Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |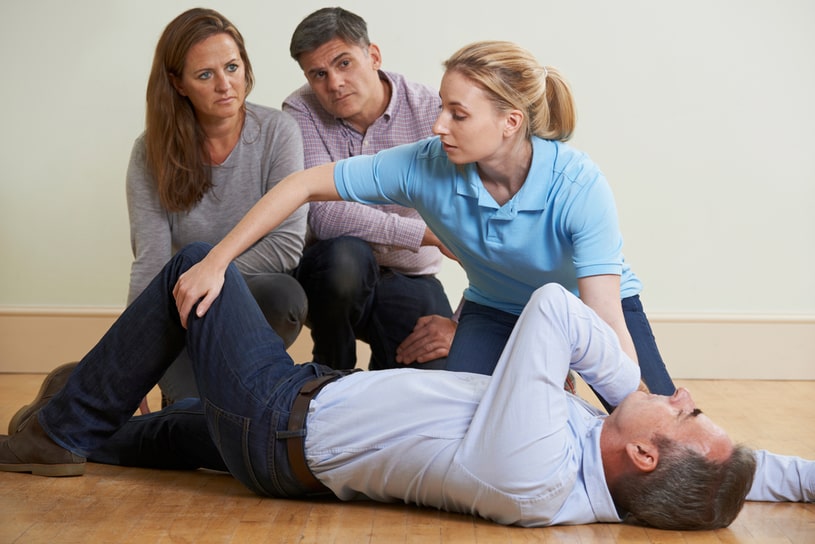  |
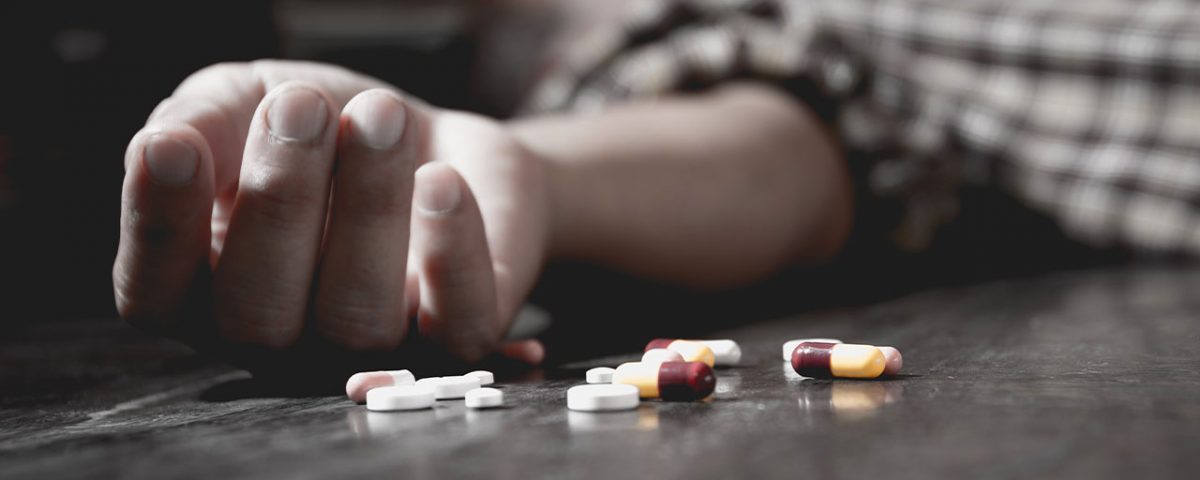
PHE and NHS England have published an expert group’s advice for prescribers on the risk of misuse of pregabalin and gabapentin, and suggestions for a balanced and rational use of these medicines. Gabapentin and pregabalin are associated with significant euphoric effects. Individuals misusing gabapentin and pregabalin variably describe improved sociability, euphoria, relaxation and a sense of calm. Gabapentin and pregabalin have the propensity to cause depression of the central nervous system, resulting in • Pregabalin and Gabapentin can cause drowsiness, sedation, slow down breathing, and in extreme cases death. • There are particular issues in secure settings where deaths have been found to involve illicit and/or diverted medication. What to be aware of • Deaths involving Pregabalin or Gabapentin have Compared with some drugs, such as opioids, gabapentin appears to be relatively non-lethal in overdose situations, meaning the morbidity associated with a toxic dose is low. 8 However, the primary danger of gabapentin overdose appears when individuals use gabapentin in conjunction with other drugs, such as alcohol or opioids. 9,10 These common side effects of gabapentin may happen in more than 1 in 100 people. They're usually mild and go away by themselves. There are things you can do to help cope with them: As your body gets used to gabapentin, these side effects should wear off. Taking too much gabapentin can cause unpleasant side effects. you take more than your prescribed dose of gabapentin and: Get help from 111 online or call 111. If you need to go to A&E, do not drive. Ask someone to drive you or call 999 and ask for an ambulance. A gabapentin overdose is rare, but it is possible. The likelihood of an overdose increases when you abuse gabapentin with other drugs like opioids and alcohol. If you or someone you know is experiencing a gabapentin overdose, seek medical help immediately. Can You Overdose on Gabapentin? Like with opiates, you can fatally overdose on gabapentin. 4 However, unlike with opiates, there is no antidote that you can administer in the case of a gabapentin overdose. Overdose is most likely to occur in cases when the medication is misused in combination with other substances. Signs of Gabapentin Overdose. Gabapentin overdose signs are challenging to spot because other types of drug and medication overdoses have similar symptoms. Signs to look for include: Gabapentin can cause side effects. The most common problem is feeling sleepy which may improve as you get used to the medicine. Some people have stomach pain and sickness. Rare problems are described in the leaflet that comes with your tablets. Important: do not drive or operate heavy machinery if you feel drowsy. While gabapentinoids have licensed indications they also have a potential for misuse. For patients with a previous / current substance misuse problem, prescribers should make a careful and thorough assessment balancing potential benefits with risks. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Gabapentin is available in the following formulations 100mg, 300mg,400mg capsules and 600mg and 800mg tablets Change (e.g. weekly / fortnightly / monthly) Morning gabapentin dose Midday gabapentin dose Evening gabapentin dose 1 900mg 1200mg 1200mg 2 900mg 900mg 1200mg 3 900mg 900mg 900mg 4 600mg 900mg 900mg A recent police report indicates the increasing tendency to use gabapentin as a ‘cutting agent’ in street heroin (and to recover gabapentin on the street and in prisons), further adding to the abuse and danger potential. 5 Like opiates, gabapentin is fatal in overdose; unlike opiates, there is no antidote and the long half-life instils the Gabapentin (also called Neurontin) is a medicine that works in a similar way to pregabalin. Like pregabalin, it can be taken to treat epilepsy and nerve pain. It can also be taken for migraines. However, there are other differences between pregabalin and gabapentin. Gabapentin is taken in different doses to pregabalin. Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. NHS medicines information on gabapentin – what it's used for, side effects, dosage, and who can take it. Adult Initially 25 mg twice daily, then increased in steps of 50 mg daily, dose to be increased at 7 day intervals, increased to 300 mg daily in 2–3 divided doses for 7 days, then increased if necessary up to 600 mg daily in 2–3 divided doses. Its overdose death risk is lower than that of opioids, but it’s not risk-free. How long can you take gabapentin for nerve pain? The safety and efficacy of gabapentin have not been examined for Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose are drowsiness, fast heartbeat, dizziness, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, lethargy, coma, and death may occur.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |