Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
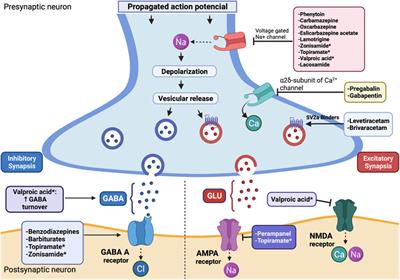
Gabapentin For Dog Seizures. Gabapentin can be prescribed to treat epilepsy in dogs, but it is not usually a go-to drug for dogs who have frequent generalized seizures. Gabapentin may be used to control focal/partial seizures or as an adjunct medication for generalized seizures if the previous medication regimen isn’t working. Gabapentin. Gabapentin is used as a pain-relieving medication and anticonvulsant. A 2005 study investigated gabapentin as an add-on anticonvulsant in dogs with refractory seizures and found that in a 4-month period, 3 of 17 dogs were seizure-free and 4 other dogs had a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication for dogs to manage pain, seizures, and anxiety. However, pet parents may wonder: can gabapentin actually cause seizures in dogs? Understanding the effects, risks, and appropriate use of this drug is crucial for your dog’s well-being. Key Takeaways: Quick Answers About Gabapentin and Seizures 📝 Can Gabapentin cause seizures? ⚠️ Rarely, usually There was a statistically significant difference in seizure frequency from the baseline to the treatment phase between participants receiving placebo and gabapentin 1200 mg, in whom seizure frequency decreased 57%. Gabapentin 900 mg appeared to be ineffective. There was a close relationship between serum gabapentin concentrations and gabapentin Gabapentin is a Pfizer-made medication for focal aware and impaired seizures. For more information, visit the Epilepsy Foundation online. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. The new antiepileptic medications are prescribed for the treatment of patients with seizure disorders since 17 years ago. Gabapentin (GBP) was approved on January 1994 as adjunctive treatment in patients 12 years or older with partial seizures, with Gabapentin is well tolerated by patients with generalized seizures. The results of this study show a trend toward an effect of gabapentin in reducing the frequency of generalized tonic-clonic seizures and suggest that further exploration of high dose gabapentin in generalized epilepsy is warranted. Keywords: Gabapentin; Epilepsy; Clinical Gabapentin for partial seizures: According to the guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society, clinicians might consider gabapentin as a potential option for patients aged 60 and older with new-onset focal epilepsy, as it could be similarly effective and better tolerated compared to carbamazepine. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower the risk of seizures. Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a prodrug of gabapentin that has been designed to overcome the Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Gabapentin (GA ba PEN tin) has been approved by the FDA as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy. Gabapentin is 1 of many antiseizure medications available for the treatment of epilepsy in adults; however, there are potential risks associated with its use. Therefore, it is important to determine the place of therapy of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy. Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Currently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends gabapentin use for postherpetic neuralgia in adults, and as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with and without secondary generalisation in adults and paediatric patients three years of age or older with epilepsy (U.S. Food and Drug Administration 201 Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin is recommended for use in focal seizures and neuropathic pain. [7] [10] Gabapentin is prescribed off-label in the US and the UK, [22] [23] for example, for the treatment of non-neuropathic pain, [22] anxiety disorders, sleep problems and bipolar disorder. [24] Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin available under the trade name Gralise or Horizant have not been studied in pediatric patients and patients with epilepsy. Use: Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization in patients 3 years of age and older. Renal Dose Adjustments Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |