Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
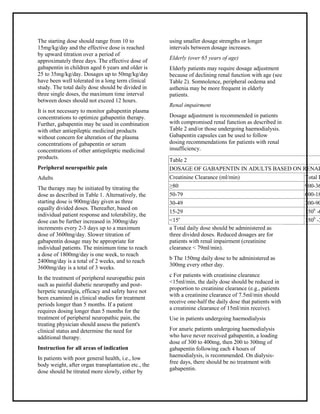
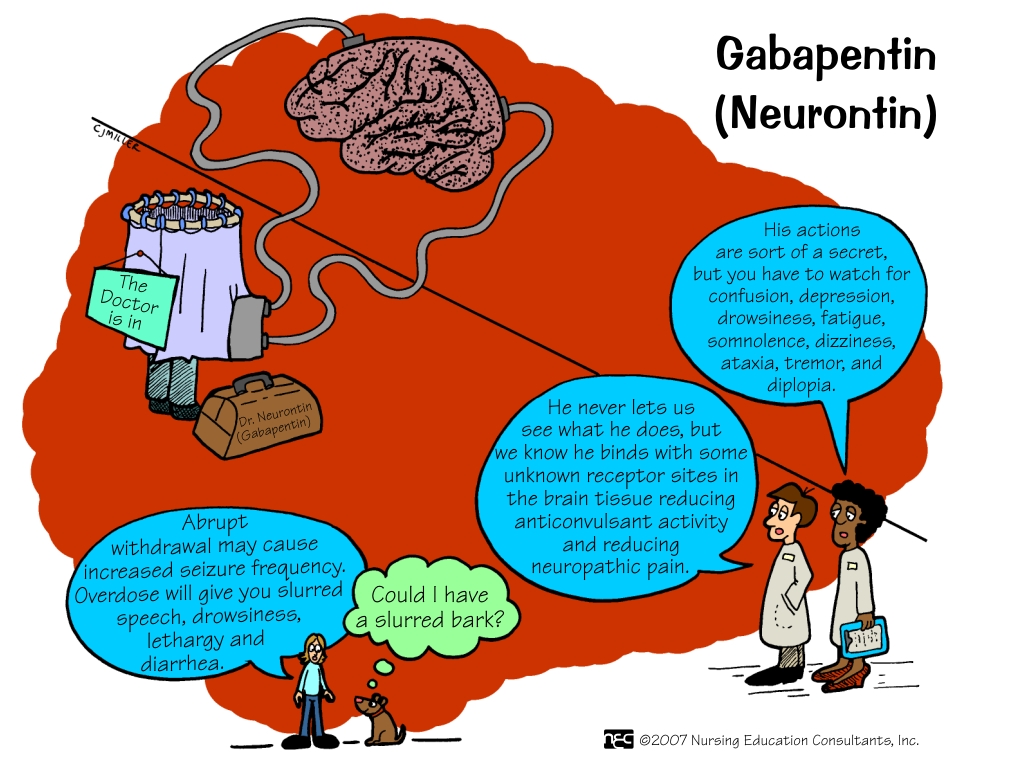
Mary Peart, 67, a retired nurse in Manchester-by-the-Sea, Mass., began taking gabapentin a year and a half ago to reduce the pain and fatigue of fibromyalgia. Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Are the side effects of gabapentin different in the elderly compared to younger patients? The adverse reactions to gabapentin in the elderly can be worse or more frequent in older adults. They usually have more health conditions and have multiple prescriptions to control chronic diseases. The mean age in these studies varied between 71 and 76 years, with the oldest participants in their 90s. In one study 81% of the patients were over 65. The highest doses for gabapentin were 3600mg/day and for pregabalin 600 mg/day. It’s easy to attribute these changes to the stresses of aging, but they could be the result of gabapentin’s influence on the nervous system. Monitoring Physical Side Effects. Physical side effects are also a concern. Gabapentin can cause dizziness, drowsiness, and balance issues, which are especially dangerous for the elderly. gabapentin The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), in conjunction with the American Geriatrics Society (AGS) and Pharmacy Quality Alliance (PQA), has developed a list of medications to be avoided in the older adult population. Gabapentin can be beneficial for many elderly patients, but it’s crucial to be aware of potentially serious side effects that require immediate medical attention. Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent complications and ensure prompt treatment. Gabapentin’s side effects can range from mild to more disruptive, and elderly individuals are particularly vulnerable to some of them. One of the most reported physical side effects is dizziness. This can lead to a higher risk of falls, which is a serious concern for older adults. If gabapentin is used for epilepsy and is to be discontinued, it should be done gradually over at least a week.1 Other adverse events that have been observed following the abrupt discontinuation of gabapentin include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain and sweating.1 Make sure people taking gabapentin for epilepsy understand Along with causing dizziness, gabapentin can worsen your coordination. This can increase your risk of falls, which is especially dangerous for older adults. If you’re just starting to take gabapentin or your dose has increased, avoid driving or doing any activity that requires alertness. Reducing Risks of Gabapentin in Elderly Patients. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to elderly patients for various health conditions. While it can be highly effective, it’s essential to minimise the associated risks, especially considering the vulnerability of the elderly population. Parkinson’s disease: bromocriptine (CYCLOSET), EMSAM, levodopa/carbidopa (SINEMET) pramipexole (MIRAPEX), ropinirole (REQUIP), COMTAN, STALEVO Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. It may be reasonable to start older adults on a low dose of gabapentin, which can be effective to treat pain while exposing patients to a lower risk of adverse mental status side effects of gabapentin (dizziness, drowsiness and confusion) [7]. Adults ages 65 and older can be more sensitive to medication side effects. In some cases, certain medications should be avoided in this age group due to possible risks. Some medications can cause confusion, low blood pressure, and falls in older adults. Others can cause constipation, dry mouth, and blurry vision. Effective pain management: Studies have shown that gabapentin can be effective in treating neuropathic pain in older adults, often with minimal side effects. Seizure control: It remains a valuable option for managing epilepsy in the elderly population. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1993 as a treatment for epilepsy. It works by binding to a type of calcium channel in nerve This article aims to illuminate the diverse side effects of Gabapentin in the elderly, enabling you to make well-informed healthcare decisions for those in your care. Gabapentin: An Overview. Before delving into its side effects, let’s understand what Gabapentin is and why it’s prescribed. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiseizure medication. It’s also used for nerve pain from shingles. Other long-acting forms called Gralise and Horizant are also available. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |