Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
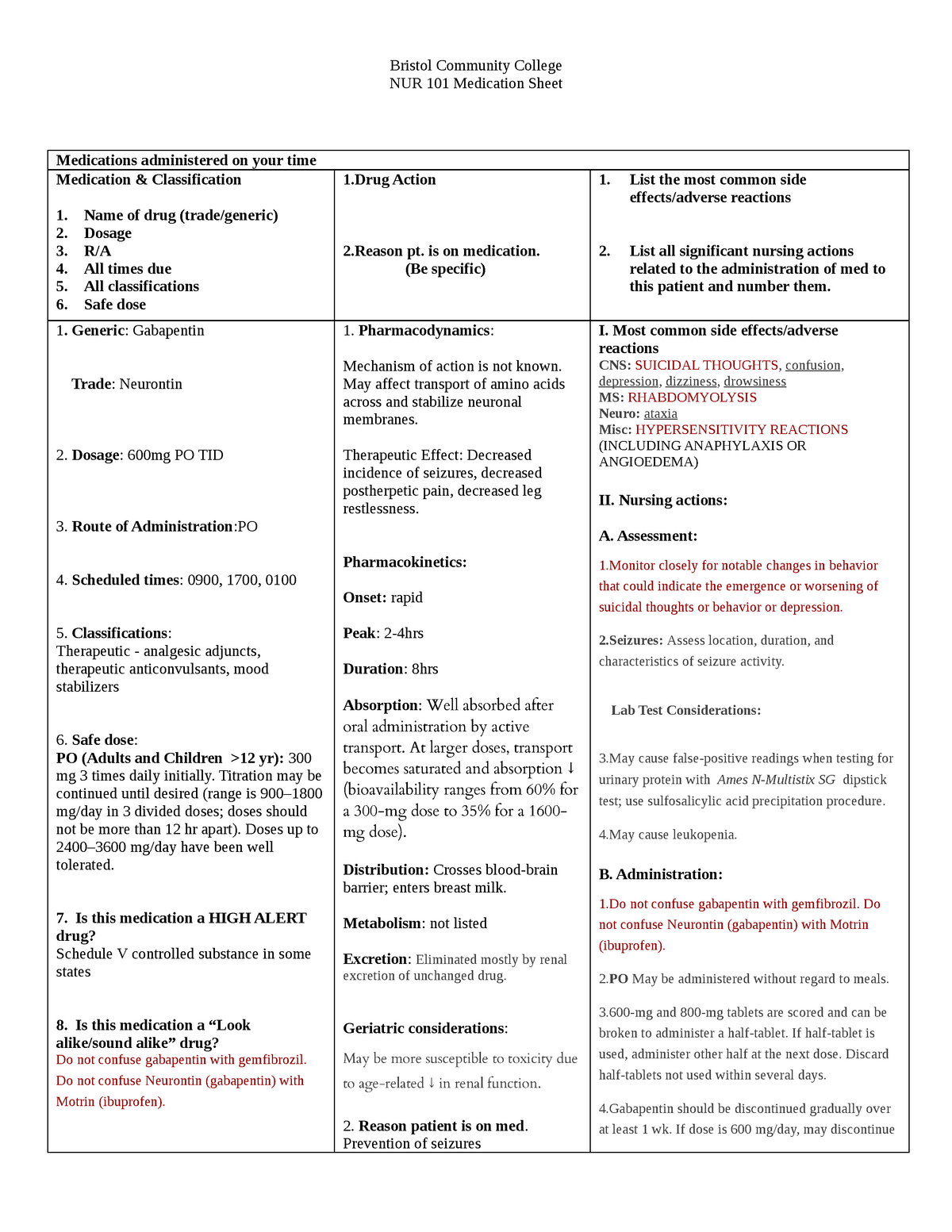
Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Seizure patients should not resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. Gabapentin Teaching 1979. SN instructed patient about Gabapentin ( Neurontin ). It is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain and hot flashes. It is also used for restless leg syndrome. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Brand Names: US Gabarone; Gralise; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada AG-Gabapentin; APO-Gabapentin; Auro-Gabapentin; BIO-Gabapentin [DSC]; Teaching points. Take this drug exactly as prescribed; do not discontinue abruptly or change dosage, except on the advice of your health care provider. Wear a medical alert ID at all times so that any emergency medical personnel will know that you have epilepsy and are taking antiepileptic medication. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Nurse Teachings on Side Effects of Gabapentin Patient/caregiver was educated on side effects of gabapentin as follows: General allergic reactions: Gabapentin use can result in general allergic reactions, such as, skin rashes, hives, and itching. Gabapentin Nursing Considerations & Patient Teachings Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. Assess the patientʼs medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Gabapentin is used to relieve pain from the nerves, from the spinal cord, or from the brain. Nerve pain may be associated with shingles (herpes zoster), diabetic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, sciatica, trigeminal neuralgia and other conditions. It is usually taken by mouth three times daily. Side effects can include dizziness and confusion. Gabapentin can be taken with a tricyclic antidepressant or duloxetine. In some cases, gabapentin can be taken at night to prevent pain during sleep. Pregabalin — Pregabalin is an anti-seizure medication, similar to gabapentin. Pregabalin is taken A nurse is teaching a client who has postherpetic neuralgia and a new prescription for gabapentin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? You should not take this medication within 2 hours of taking an antacid **Antacids can decrease the absorption pattern of the medication and decrease the levels of Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Generic name: Gabapentin. Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, Gabarone. Pharmacologic class: Anticonvulsant, Antiepileptic. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant, Analgesic for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Disclaimer: The content of this site including, but not limited to teachings, corrections and comments are not intended to teach a person how to perform duties of a health professional. If you want to report an issue with the site, complain about an ad, or contact the site admin, use the contact form in the right menu. 8-) gabapentin. 2. Relate general characteristics of gabapentin to specific patient situations. 3. Apply nursing process considerations for gabapentin to specific patient situations. 4. Correctly calculate dosage for gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid that serves as a neurotransmitter in the normal central nervous system. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Patient Education and Teaching. 1. Explain the purpose of gabapentin, such as managing seizures, nerve pain, or other conditions. Understanding why they are taking the medication helps patients recognize the potential benefits and motivates adherence to the prescribed treatment plan. 2. Hypertension Teaching 2004. SN instructed patient and caregiver on hypertensive urgency which is a situation where the blood pressure is severely elevated and that experiencing hypertensive urgency may or may not experience one or more of these symptoms: severe headache, shortness of breath, nosebleeds, and severe anxiety, chest or back pain, numbness or severe weakness, change in vision or
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |