Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
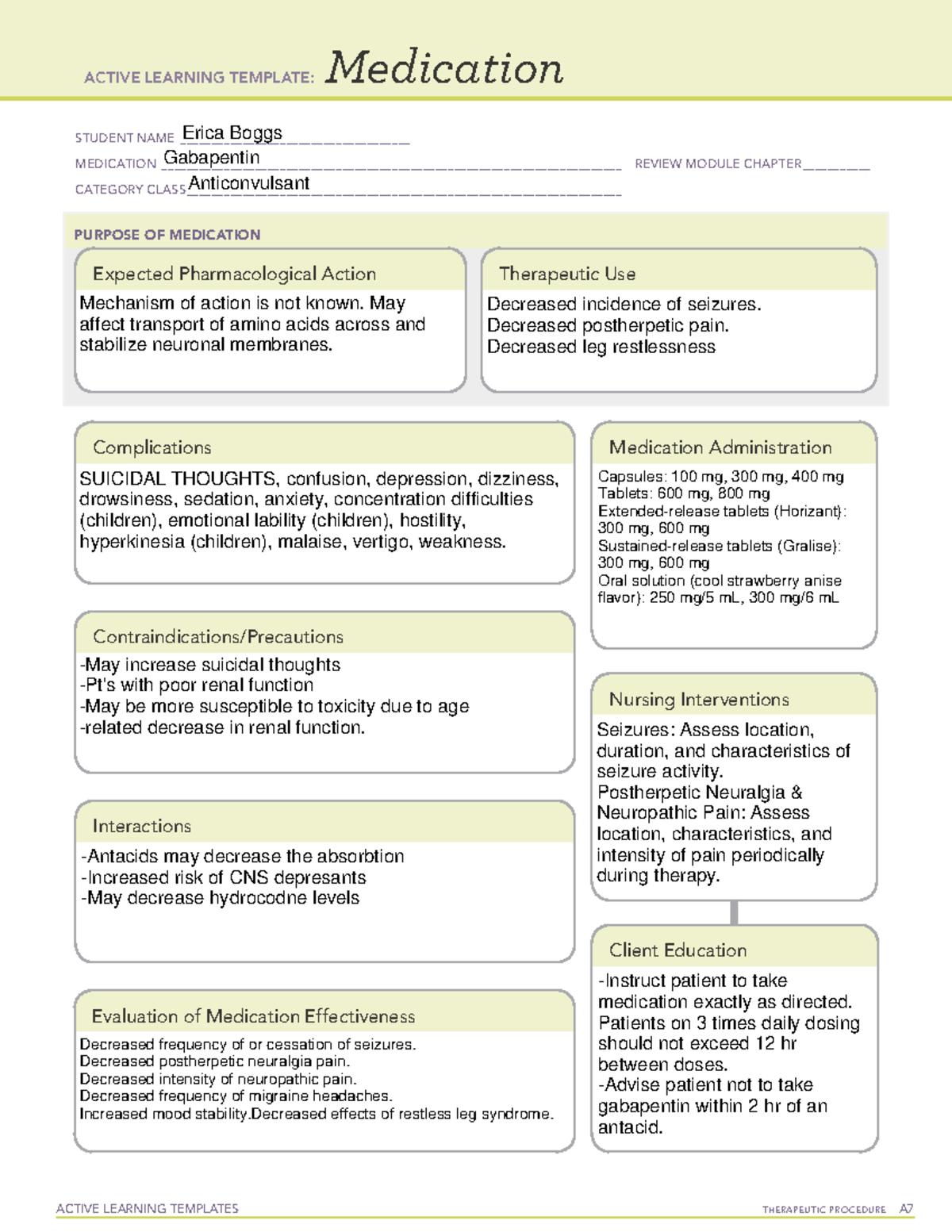
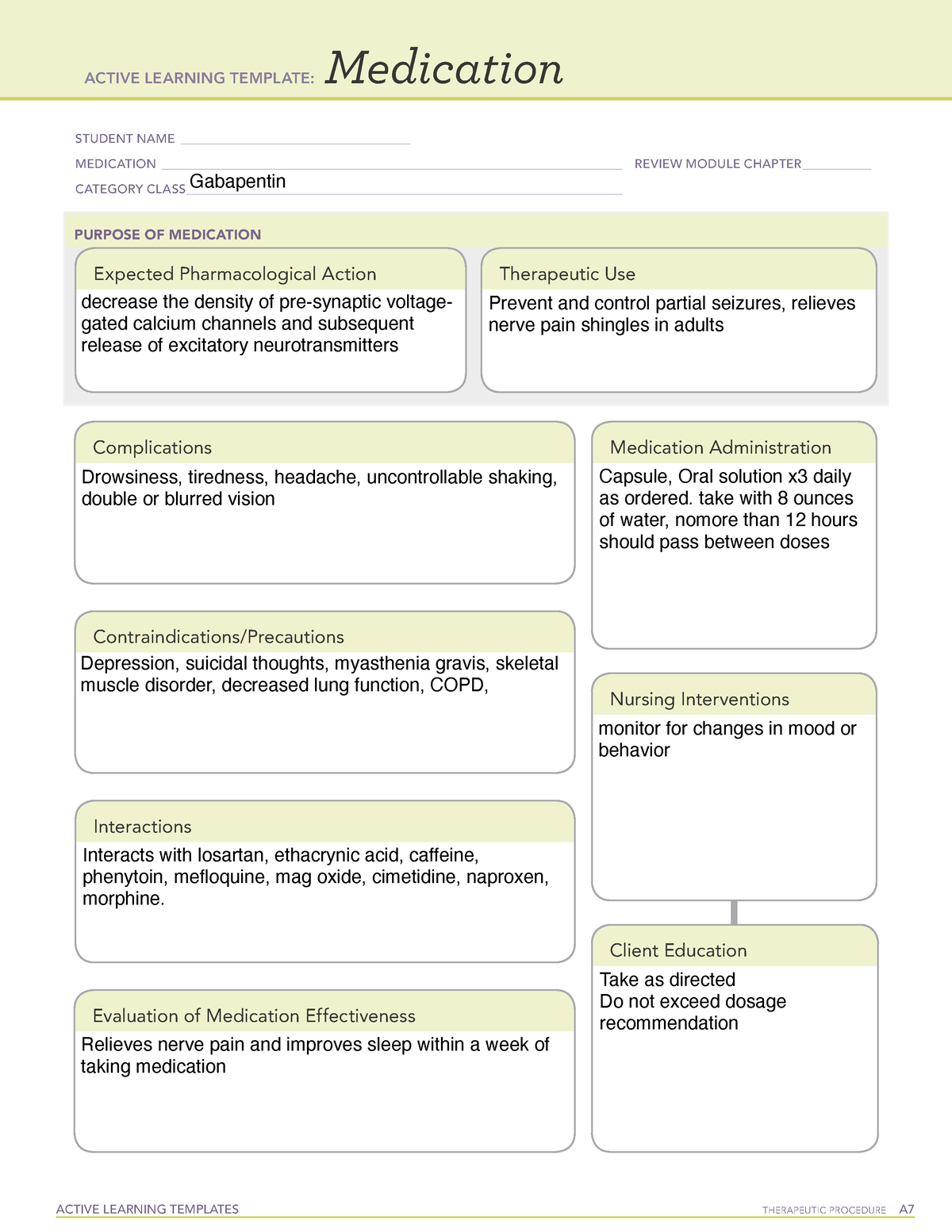
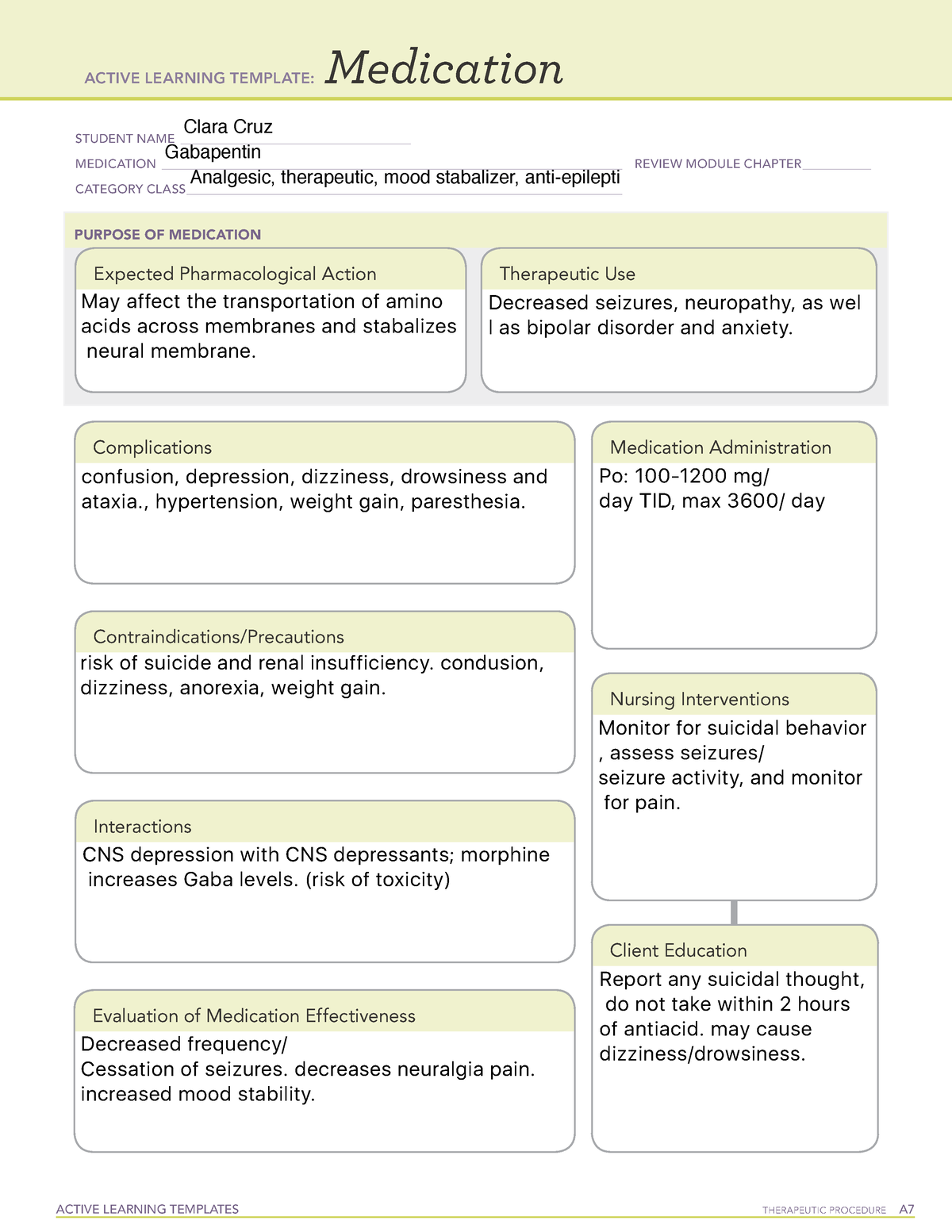
Gabapentin administration requires meticulous nursing care. Nurses ensure proper medication administration, closely monitor side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and assess for drug interactions. Patient education is crucial to promote adherence and minimize adverse effects. Gabapentin is a valuable medication in the management of neuropathic pain and epilepsy. Nurses play a critical role in administering the drug, monitoring for side effects, educating patients, and ensuring proper follow-up. Identify appropriate indications for use of gabapentin. Relate general characteristics of gabapentin to specific patient situations. Apply nursing process considerations for gabapentin to specific patient situations. Correctly calculate dosage for gabapentin. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Point of Care - Clinical decision support for Gabapentin. Treatment and management. Indications, Mechanism of Action, Administration, Adverse Effects, Contraindications, Monitoring, Toxicity, Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Editor's Note: This VA/DoD guideline on management of headaches is impressive in that it covers many headache types and has a comprehensive evidence review. The recommendation to use amitriptyline In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Generic Name: Gabapentin. Brand Names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant. What are the indications of gabapentin (Neurontin)? Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. gabapentin Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) advocate for a multidisciplinary team approach to improve the care of patients with acute and chronic TN. Evidence-based discussions and decisions are encouraged to establish care pathways for prompt diagnosis and treatment, and long-term outcomes data collection to improve care. The guidelines include Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Created Date: 3/23/2022 10:18:38 PM Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder.Antiseizure agents of choice depend on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Multiple studies and reviews have examined the efficacy and safety of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal. 22, 56 – 58 A retrospective cohort study of 100 patients who presented to an ED found that those who received high-dose gabapentin (1800 mg/day) during the first two days of hospital admission required a significantly lower total dose of Gabapentin and pregabalin are ligands of the Findlay T, Moga C, Scott NA, Harstall C, Taenzer P. Guideline for primary care management of headache in adults. Can Fam Physician 2015;61:670-679 Gabapentin is structurally related to the neurotransmitter GABA but is neither a GABA agonist nor antagonist. Gabapentin-binding sites have been identified throughout the brain tissues e.g. neocortex and hippocampus. However, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. Learn about the nursing care plan and management for chronic pain, including assessment, nursing diagnosis, and intervention strategies. Discover how nursing care can improve the quality of life for patients with chronic pain and promote better pain management outcomes. Patients were given gabapentin (n = 52) or placebo (n = 49) and a multimodal anesthesia plan that included oral acetaminophen 1,000 mg and ketorolac 15 mg, neuraxial anesthesia with combined hyperbaric bupivacaine and fentanyl, and no other opioids or local infiltrations, and Patient-care analgesia (PCA) morphine postoperatively. Mechanism of action: Gabapentin helps to stabilize cell membranes by changing cation (sodium, calcium, and potassium) transport, reducing excitability, and suppressing seizure focus or discharge. Indications for use: Adjunctive treatment for seizure control, postherpetic neuralgia, moderate to severe primary restless legs syndrome.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |