Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
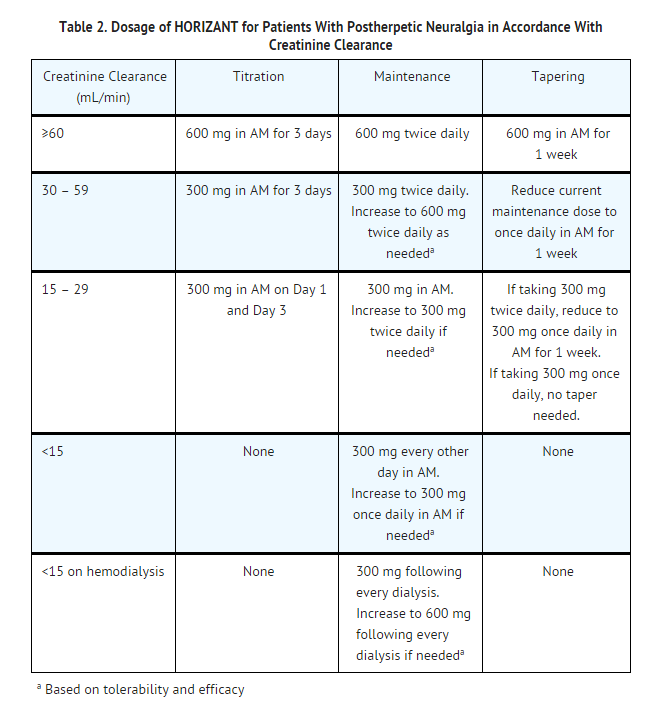
Administer gabapentin tablets orally with or without food. Inform patients that, should they divide the scored 600 mg or 800 mg gabapentin tablet in order to administer a half-tablet, they should take the unused half-tablet as the next dose. Half-tablets not used within 28 days of dividing the scored tablet should be discarded. 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg GABAPENTIN- gabapentin capsule Major Pharmaceuticals-----HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GABAPENTIN CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GABAPENTIN CAPSULES. GABAPENTIN capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 INDICATIONS AND USAGE See full prescribing information for GABAPENTIN ORAL SOLUTION. Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily. GABAPENTIN CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GABAPENTIN CAPSULES. GABAPENTIN capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1993----- RECENT MAJOR CHANGES -----Warnings and Precautions, Respiratory Depression (5.7) consider initiating gabapentin at a low dose. An increase in gabapentin AUC values have been reported when administered with morphine. (7.7) An antacid containing aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide reduced the bioavailability of gabapentin immediate release by about approximately 20%, but by only 5% when gabapentin was taken 2 hours after antacids. Administer NEURONTIN three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules, or 600 mg or 800 mg tablets. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Administer gabapentin capsules orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with water. If the gabapentin capsules dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week (a longer period may be needed at the discretion of the prescriber). Gabapentin capsules, hard (called Gabapentin capsules in the rest of this lea et) belong to a group of medicines used to treat epilepsy and peripheral neuropathic pain (long lasting pain caused by damage to the nerves). Gabapentin capsules are used to treat: indicate that gabapentin may cause significant driving impairment. Prescribers and patients should be aware that patients’ ability to assess their own driving competence, as well as their ability to assess the degree of somnolence caused by NEURONTIN, can be imperfect. The duration of . TEVA-GABAPENTIN (gabapentin) Product Monograph Page 7 of 32 administration was revealed in reproduction studies in mice at doses up to 62 times, and in rats and rabbits at doses up to 31 times the human dose of 2400 mg/day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/ day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may Gabapentin is a prescription medicine used to treat: • Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults. This document contains the label information for Neurontin (gabapentin) capsules, tablets, and oral solution. It includes the description, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and indications of gabapentin for epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been administered in a long-term clinical study. The maximum time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Oral Solution Dosage Based on Renal Function. For a complete listing, see 6 DOSAGE FORMS, STRENGTHS, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |