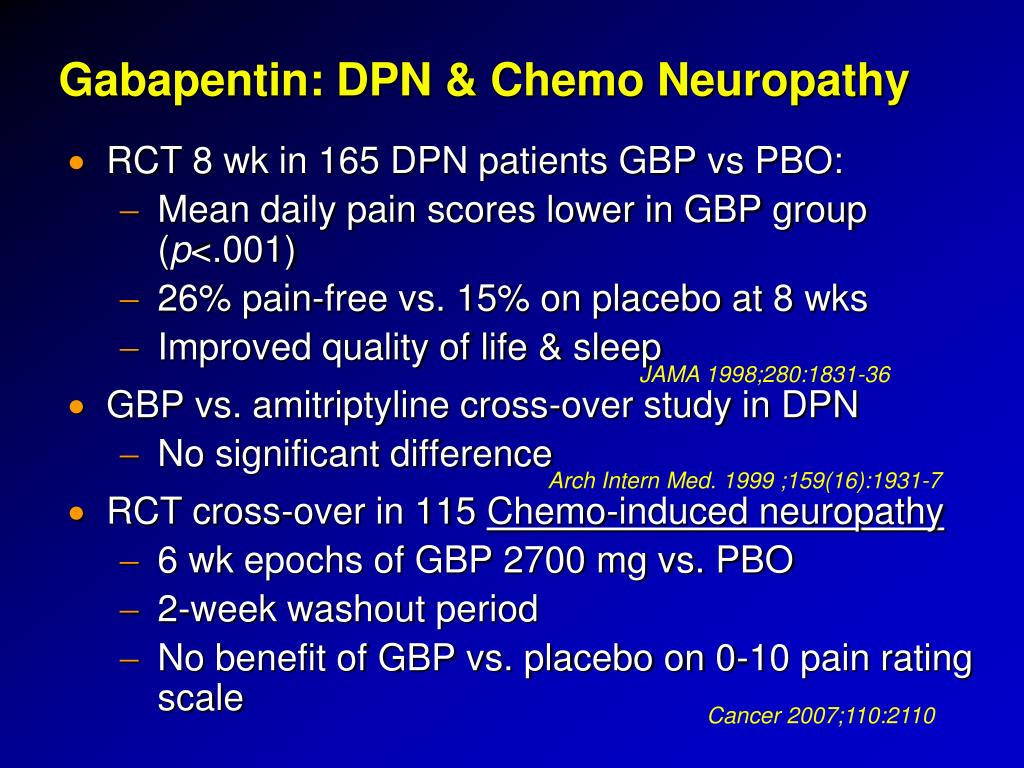 | 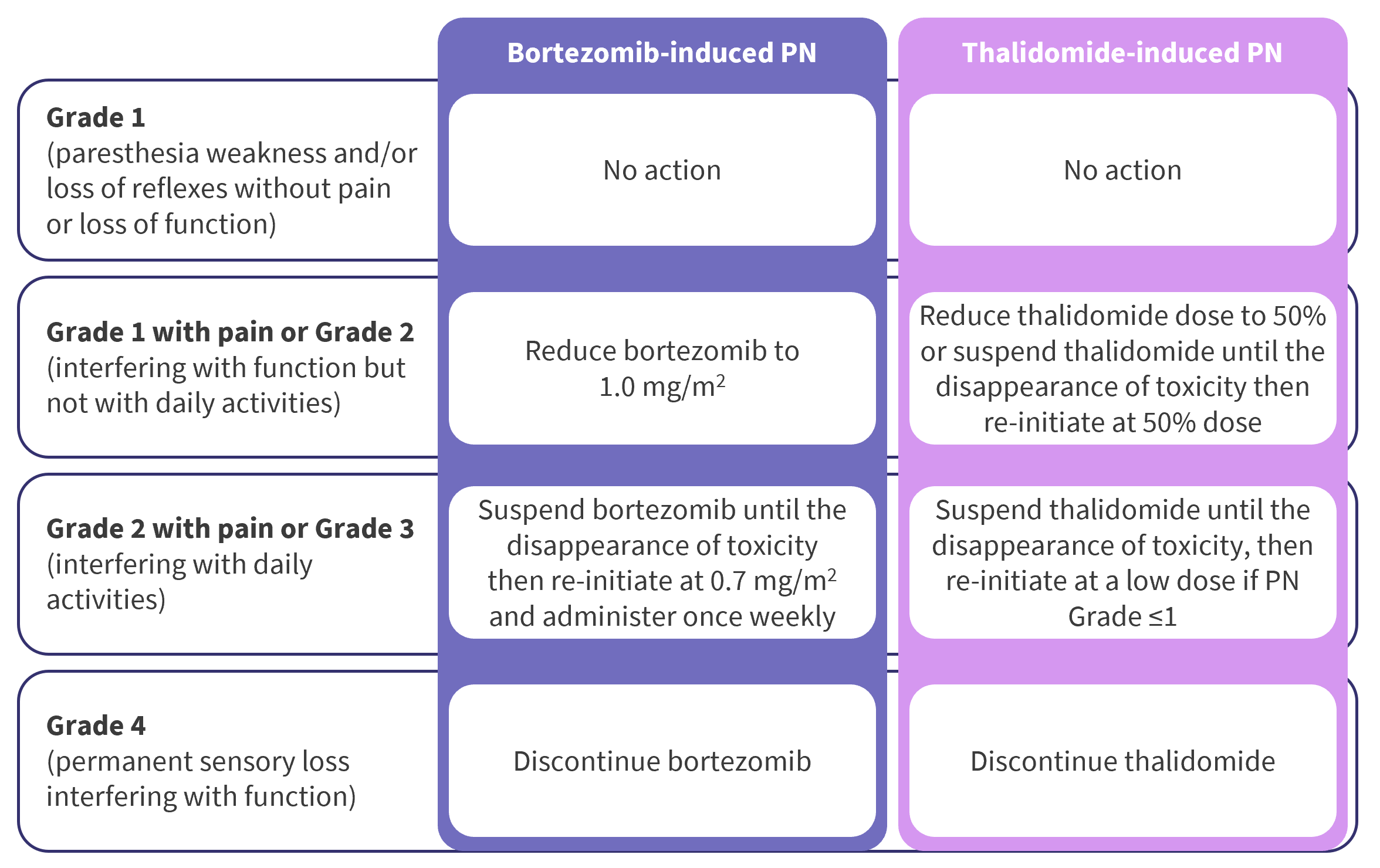 |
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a progressive, enduring, and often irre-versible adverse effect of many antineoplastic agents, among which sensory abnormities are common and the most suffering issues. The pathogenesis of CIPN Rao RD, Michalak JC, Sloan JA, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial (N00C3). Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy is a serious clinical problem caused by a substantial number of cytotoxic drugs, including taxanes, platinums, vinca alkaloids, epothilones, eribulin, and bortezomib; these drugs cause different pathologic insults to neurons. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is one of the most disabling and demoralizing problems that arise for cancer survivors. When investigating symptoms of numbness, tingling, or pain in the extremities, it is critical to determine whether the problem is neuropathic, somatic, or mixed. Gabapentin in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a placebo controlled, double blind, crossover trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry . 1999;66(2):251-252. Moore RA, Wiffen PJ, Derry S, Toelle T, Rice AS. Introduction: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) affects patients' quality of life and treatment effectiveness. Gabapentinoids, like gabapentin and pregabalin, are often used for CIPN treatment, but their efficacy and safety remain uncertain. The combination of “chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy” and each of the following keywords were used to search for CIPN treatment: “calcium and magnesium”, “goshajinkigan”, “duloxetine”, “vitamin B12”, “pregabalin”, “gabapentin”, and “pancreatic cancer”. Treatment. Treatment goals are to manage the condition causing your neuropathy and to improve symptoms. If your lab tests show no condition that's causing the neuropathy, your health care professional might recommend watchful waiting to see if your neuropathy stays the same or gets better. Medicines An overview of neurologic complications with platinum and non-platinum chemotherapy drugs, and recommendations for dose modification for platinum and non-platinum chemotherapeutic drugs when neuropathy develops during therapy are provided elsewhere. On the basis of these data, a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, randomized trial was conducted to evaluate the effect of gabapentin on symptoms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Unfortunately, it can take many months or even longer to find a treatment that works. Doctors have little guidance to know which ones to start with. That’s why research comparing treatment options is so important — and yet, precious little comparative research on treatments for idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy has been published. Paclitaxel and carboplatin treated patients may benefit from gabapentin therapy in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Chemotherapy substantially deteriorates the neurologic condition of the patients and the quality of life. An ongoing phase III study is evaluating the efficacy of oral gabapentin in preventing paclitaxel-induced neuropathy.33 Some experts recommend integrated care approaches, such as acupuncture, exercise and scrambler therapy, for treatment and prevention. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is one of the main dose-limiting side effects of neurotoxic anticancer drugs. The chemotherapy dose needs to be reduced or completely paused when CIPN develops. Peripheral neuropathies in cancer patients are most often due to neurotoxic chemotherapeutic agents, the so-called chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN); less frequently they occur as paraneoplastic, immune-mediated, or neoplastic neuropathies. Compared with the control group, gabapentin therapy led to a statistically significant better response in patients of each baseline neurotoxicity group. Conclusions: Gabapentin monotherapy seems to be well tolerated and useful for the management of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. When peripheral neuropathy occurs due to chemotherapy treatment, it is referred to as chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Typically, symptoms are sensory rather than motor and include reduced feeling and heightened sensitivity to pressure, pain, temperature, and touch. On the basis of these data, a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, randomized trial was conducted to evaluate the effect of gabapentin on symptoms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Compared with the control group, gabapentin therapy led to a statistically significant better response in patients of each baseline neurotoxicity group. Conclusions. Gabapentin monotherapy seems to be well tolerated and useful for the management of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |