Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
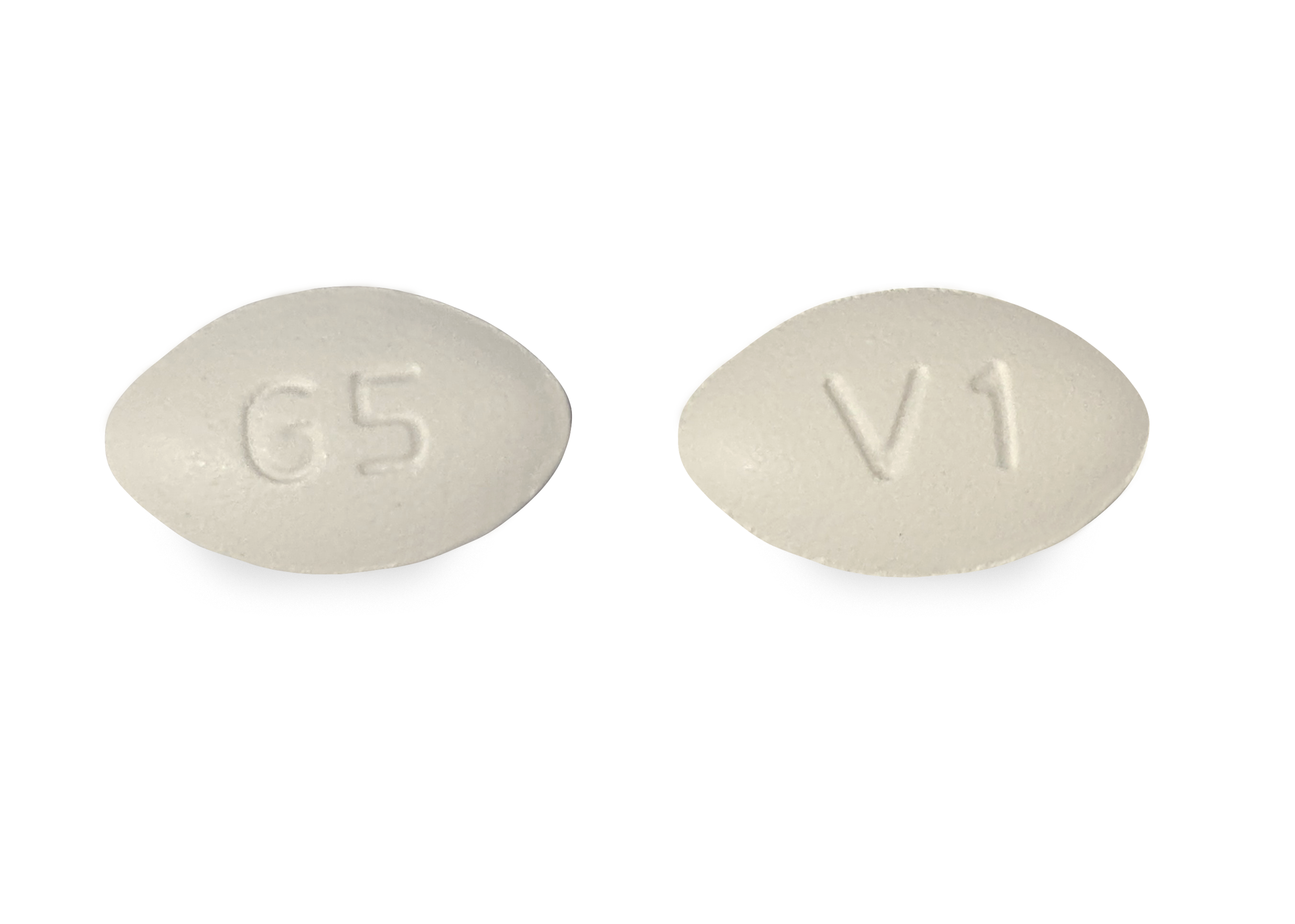
Oral steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that may be an effective treatment for low back pain from degenerative disc disease. Typically, oral steroids are prescribed in a Medrol Dose Pack, starting with a high dose to provide initial low back pain relief, then tapering down to a lower dose over 5 or 6 days. SNRIs were also beneficial for treating low back pain. (SOR: B, based on inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence.) Pregabalin/gabapentin vs. placebo: Meloxicam vs For chronic low back pain, physical therapy and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) tend to work better. Gabapentin for sciatica The cause of sciatica back pain is compression of the sciatic nerve. This type of back pain typically starts in the lower back and travels down the back of one or both legs. A small study comparing gabapentin to pregabalin for chronic sciatica found that gabapentin might be the better option. The study showed that treatment with gabapentin resulted in more pain relief and had less risk of side effects when compared to pregabalin. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and One of the key differences between Meloxicam and Gabapentin is their mechanism of action. Meloxicam works by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause pain and inflammation, while Gabapentin affects the way that nerves send messages to the brain. Gabapentin is primarily used to manage nerve pain (neuropathic pain), while meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that targets inflammatory pain. Therefore, the best choice is dependent on the underlying cause of your pain. Several types of medications may be used for sciatic pain. Oral medications include: Do not give aspirin to a child aged 18 years of age or younger because of the increased risk of Reye's In this systematic review we determined the efficacy and tolerability of analgesic and adjuvant pain drugs typically administered in primary care (orally, topically, or parentally) in the management of patients with sciatica when compared with other treatment options or no treatment. This review focuses on the management of sciatica only. Pharmacological management of low back pain, and mixed populations of low back pain and sciatica are considered in a separate chapter in the full guideline: Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s: assessment and management. For full details see the review protocol in Appendix A. Sciatica is a symptom rather than a specific diagnosis 4 and is used broadly to refer to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve. 5. The commonest cause of sciatica is impingement of lumbosacral nerve roots, as they emerge from the spinal canal, by a herniated intervertebral disc (fig 1). Meloxicam: 7.5 to 15 mg per day Maximum: 15 mg per day: $10 ($500) Selective COX-2 NSAIDs: Meloxicam: 7.5 mg per day: Mild to moderate: Migraine Low back pain Dysmenorrhea Renal colic Medications included meloxicam (Mobic), lornoxicam (not available in the United States), piroxicam (Feldene), and diclofenac. Gastrointestinal adverse effects were common (5% to 10%). Lifestyle and home remedies. For most people, sciatica responds to self-care measures. Although resting for a day or so may provide relief, staying inactive will make symptoms worse. Introduction. The clinical syndrome of sciatica has been recognised since ancient times. Currently believed to arise from a disorder of the nerve root, the syndrome is known by a range of synonyms such as lumbosacral radicular syndrome, nerve root compromise, nerve root pain, and nerve root entrapment or irritation.1 2 Sciatica is considered to be a prognostic indicator of poor outcome among Compare Gabapentin vs Meloxicam head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Gabapentin can effectively treat chronic lower back pain caused by diabetes and shingles . High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can lead to nerve pain called diabetic neuropathy ( 19 ). Although this condition usually results in pain in the feet and legs, it can also affect the hips, buttocks, or thighs ( 19 ). Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Meloxicam vs. Gabapentin. When comparing meloxicam to gabapentin, another medication sometimes used for pain, the differences are notable. Gabapentin is primarily used for nerve pain, whereas meloxicam focuses on inflammatory pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |