Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
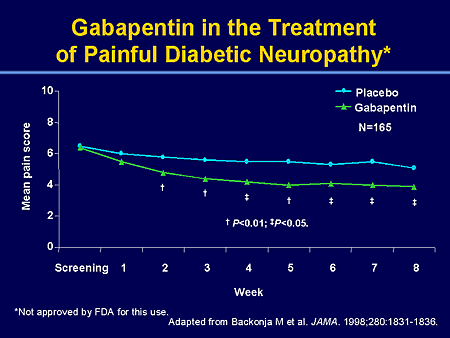
Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. Gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia: discrepancies between direct and indirect meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24:178–88. doi: 10.1007/s11606-008-0877-5. Gabapentin in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a placebo controlled, double blind, crossover trial (letter). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;66(2):251-252. The same review compared gabapentin to an inactive medicine (placebo) in almost 6,000 adults with chronic pain from PHN or diabetic neuropathy. Study participants were given either gabapentin or a placebo for 4 to at least 12 weeks. Diet and exercise in type 2 diabetes — The American Diabetes Association recommends lifestyle interventions, specifically diet and exercise, as the first line in treating diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes . The goal is to achieve and maintain a normal body weight with a nutrient-dense diet low in saturated fats and high in whole grains First-line drug therapy for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy includes duloxetine, gabapentin, amitriptyline, and pregabalin; however, these medications do not restore sensation to affected Background: One of the most common peripheral nerve complications of diabetes is painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). Although tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) have traditionally been used to relieve the pain of this condition, gabapentin's reported efficacy in various neuropathic pain states and its favorable side-effect profile Gabapentin has been shown to be beneficial in treating several types of neuropathic pain; however, the mechanism of action by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic effect is still unknown.¹ It is suggested that gabapentin may block the calcium channel alpha (2)delta (a2d)-1 receptor in the brain. Anecdotal reports suggest that gabapentin ameliorates pain associated with neuropathy and other neurological conditions with few side effects.2 3 We conducted a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial to study the effect of low dose gabapentin in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. The authors conclude that gabapentin provides safe, effective pain relief in patients with diabetic neuropathy. The effects of gabapentin are similar to those found with tricyclic Pregabalin (Lyrica), gabapentin (Neurontin), amitriptyline (except in older adults), or duloxetine (Cymbalta) should be used as first-line treatment for painful diabetic peripheral Gabapentin at a dose of 1800 to 3600 mg daily (1200 to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. This summary uses a Cochrane review, updated in 2014, to address the efficacy of gabapentin compared with placebo to palliate neuropathic pain. 3 The Cochrane review includes 37 trials enrolling Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other neuropathic pain syndromes. It relieved symptoms of allodynia, burning pain, shooting pain, and hyperesthesia. Adverse effects were typically mild to moderate and usually subsided within approximately 10 days from the initiation of treatment. Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most prevalent chronic complications in adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes while also affecting individuals with prediabetes and young people with diabetes, with an estimated lifetime prevalence exceeding 50% (1 – 4). Pregabalin and duloxetine are the only medications approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating this disorder. Based on current practice guidelines, these medica-tions, with Painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) is a common complication of diabetes mellitus that is associated with a significant decline in quality of life. Like other painful neuropathic conditions, PDN is difficult to manage clinically, and a variety of Some medications used to treat seizure disorders (epilepsy) are also used to ease nerve pain. The ADA recommends starting with pregabalin (Lyrica). Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) also is an option. Side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, and swelling in the hands and feet. Antidepressants. Gabapentin is a new oral antiepileptic agent that has been used in the treatment of neuropathic pain .We conducted a double-blind, controlled trial that compared gabapentin with placebo in the treatment of 32 diabetic patients referred for the management of neuropathic pain (visual pain score >60 on a 100-point scale) after conventional treatment failed. Context.— Pain is the most disturbing symptom of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. As many as 45% of patients with diabetes mellitus develop peripheral neuropathies.Objective.— To evaluate the effect of gabapentin monotherapy on pain associated with diabetic peripheral
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |