Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | 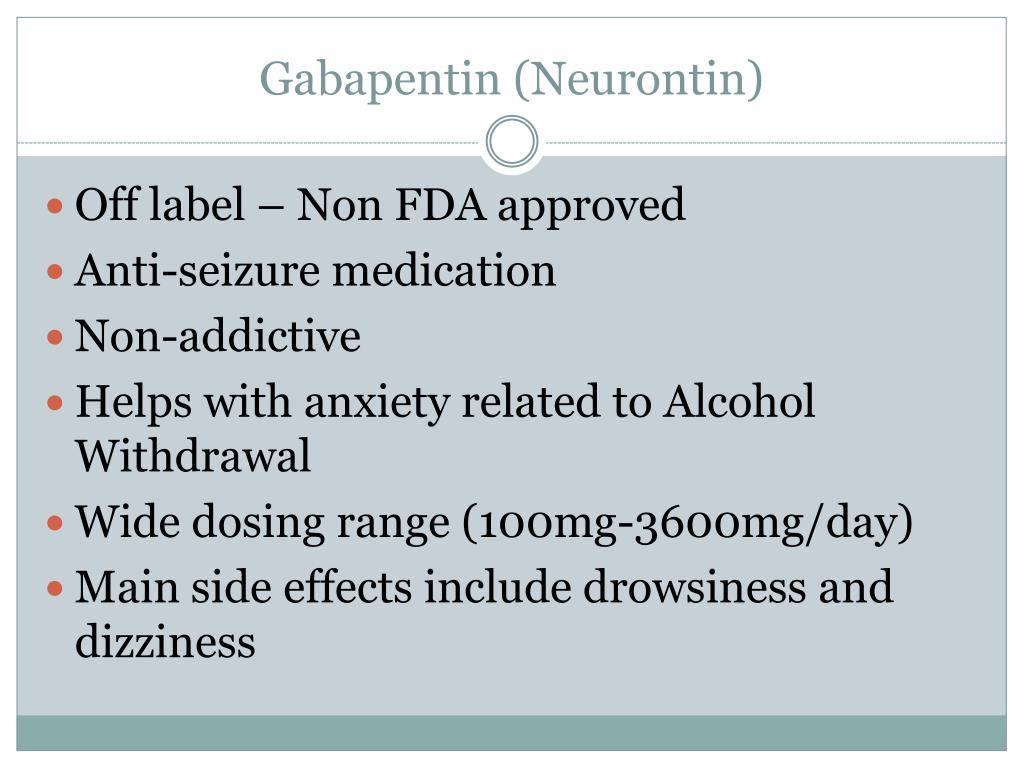 |
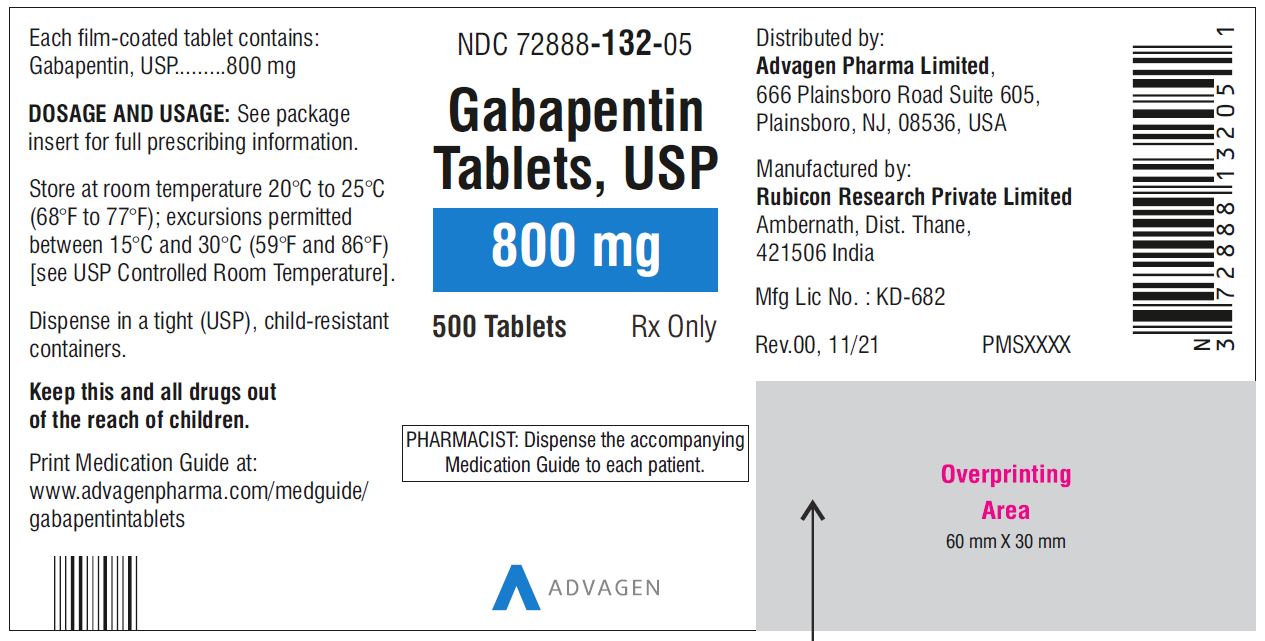
Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). Gabapentin’s off-label uses—meaning prescribing gabapentin for a problem not on the FDA approval list for this medication—that physicians are finding include: Alcohol withdrawal; Anxiety; Cocaine withdrawal; Fibromyalgia; Headaches; Hiccups; Hot flashes; Hyperhidrosis; Insomnia; Migraines; Mood disorders; Pain syndromes; Peripheral Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Radley et al. indicated that gabapentin was among the medications with the highest proportion of off-label use, with 83% of its use being off label.9 Gabapentin was initially approved in Canada in April 1994 as adjunctive therapy for the management of epilepsy among patients over 18 years of age who are not controlled by conventional therapy.11 Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids. Gabapentin in the treatment of anxiety and depression: Gabapentin is sometimes prescribed off-label for patients with bipolar disorder to reduce anxiety levels or for anxiety disorders. Clinicians have also used it for patients who have anxiety and depression. Off-label: It is estimated that approximately 9/10 prescriptions for Gabapentin are “off-label” or for conditions that the drug isn’t approved to treat. Off-label prescriptions have a reduce chance of actually working for the treatment of anxiety. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. Keywords: Central nervous system depressants; Drug treatment/psychopharmacology; Gabapentin; Off-label use; Primary care; Psychiatry. In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. Because doctors prescribe gabapentin off-label for anxiety, there’s no specific dosage for treating anxiety symptoms. Your dosage will depend on your: age; weight; health history; The next step was to read all of this article’s references. 2-6 Surprisingly, all 5 references focused on the relationship of gabapentin with the use of opioids or in the treatment of pain, with no mention of the common off-label use of gabapentin in various psychiatric disorders such as anxiety and insomnia. Hence, I embarked on a literature Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Objective: Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system de-pressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. Gabapentin for Anxiety, Depression, and Bipolar Disorder. The prescription drug is being used off-label to treat common mental illnesses and even alcohol use disorder. But does it work? Outpatient prescription of gabapentin for FDA-approved indications (i.e., partial-onset seizures and postherpetic neuralgia) was less than 1%, and depression and anxiety disorders were the most frequent psychiatric diagnoses among off-label users. This use of gabapentin for the treatment of anxiety is referred to as an off-label use, meaning there is limited data on its effectiveness to treat anxiety. Other off-label uses include treating alcohol withdrawal for alcohol use disorder and hot flashes associated with menopause. related to off-label gabapentin use; (3) review medical information pertaining to the off-label use of gabapentin; (4) outline alternatives to off-label use of gabapentin in an evidence-based fashion, where literature exists to support such alternatives; and (5) encourage key clinicians and decision makers in managed In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Off-label use of medications is common. Although common, many patients may not know that a medication is prescribed off-label. So why are medications used off-label? One reason may be that the FDA approval process is expensive and time-consuming. If the company would like to add an indication to a medication, an additional application is required.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |