Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
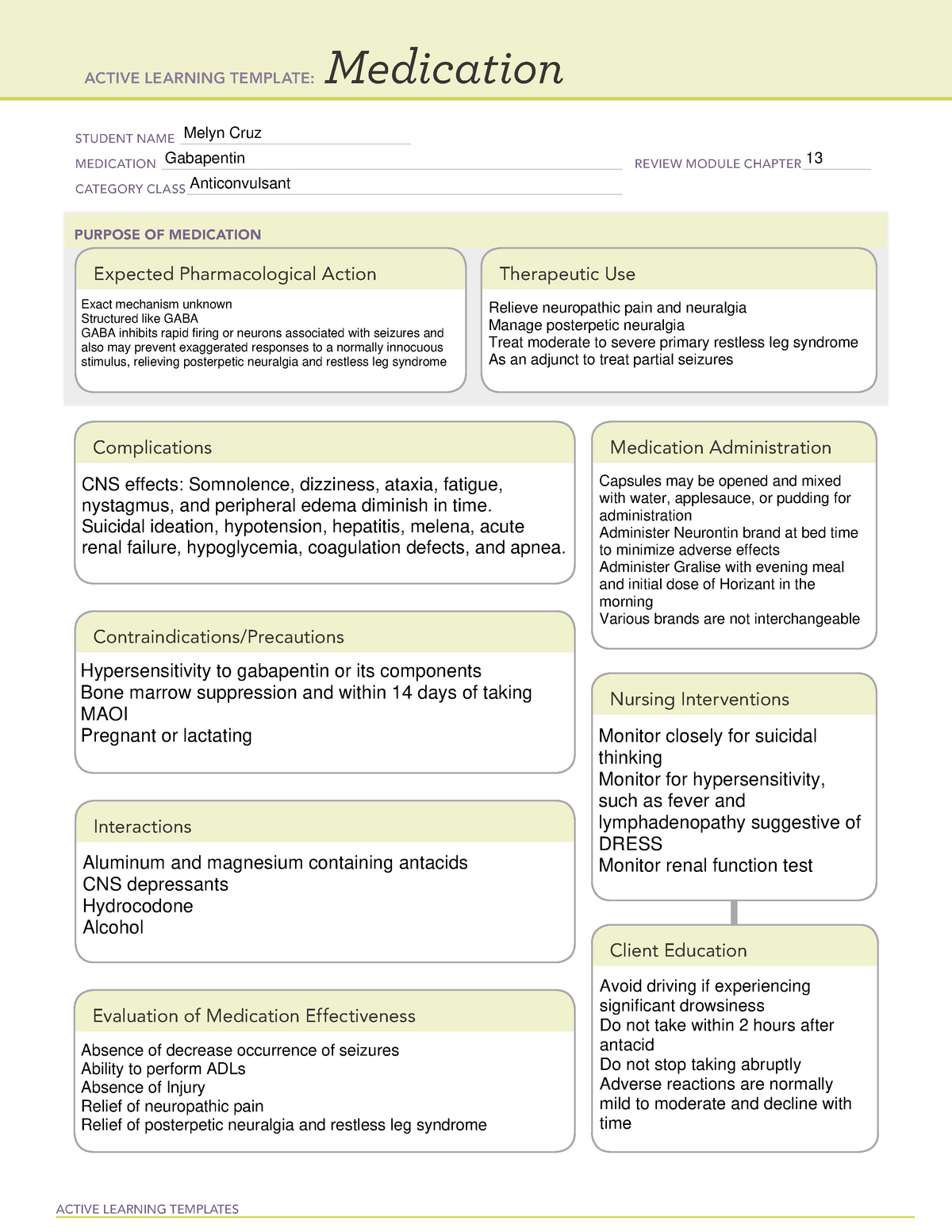
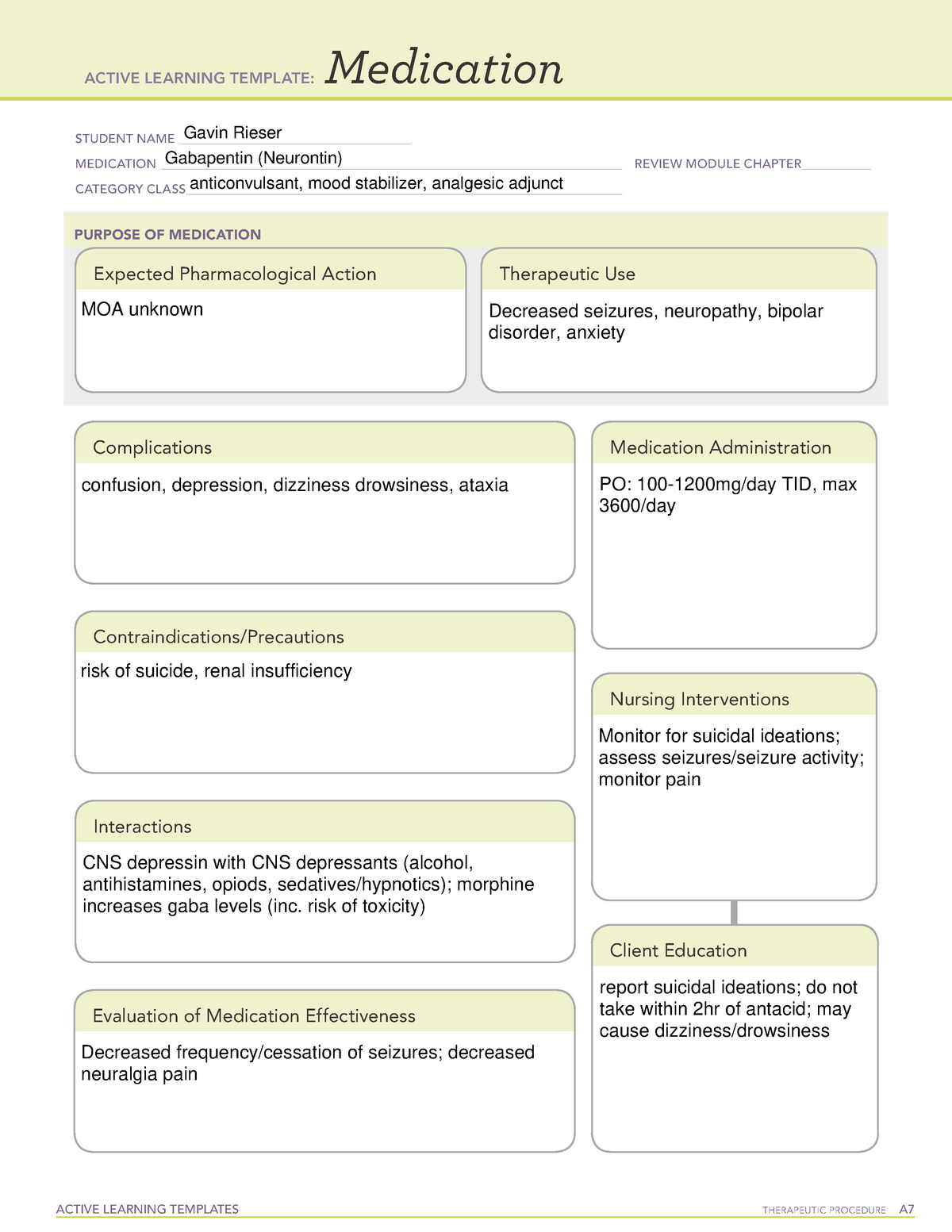
Gabapentin Nursing Interventions. Administer gabapentin according to the prescribed dosage and schedule. This ensures that the patient receives the appropriate dose of medication at the right time, promoting therapeutic effects. gabapentin Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Generic Name: Gabapentin. Brand Names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant. What are the indications of gabapentin (Neurontin)? Nursing Interventions. Implement fall precautions due to drowsiness and dizziness. Monitor for and document effectiveness in pain relief or seizure control. Assess for and document side effects. Monitor for signs of abuse or dependence. Provide emotional support and frequent monitoring for patients at risk for suicidal ideation. Ensure proper Nursing interventions Monitor closely for notable changes in behavior that could indicate the emergence or worsening of suicidal thoughts or behavior or depression. Assess location, duration, and characteristics of seizure activity. Gabapentin is used for partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Nursing Considerations Across the Lifespan. This drug can cause harm to the fetus of pregnant women. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients with epilepsy 3 to 12 years of age is associated with the occurrence of central nervous system related adverse events. Chronic Pain (Pain Management) Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan. Learn about the nursing care plan and management for chronic pain, including assessment, nursing diagnosis, and intervention strategies. Discover how nursing care can improve the quality of life for patients with chronic pain and promote better pain management outcomes. Gabapentin Nursing Interventions. 1. Administer gabapentin according to the prescribed dosage and schedule. This ensures that the patient receives the appropriate dose of medication at the right time, promoting therapeutic effects. 2. Interventions. Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. WARNING: If overdose occurs, hemodialysis may be an option. Teaching points. Take this drug exactly as prescribed; do not discontinue abruptly or change dosage, except on the advice of your health care provider. Learn about gabapentin, an anticonvulsant used for seizures and neuropathic pain, and its nursing implications. Find out how to assess, administer, monitor, and teach patients on gabapentin. Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents Drugs used to treat generalized seizures include hydantoins, barbiturates, barbiturate-like drugs, benzodiazepines, and succinimides. Succinimides and drugs that modulate the inhibitory GABA are used to treat absence seizures. The desired and beneficial actions of hydantoins are as follows: However, gabapentin is often used off-label for a variety of conditions. In fact, one study revealed that 83% of gabapentin prescriptions were for off-label use. Some of the common reasons gabapentin is prescribed are: Neuropathic pain and diabetic neuropathy (this is very common) Bipolar disorder and anxiety; Migraine prevention On Studocu you find all the lecture notes, summaries and study guides you need to pass your exams with better grades. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to gabapentin (ga-ba- pen -tin) Neurontin. Therapeutic: analgesic adjuncts, therapeutic, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers. Partial seizures (adjunct treatment). Postherpetic neuralgia. Unlabeled Use: Chronic pain. Prevention of migraine headache. Bipolar disorder. Anxiety. Mechanism of action is not known. Learn about gabapentin, a GABA analogue used for postherpetic neuralgia and seizures, and its nursing process considerations. Find out how to calculate dosage, monitor adverse effects, and avoid interactions with opioids. Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |