Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
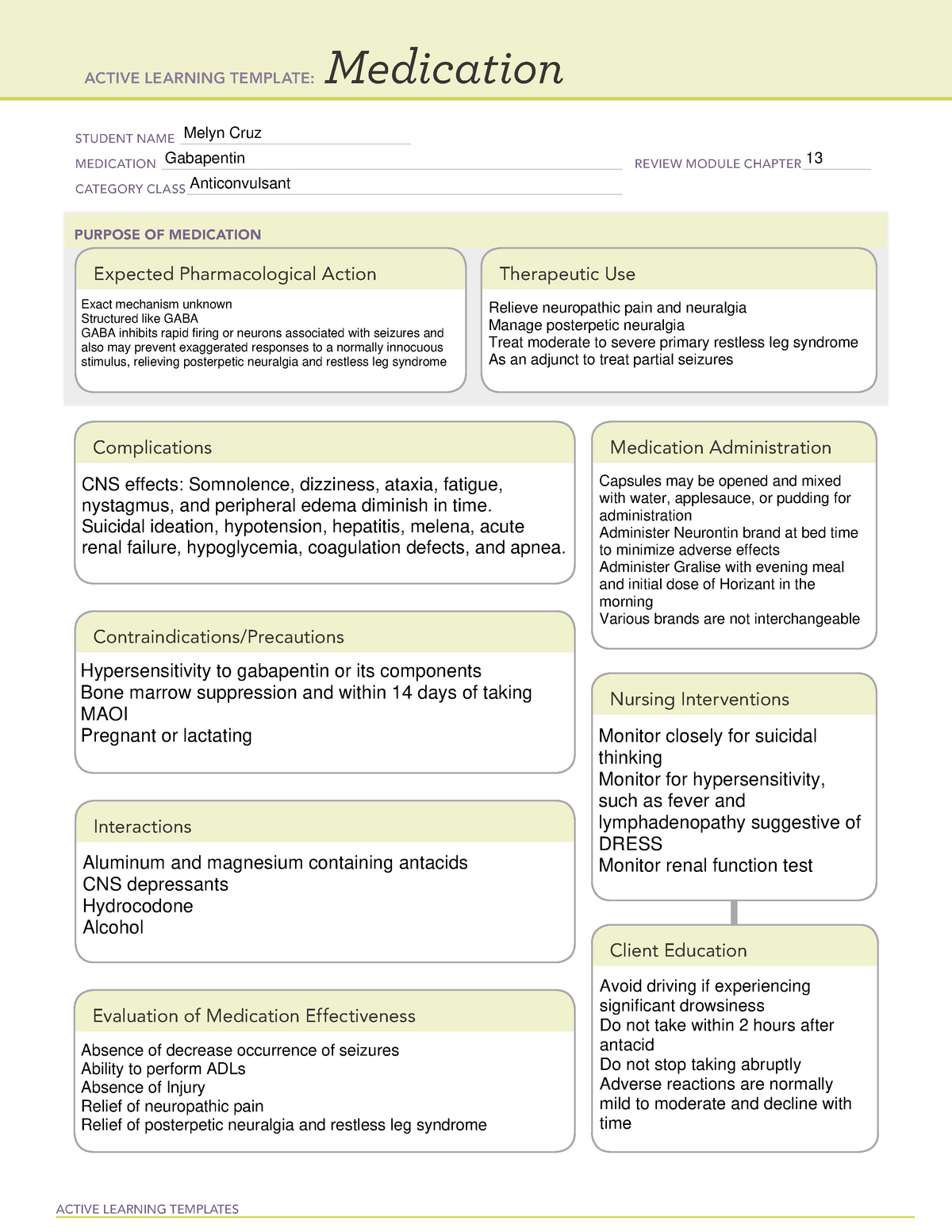
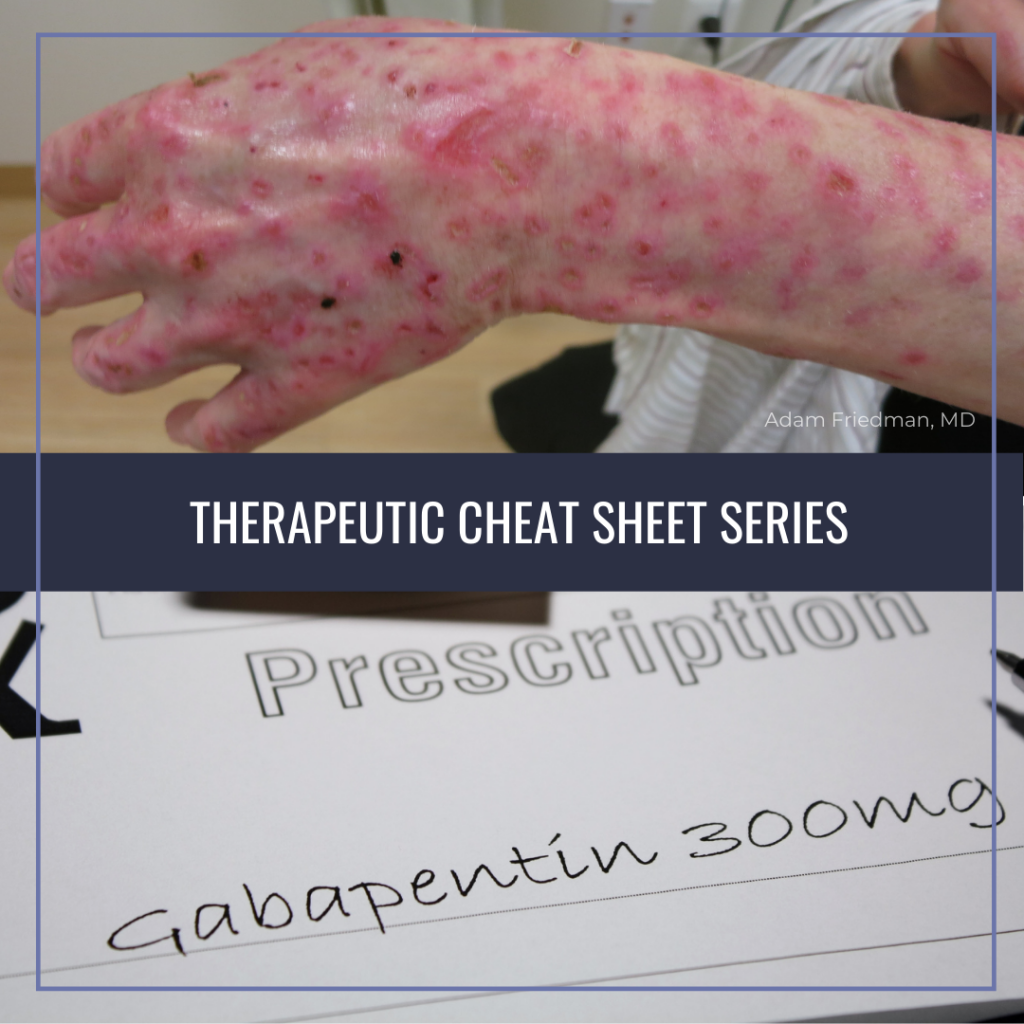
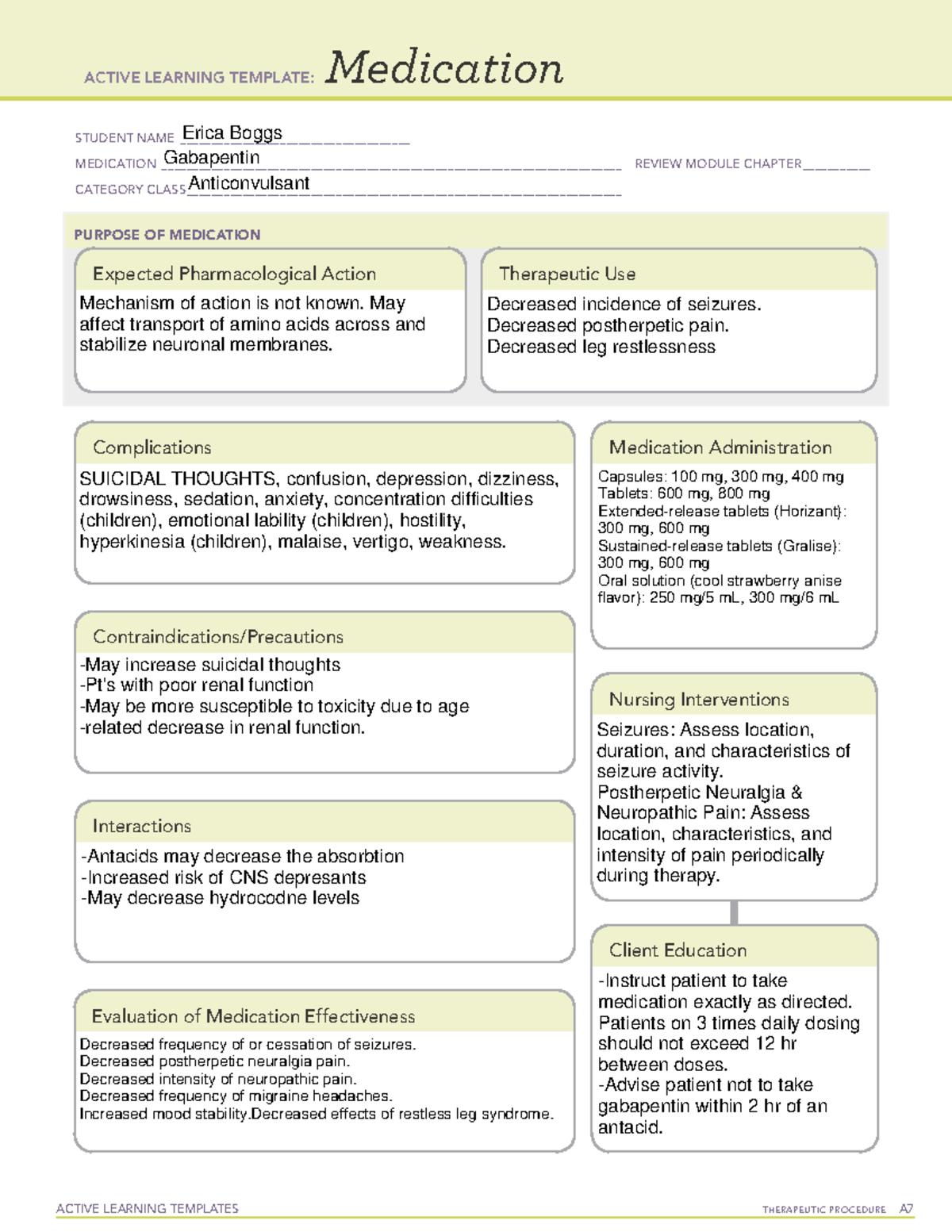
Take this drug exactly as prescribed; do not discontinue abruptly or change dosage, except on the advice of your health care provider. Wear a medical alert ID at all times so that any emergency medical personnel will know that you have epilepsy and are taking antiepileptic medication. Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Gabapentin Nursing Interventions. Administer gabapentin according to the prescribed dosage and schedule. This ensures that the patient receives the appropriate dose of medication at the right time, promoting therapeutic effects. Horizant (gabapentin enacarbil) is an extended release tablet used to treat restless legs syndrome and for the pain from having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). Generic brands of gabapentin capsules, USP are used for postherpetic nerve pain and for add on therapy for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Warnings Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Brand Names: US Gabarone; Gralise; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada AG-Gabapentin; APO-Gabapentin; Auro-Gabapentin; BIO-Gabapentin [DSC]; To discontinue gabapentin or start an anticonvulsant, titrate gradually for at least one week to reduce the risk of seizure. Implement seizure precautions. Implement strict hand hygiene and infection control. Report observations of depression, suicidal thoughts, or unusual behavior. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. What are the brand names of gabapentin? Gabapentin is available as both a brand name product and a generic product (chemically the same, usually lower cost than the brand name product). Brand names of gabapentin include Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to GRALISE is indicated for the management of Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN). Important Limitation: GRALISE is not interchangeable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration (See Warnings and Precautions ) Gabapentin enacarbil available under the trade name Horizant is the only gabapentin product approved for treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). A daily dose of 1200 mg provided no additional benefit compared with the 600 mg dose, but caused an increase in adverse reactions. Nursing Considerations Therapeutic Effects Side/Adverse Effects; Anticonvulsant: gabapentin: Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Taper dose; do not stop abruptly: Decreased neuropathic pain or seizures Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Identify appropriate indications for use of gabapentin. Relate general characteristics of gabapentin to specific patient situations. Apply nursing process considerations for gabapentin to specific patient situations. Correctly calculate dosage for gabapentin. Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Seizure patients should not resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. You’ve learned about gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications (aka nursing considerations) and patient teachings in this article. In addition, you’ve learned about gabapentin’s mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, dosage, indications, contraindications, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Gabapentin administration requires meticulous nursing care. Nurses ensure proper medication administration, closely monitor side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and assess for drug interactions. Patient education is crucial to promote adherence and minimize adverse effects. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Nursing Considerations Created Date: 3/23/2022 10:18:38 PM
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |