Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
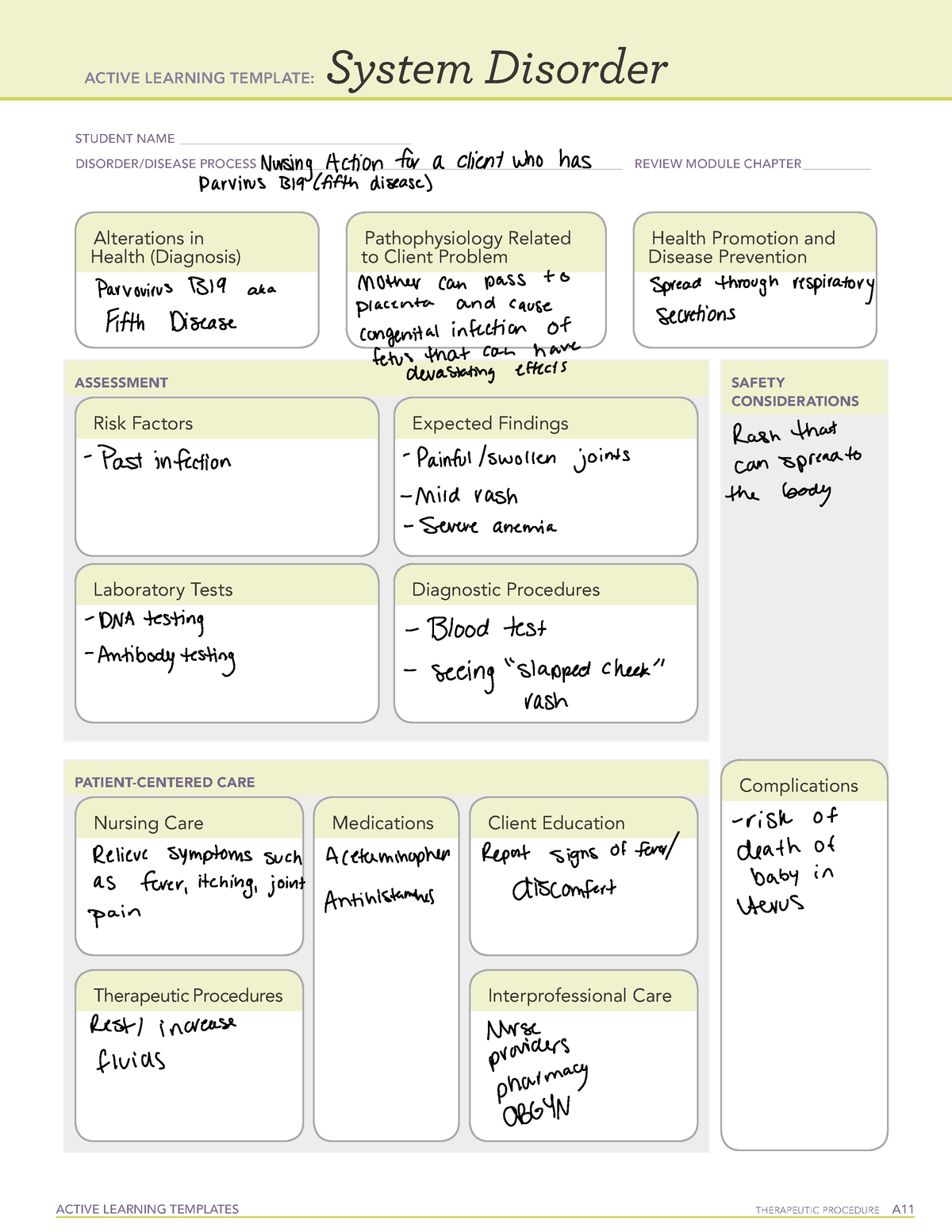
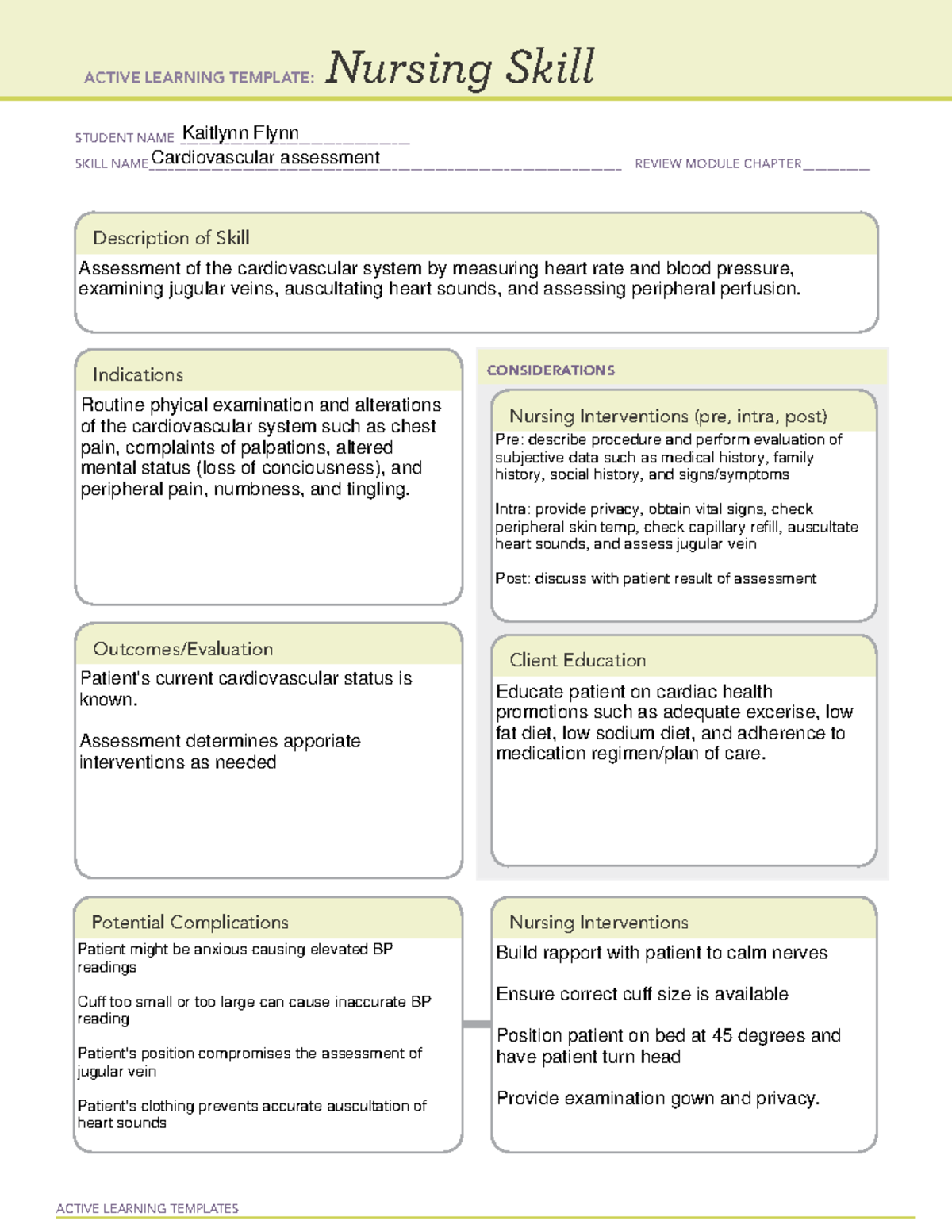
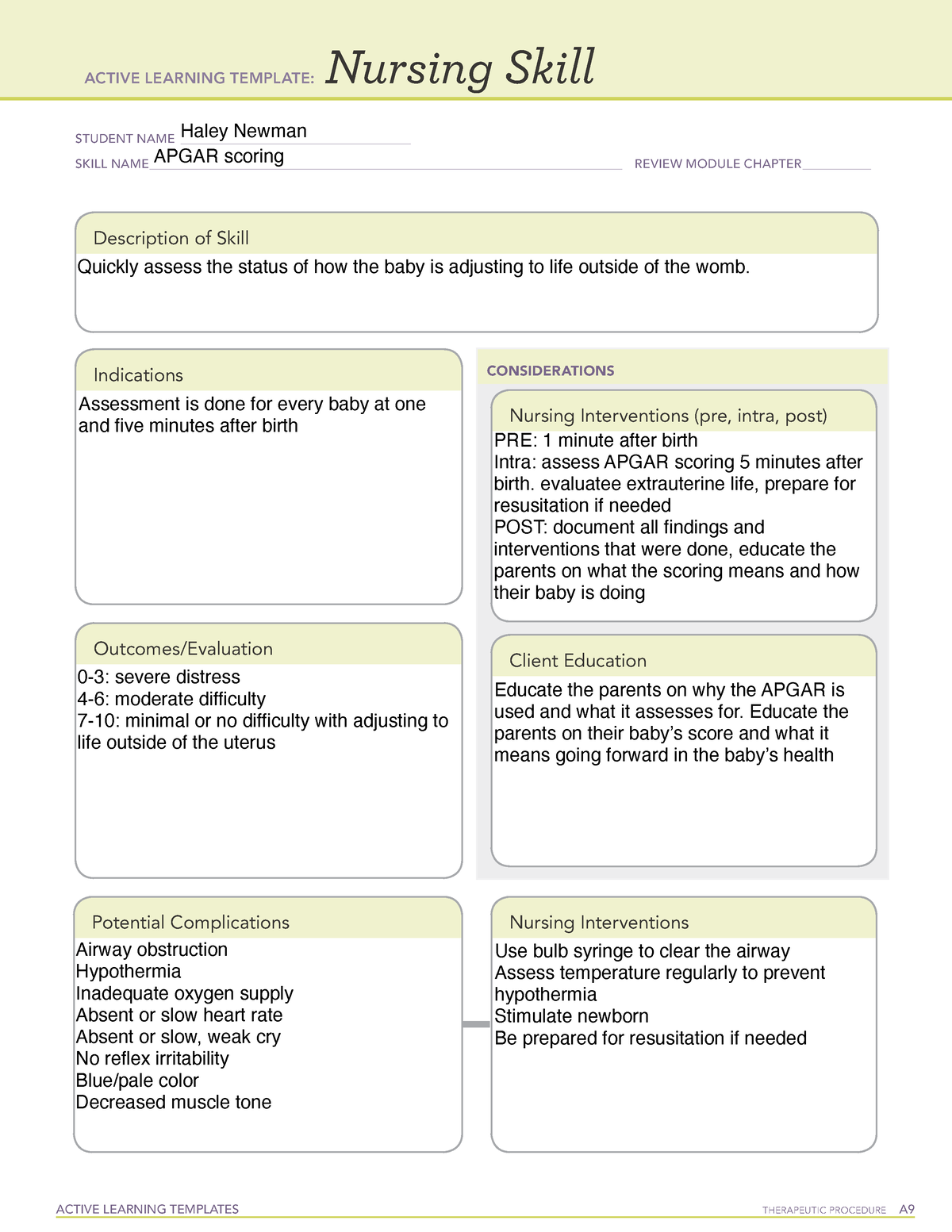
Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. So the therapeutic class of Gabapentin is an analgesic adjunct, also an anti-convulsant and a mood stabilizer and Gabapentin. The pharmacologic class act. There is none. So the action of Gabapentin is actually not known or understood. It is thought that Gabapentin may play a role in neural membranes. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is one of the top 100 drugs prescribed in the US, so there’s a very good chance it will show up on NCLEX or your nursing school exams. Let’s go through the key things you need to know about this medication using the Straight A Nursing DRRUGS framework. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA but is neither a GABA agonist nor antagonist. Gabapentin-binding sites have been identified throughout the brain tissues e.g. neocortex and hippocampus. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. Mechanism of action: Gabapentin helps to stabilize cell membranes by changing cation (sodium, calcium, and potassium) transport, reducing excitability, and suppressing seizure focus or discharge. Indications for use: Adjunctive treatment for seizure control, postherpetic neuralgia, moderate to severe primary restless legs syndrome. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Generic Name: Gabapentin. Brand Names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant. What are the indications of gabapentin (Neurontin)? gabapentin Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior The gabapentin receptor α2δ-1 is a neuronal thrombospondin receptor responsible for excitatory CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 2009; 139: 380–392. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 33. Bannister K, Qu C, Navratilova E, et al. Multiple sites and actions of gabapentin-induced relief of ongoing experimental neuropathic pain. Gabapentin in the management of restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been evaluated in small controlled trials, demonstrating benefits compared with placebo. Gabapentin enacarbil is FDA-approved for the treatment of RLS Garcia-Borreguero 2002, Saletu 2010. The . Social anxiety disorder, adjunct to antidepressants or monotherapy (alternative agent)c Acion: Exact method of action unknown, may play a role in stabilizing neural membranes Indicaion: Seizures Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Seizure patients should not resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Grab our free cheatsheet covering the 50 most commonly prescribed medications right here: to all the episodes at: Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity Mechanism of action: Gabapentin’s exact mechanism remains unclear. It is structurally similar to GABA but does not bind to GABA receptors. It is believed to bind to voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |