Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
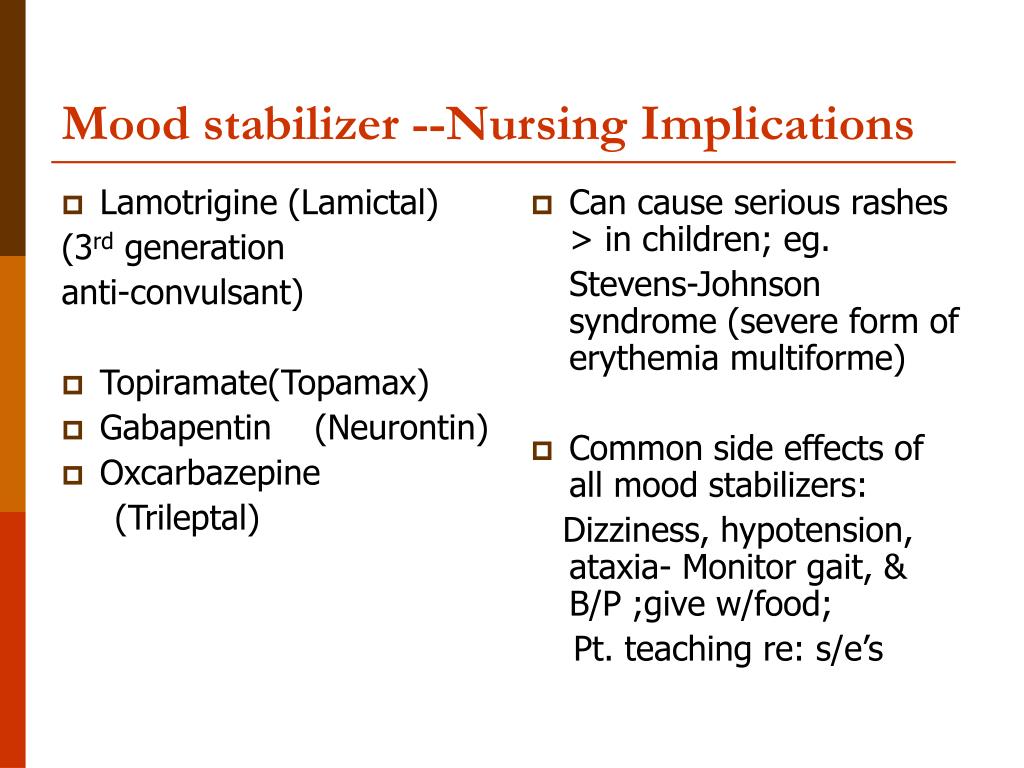
Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Seizure patients should not resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents Gabapentin is one of the top 100 drugs prescribed in the US, so there’s a very good chance it will show up on NCLEX or your nursing school exams. Let’s go through the key things you need to know about this medication using the Straight A Nursing DRRUGS framework. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Generic Name: Gabapentin. Brand Names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Nursing Implications Monitor of therapeutic effectiveness; may not occur until several weeks following initiation of therapy, in those treated for seizure disorders , assess frequency of seizures: In rare cases, the drug has increased the frequency of partial seizures, Monitor dizziness and CNS depression, monitor for changes in behavior that If you are 65 or older, use this drug with care. You could have more side effects. If the patient is 3 to 12 years of age, use this drug with care. What is the generic name? GABAPENTIN. What is the Trade Name for GABAPENTIN? Neurontin. What are the Indications for GABAPENTIN? 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE NEURONTIN ¬Æ is indicated for: Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. MoA: Increases release of GABA into the synapse. Indications: Seizures. Side Effects: Fatigue, Xerostomia, Dizziness. Drug Interactions: Antacids. Nursing Implications: Monitor for possible suicidal ideation. Educate Patient on reporting changes in vision, hallucinations, and fever to their healthcare provider. Gabapentin is used for partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Nursing Considerations Across the Lifespan. This drug can cause harm to the fetus of pregnant women. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients with epilepsy 3 to 12 years of age is associated with the occurrence of central nervous system related adverse events. The most common side effects include headache, dizziness, and dysmenorrhea. On rare occasions, lamotrigine can also cause more severe side effects, such as suicidal thoughts, and hematologic side effects, including disseminated intravascular coagulation, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia. Learn about gabapentin, an anticonvulsant used for seizures and neuropathic pain, and its nursing implications. Find out the indications, precautions, adverse effects, dosages, and patient teachings for gabapentin. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA but is neither a GABA agonist nor antagonist. Gabapentin-binding sites have been identified throughout the brain tissues e.g. neocortex and hippocampus. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. Learn about gabapentin, a GABA analogue used for postherpetic neuralgia and seizures, and its nursing implications. Find out indications, pharmacokinetics, adverse effects, interactions, and nursing process for gabapentin. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Generic name: Gabapentin. Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, Gabarone. Pharmacologic class: Anticonvulsant, Antiepileptic. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant, Analgesic for neuropathic pain. The Eleventh Edition of Lehne’s Pharmacology for Nursing Care provides a thorough understanding of key drugs and their implications for nursing care. This text, written by renowned nursing educators, helps you comprehend and apply pharmacology principles.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |