Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
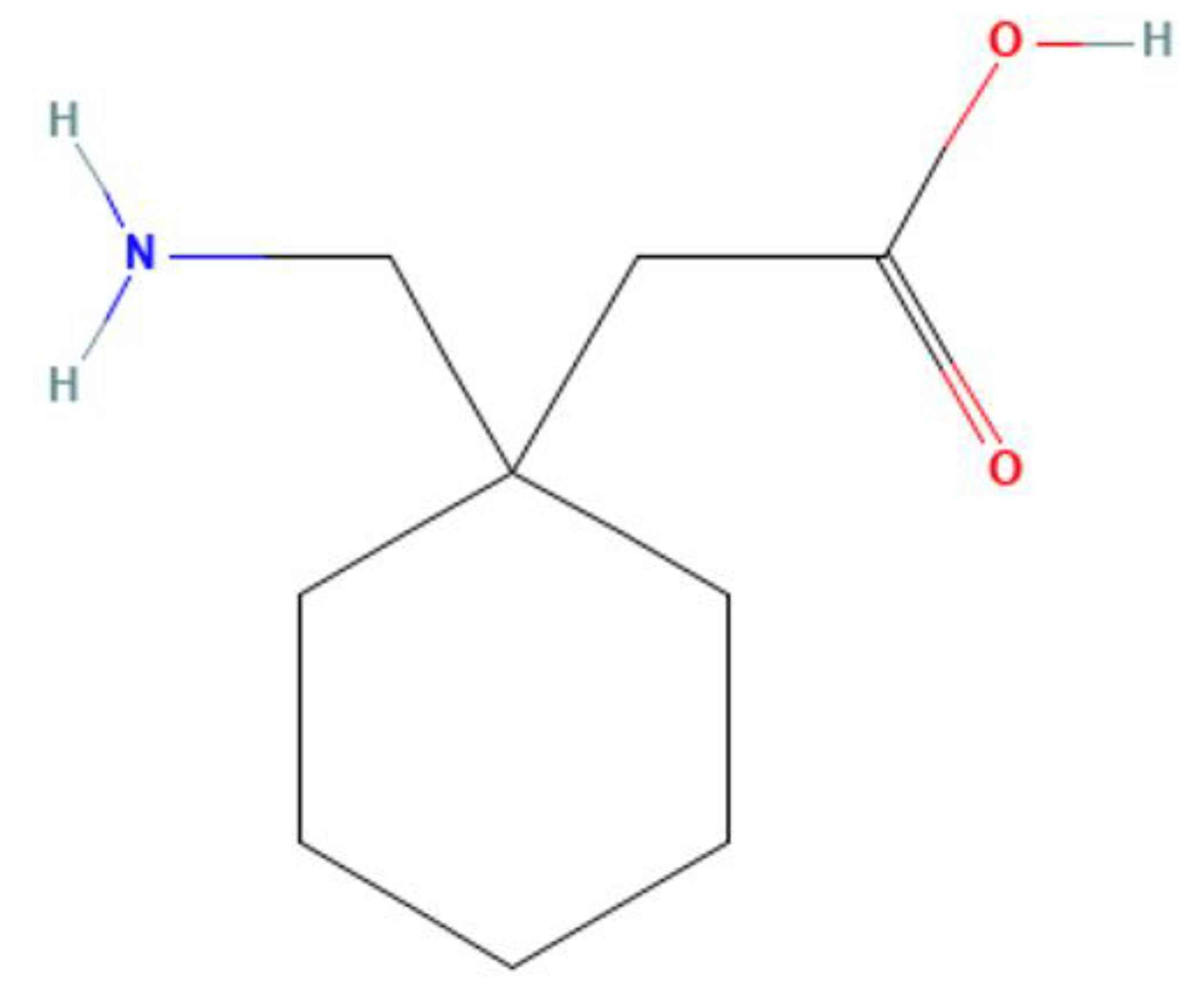
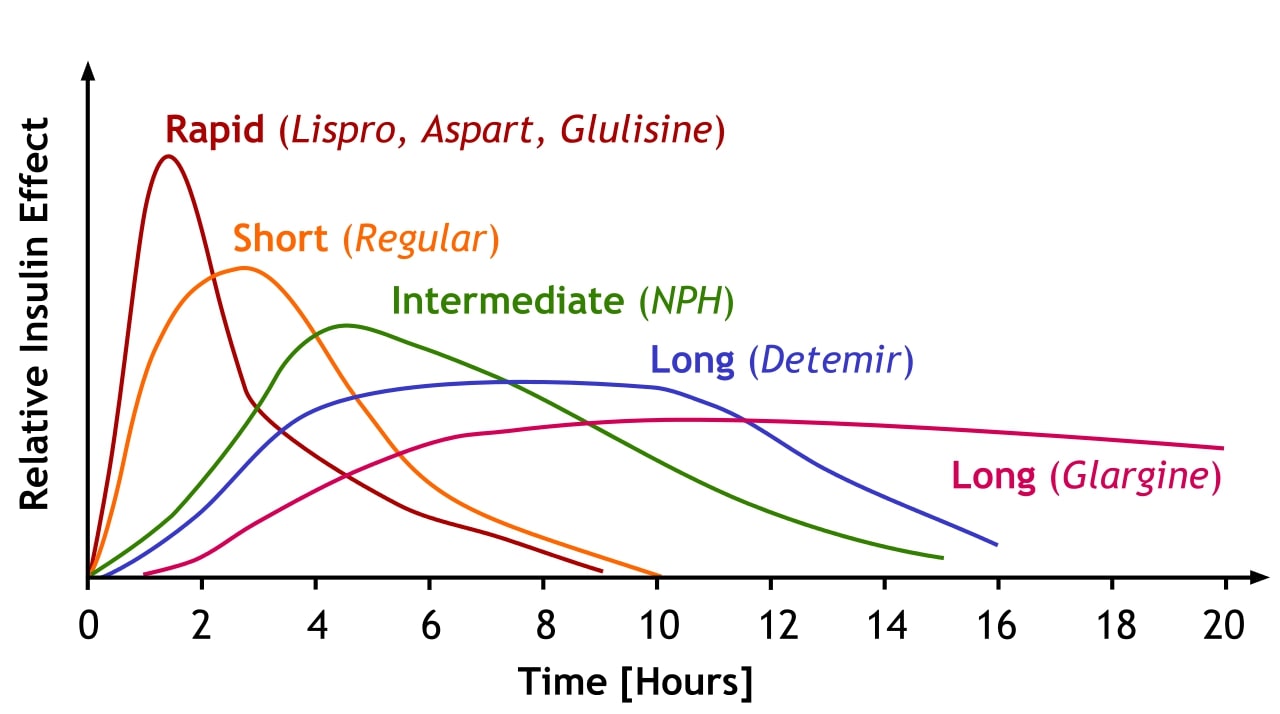
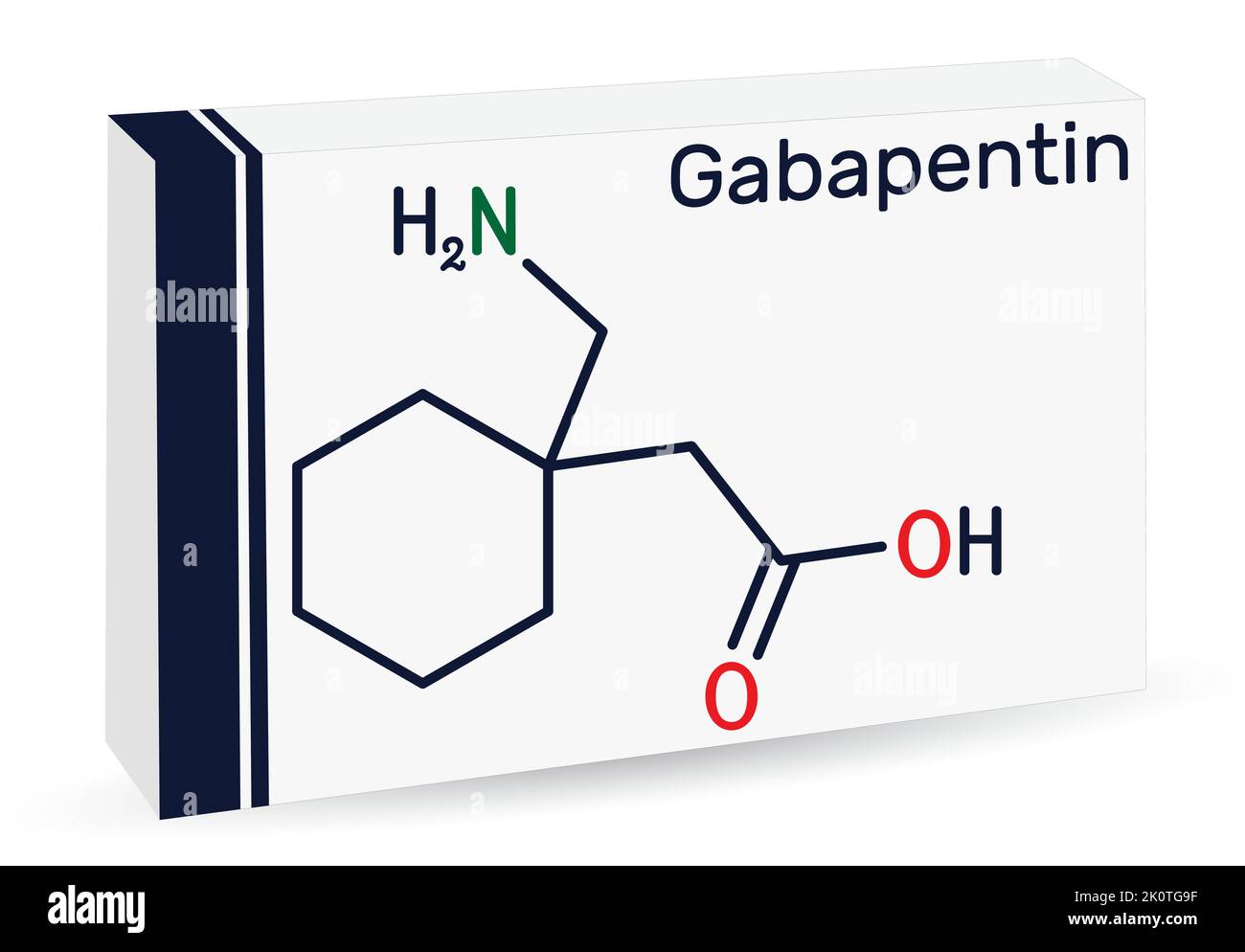
*The dose is normalized to 1,000 mg equivalent (mg-eq) of gabapentin. t max is presented as median (minimum, maximum). b.i.d. = twice daily; q.d. = once daily; t.i.d. = 3 times daily; C max = maximum plasma concentration over the last dosing day; t max = time to reach maximum concentration over the dosing interval in which the C max was observed (if the maximum value occurred more than once in Understanding Its Onset of Action. 1. How long does it take for gabapentin to work for nerve pain? 2. Can gabapentin help with anxiety immediately? 3. Is gabapentin a strong painkiller? 4. What should I avoid while taking gabapentin? 5. How long does gabapentin take to reach its peak concentration in the blood? 6. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Gabapentin is really in a class of its own.. I'd call it a disbenzopiate haha. It has the warmth and optimism that you get from opiates with a nice anxiolytic effect on par with Xanax. That's great and all but the real reason I use Gabapentin is for the dissociative effects. It feels very much like MXE if you've ever done that. NEURONTIN is indicated for: • Postherpetic neuralgia in adults ()Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy () Gabapentin generally takes about 3 to 4 hours to reach maximum plasma concentrations after oral administration. For pain relief, significant effects can be observed within a few days to a week, while its anticonvulsant effects can be seen relatively quickly, even within the first few days of treatment. The peak plasma concentration for gabapentin is 2 to 4 hours. The time to peak plasma concentration for gabapentin enacarbil is 5 hours for subjects in a fasting state and 7.3 hours for under-fed conditions. The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin available under the trade name Gralise or Horizant have not been studied in patients with epilepsy. Use: Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization Usual Adult Dose for Postherpetic Neuralgia. Immediate-release: Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. It is not completely known how this drug works. When used to treat a type of seizure disorder, called a partial onset seizure, gabapentin decreases the abnormal activity in the brain that causes the seizures. GABAGoodness is devoted to the discussion of all GABAergics, Gabapentnoids and VDCC inhibitors such as Pregabalin, Gabapentin, Phenibut, Carisoprodol, GHB, Benzodiazepines, Barbiturates, and more! This is a great place to ask general or recreational questions, get harm reduction advice, or share your experience with withdrawal syndromes. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Chemical structure of gabapentin [].It is an anticonvulsant drug synthesized nearly 40 years ago and first approved in 1993 for the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia in human patients that later proved to be clinically effective in humans suffering from refractory partial seizures and secondarily generalized tonic–clonic seizures. Peak concentrations of gabapentin (immediate-release) occur within 2 to 3 hours. Although gabapentin may improve sleep problems due to nerve pain within a week, it may take up to two weeks for symptom relief from nerve pain to occur. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy , radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Time to Peak. Immediate release: Infants 1 month to Children 12 years: 2 to 3 hours; Adults: 2 to 4 hours; Extended release: 8 hours. Half-Life Elimination. Infants 1 month to Children 12 years: 4.7 hours. Adults, normal: 5 to 7 hours; increased half-life with decreased renal function; anuric adult patients: 132 hours; adults during Table 2. Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment in Adults Receiving Gabapentin Gastroretentive Tablets60; Cl cr (mL/minute). Adjusted Dosage Regimen. 30–60. 600 mg to 1.8 g once daily; initiate at 300 mg once daily and may titrate according to same schedule recommended for those with normal renal function based on individual patient response and tolerability ONSET, PEAK AND DURATION OF COMMON PAIN MEDICATIONS Medication Onset of Action (minutes)* Peak Effect (hours)* Duration of Action (hours)* Route of Admin. Comments Non-Opioid Analgesics Acetaminophen 30 -45 0.5 -1 4 -6 Oral Headache, nausea, vomiting May cause hepatic complications in doses over 3000mg/24hr in the elderly Answer. Neurontin has a relatively short half-life and duration of action.The reported half-life (the time it takes for 50% of the drug to be metabolized) is 5 to 7 hours, which necessitates a dosing frequency of 3 to 4 times daily for it to be effective. Chemistry document from University of Texas, Arlington, 1 page, Onset & Peak Indications Onset: Unknown Peak IR:2-4 Hrs, ER: 8 hrs Encarbil:5-7.3 hrs Typically dosages titrated up to 1800 mg daily divided in three doses. Concentrations of gabapentin are thought to peak between 2 to 4 hours after administration. The drug is distributed at a volume of 50-60 L and effectively penetrates the blood-brain barrier. Once the drug has been absorbed and distributed, it is processed by the kidneys prior to excretion.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |