Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
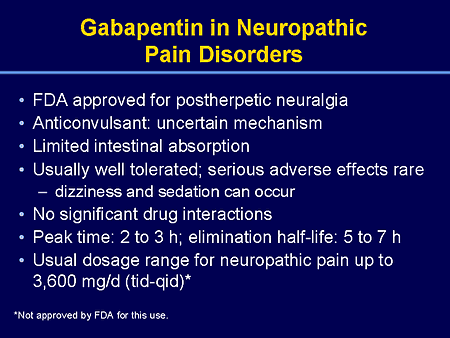 |  |
Gabapentin overdose can be serious and may result in many symptoms, from mild drowsiness to life-threatening complications. Understanding the signs, risks, and proper management of gabapentin overdose is crucial for medical professionals and individuals using the medication. Gabapentin overdose management may also involve supportive measures, such as intravenous fluids and cardiac monitoring, to ensure the individual's vital signs remain stable. If the overdose was purposeful, psychiatric assessment and treatment may be required. Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. Thirty-three Misusing gabapentin can lead to a fatal overdose, though the risk is much less if you take it as prescribed. However, unlike opioids, there is no antidote to reverse the overdose like naloxone. A gabapentin overdose is a medical emergency. Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally similar to gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) but have little to no activity on the GABAergic system. Instead, they inhibit the α 2-δ subunit of P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels, thereby reducing presynaptic calcium influx and thus subsequent release and activity of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate and substance P. 9 Gabapentin was Treatment for Gabapentin Overdose. Once medical services arrive, they can begin treating the symptoms of a gabapentin overdose. If the person has combined gabapentin with opioids, the person may be given naloxone to help reverse the overdose. If no opioids are suspected, other treatment will happen. The management of a gabapentin overdose primarily involves supportive care, as there is no specific antidote. In some cases, hemodialysis has been used to remove gabapentin from the system, particularly in severe instances of toxicity. Identifying Physical Symptoms of Gabapentin Overdose Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose are drowsiness, fast heartbeat, dizziness, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, lethargy, coma, and death may occur. If someone takes too much gabapentin or takes gabapentin by accident, get guidance from Poison Control immediately. Prevention and Management of Gabapentin Overdose. Preventing gabapentin overdose involves careful monitoring of the patient’s condition, adherence to the prescribed dosage, and awareness of potential interactions with other medications. In cases of suspected overdose, immediate medical attention is necessary. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal. Supportive care strategies for gabapentin overdose include: Airway management: If the patient is unable to breathe on their own, they will need airway management, supplemental oxygen, and ventilation assistance; Use of activated charcoal or gastric lavage: This process flushes out any residual gabapentin from the gastrointestinal system Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Gralise (gabapentin) is only used for pain after having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It should not be used for any other medical condition. The purpose of this study is to document the clinical manifestations and outcomes of gabapentin exposures reported to poison centers. Methods: A multicenter prospective observational study of all gabapentin exposures reported to three poisoncenters was conducted between 4/1/98 and 4/1/2000. Cases involving gabapentin only were evaluated. What should you do if you suspect a Gabapentin overdose? Unfortunately, as of this writing, there is no known antidote or way to reverse a Gabapentin overdose. Call for emergency medical help if you suspect a Gabapentin overdose. Individuals who overdose on a combination of gabapentin and another drug with depressant effects (e.g., alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, etc.) are at serious risk of significant adverse effects, and these individuals may require immediate medical attention.Gabapentin may cause respiratory depression when used alone or with other substances. Postmortem toxicology tests detected gabapentin in almost 1 in 10 US overdose deaths between 2019 and 2020. In about half of the cases, a medical examiner or coroner ruled the drug was a cause of the death, according to a report from the CDC’s Division of Overdose Prevention. Preventing gabapentin overdose involves educating patients on the correct dosage and the dangers of mixing gabapentin with other substances. Healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of following the prescribed dosage and not adjusting it without medical advice. In general, gabapentin is well tolerated over a wide range of doses. However, it is possible to overdose on gabapentin, especially when taken in combination with other substances. A growing body of literature shows that gabapentin overdoses can cause potentially serious physical and psychological effects. Pregabalin is commonly used for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Overdose leads predominately to CNS effects. Management is supportive. Toxicity / Risk Assessment Management - Lone Pregabalin or Gabapentin exposures are usually well - Supportive care is the mainstay of management The objective of this review is to provide a repository of standard and emerging treatment modalities for loperamide, gabapentin and modafinil for the emergency medicine team. Expert opinion: Loperamide, gabapentin, and modafinil are becoming drugs of abuse, and as such, should be on the radar of healthcare providers. Recognizing their unique
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |