Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
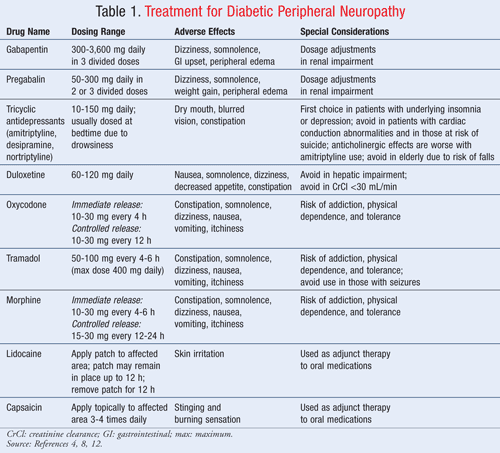 |  |
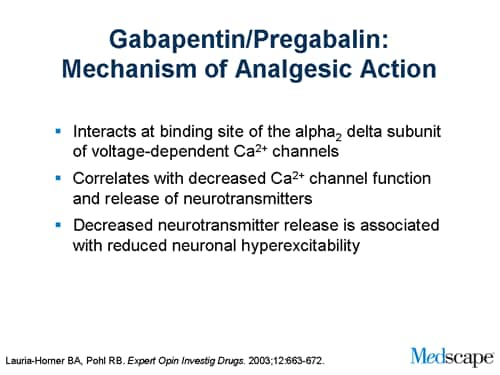
This summary uses a Cochrane review, updated in 2014, to address the efficacy of gabapentin compared with placebo to palliate neuropathic pain. 3 The Cochrane review includes 37 trials enrolling Common Trade Names: Neurontin, Gralise; Adult Dosing Partial Seizures. Adjunctive therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Initial: 300mg PO q8hr; May increase up to 600mg PO q8hr; Post herpetic neuralgia. Day 1: 300mg PO qDay; Day 2: 300mg PO q12hr; Day 3: 300mg PO q8hr; Muscle Cramps (Off-label) Several mechanisms of gabapentin have been proposed after neuropathy including an inhibition of NMDA receptors, inhibition of sodium currents and reducing β4a subunit mediated VGCC trafficking (Hara and Sata 2007; Mich and Horne 2008; Yang et al. 2009). Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Gabapentin binds preferentially to neurons in the outer layer of the rat cortex at sites that are distinct from other anticonvulsants Gabapentin has been clearly demonstrated to be effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain in diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. This evidence, combined with its favourable side-effect profile in various patient groups (including the elderly) and lack of drug interactions, makes it an attractive agent. Gabapentin's mechanism in RLS is unclear, but it is known to bind strongly to α2δ-subunits of voltage-activated calcium channels. This binding likely inhibits calcium entry, normalizing neurotransmitter release, including excitatory glutamate; however, the precise mechanism remains unknown. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy , postherpetic neuralgia , and central pain . [ 11 ] Data from meta-analyses support the use of IR gabapentin for reducing pain by more than 50% in diabetic neuropathy Moore 2014, Rudroju 2013. Data from a limited number of clinical trials support the use of ER gabapentin in reducing pain by more than 50% and improving sleep in diabetic neuropathy Sandercock 2009, Sandercock 2012. Gabapentin at a dose of 1800 to 3600 mg daily (1200 to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin has been shown to be beneficial in treating several types of neuropathic pain; however, the mechanism of action by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic effect is still unknown.¹ It is suggested that gabapentin may block the calcium channel alpha(2)delta (a2d)-1 receptor in the brain. This protein-modulated receptor is involved in Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific bindin Gabapentin (GBP) is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy “Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. Gabapentin has become popular as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain because of its efficacy as an antineuropathic agent and relatively benign side-effect profile. However, its mechanism of action is far from clear. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: Mechanism of action of gabapentinoids Site of action The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake.21 They were originallydesigned as g aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogues but do not have any effects on GABA receptors. Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that has been used for a number of off-label indications, including neuropathic pain. It is thought to act by binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, or by blocking new synapse formation. Neuropathic pain tends to be chronic, is complex, and can be difficult to treat effectively.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |